The only armoured variant of the Sd.Kfz.8
The only armed and armoured variant (factory-converted, not field converted) was developed in 1940, a bit as its "little brother", the 8.8cm Flak 18(Sf.) auf Schwere Zugkraftwagen 12t (Sd.Kfz.8) based on its name indicates on the Sd.Kfz.8, also dubbed "Bunkerflak". It was ordered before the first prototype vehicle was even completed at the end of October 1942, with 112 equipped with the FLAK 37, but due to disappointing performances, production was cut short to 14. They all served in Italy, as part of the Heeres-Flak-Abteilung 304 of 26. Panzer Division in 1943-45.
The previous 8.8 cm Flak 18 Sfl. auf schwere Zugkraftwagen 12 t (Sd.Kfz.8) als Fahrgestell
There are some conflicting information about them, between the number built and possible variants: They revolved around the gun mount, either the 8.8 cm Flak 37 (called the "8.8cm Flak 37 Selbstfahrlafette auf Zugkraftwagen 18 ton" as the successor of the Sd.Kfz 7/Flak 18 and the FLAK 18, which seems to have been the pre-production with an earlier gun, unshielded. The origin of the preserie is unknown, but the second one was a Luftwaffe order in 1942, which it ended with 112 vehicles being ordered, to be converted from stock SdKfz 8 at FAMO and simply known as "Flak 37". And all were indeed based on the FAMO Sd.Kfz 9 chassis, but with a armored cabine and the design changed little between the two series. The gun itself had limited traverse with the obstruction of the armored cab and needed to be elevated to fire forward or just clear the cab when moving. The first 14 vehicles were delivered in June and July of 1943, but the order was cancelled and further production did not continue.
Design
The flatbed was reinforced to accomodate a pivot-mounted 8.8 cm Flak 18 anti-aircraft gun, for the prototype apparently since the 1943 "production" vehicles were given the FLAK 37. The rest of the vehicle received 14.5 mm (0.57 in) armor panels on the cabin, radiator and hood, so as to make it at least partially armoured. This conversion was made on fifteen stock vehicles in 1940, using the famous "88". It was known as the "8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf Zugkraftwagen 18t (Sd.Kfz. 9)" and not meant for AA defence but specifically for anti-tank duties.The crew and engine compartments were protected, but the gun could not deflect when firing directly ahead. The rear bed had drop-down sides whith outriggers bracing the platform sides also held by chains, and their weight when deployed was supported by four (two per side) outriggers stored under brackets underway. These were making for a walkaround platform, supporting the weight of the gun crew when deployed. The vehicle after these modifications jumped to 25 tonnes, and it was 9.32 metres (30.6 ft) long. There was a stowage bin at the rear of the platform, on the right side.
The driver and co-driver could see forward through two removable sight slits and could exit through top-opening and sliding panels. They still could access and exit the vehicle via two small side doors (a ladder was welded for better access), but also from the open rear of the armored cab. There were also folding upper panels at the top of the rear open cabin.
The engine hood was entirely protected by thick armor panels, opening from the middle, and the radiator hood was behind two folding armoured panels (hinged and optional), still leaving a gap to let air pass and be sucked by the radiator. Large louvres were also welded on the side hood panels for better cooling. These were forward-opened on hinges too to leeave the engine cooling. They were completely out on some photos, suggesting a cooling problem which perhaps contributed to the demise of the vehicle.
The only part of the design that was left unchanged, was the 12-cylinder water-cooled 10.8L Maybach engine HL 108, which provided plenty of torque, so engineers believed it could support the weight of the 8.8 cm FLAK and an armoured cab, but of course performances were degraded: The original vehicle could reach 50 kph, barely 45 for the conversion, and consumption augmented, reducing range, still around 220-240 km depending on the terrain. The chassis was much reinforced to support both the armoured riveted panels and flatbed.
About the 8.8cm FLAK 37

Front view of the new gun shield, which was slightly enlarged. As the upper part of the shield was enclosed, the gun could not be used to target enemy aircraft. Source: T.L. Jentz and H.L. Doyle Panzer Tracts No. 22-5 Gepanzerter 8t Zugkraftwagen and Sfl.Flak
There is no need to introduce this legendary ordnance which terrified the allies during WW2. A former AA gun turned into an impromptu anti-tank gun an later refined as a proper tank gun, the "88" literraly rule the battlefield until late into the war. No allied tank was immune to it before very heavy models were introduced. The FLAK 18 was essentially mounted on a cruciform carriage, while the Flak 36 had a two-piece barrel for easier replacement of worn liners and was often seen with an armoured shield, which couyd be retro-fitted on Flak 18s. Later came Krupp's Flak 37, with updated instrumentation to follow intructions from a single director (Übertragungser 37) and used in dual role, also fitted with a shield by default.
Performances: Elevation −3° to +85°, Traverse 360°, Rate of fire 15–20 rpm, Muzzle velocity 840 m/s (2,690 ft/s) effective 14,860 m (16,250 yd) ground and 8,000 m (26,000 ft) ceiling up to 9,900 m (32,500 ft) maximum ceiling. Using ZF.20 sights, Fixed QF 88×571mmR shells were fuzes-equipped and adapted to their AA or antitank role.

8.8 cm Flak 36 with Flak Rohr 18 barrel at the Imperial War Museum in London
The vehicle also had a rear stowage bin with twenty ready rounds. The photos seems to show a wide box, housing more up to 40 shells, although closed on the opposite side. There was a folding bunk next to it and another in the rear open cab. More could be stored if possible under it, but more likely tooling for the gun's maintenance was carried instead. As showing in photos, the vehicle was most often presented with its gun facing forward, instead of the contrary. The vehicle for prolongated fire needed an ammunition supplier.
Operational History
The concept was inspired by the previous 8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf schwere Zugkraftwagen 12t (Sd.Kfz 8) which saw action in poland and the Campaign of France. It was designed to succeed the lighter Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf Zugkraftwagen 9t (Sd.Kfz. 7). With just fourteen 8.8cm Flak 37 (Sf.) auf s. Zgkw. 18t available in september 1943 (first out in July), it was decided to concentrate them all in a single unit, the Heeres-Flak-Abteilung 304 of 26. Panzer Division in which they served in Italy from late 1943 to the end of the war in April 1945. Their individual fate is hard to track, but the unit was used for AA defence first and foremost. 304 Abt. was composed of three batteries and a light reconnaissance column.The Army Flak Artillery Battalion (Sfl.) 304 was formed on January 20, 1943 in Gotha, in Military District IX. The department was set up by the Army Flak Replacement Department 279. The department was set up as an army force of 3 batteries. From September 27, 1943, the department was assigned to the 26th Panzer Division in Italy. The Army Anti-Aircraft Artillery Replacement Department 279 was responsible for providing the department with a replacement.
The department was set up as a teaching and experimental department. All guns were mounted on self-propelled guns. As an experimental department, the department was the first department of the Wehrmacht with heavy guns on self-propelled guns, which were suitable for both air and ground fire, while earlier experimental designs of this type were only capable of ground fire.
On October 30, 1943, the department was structured as follows: Staff with staff battery, I and towing squadron, 1st and 2nd heavy battery each with 6 guns 8.8 cm Flak 37 (Sf.) and 4 guns each 2 cm Flak 38 (Sf.), 3. le. Battery with 9 guns 2 cm Flak 38 (Sf.) - divided into 3 platoons -, and 2 guns 2 cm Flak-Querling 38 (Sf.) = 1 platoon and 1 searchlight squadron with 4 60cm launchers, 1 light army anti-aircraft artillery column (36 tons). The 26th Panzerdivision was created on 14 septembre 1942 under command of Smilo von Lüttwitz, and at first it was based in the North of France, Amiens, for occupation and coastal protection. In July 1943, she was assigned to Army Group C, 14th Army in Italy. She took part in the attack on the Allied landing in Salerno, Anzio and Nettuno. It covered the retreat in Tuscany and was annihilated there, surrendering to British forces near Bologna in May 1945.
specifications | |
| Dimensions | 9.32 x 2.6 x 2.85 (30 ft x 8 ft 6 in x 9 ft 4 in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 25 tonnes (50,000 Ibs) |
| Crew | 6: Driver, co-driver/gun commander, 4 gun crew (loaders, pointer) |
| Propulsion | 10.8L Maybach HL 108 petrol, 12-cylinder, water-cooled 270 hp |
| Top Speed | 45 kph (estimated) |
| Max Range (on/off road) | 240 km (estimated) |
| Armament | 88 mm FLAK 18 |
| Armor | 14.5 mm (0.57 in) forward arc, 8 mm sides and rear. | Production | 14 conversion |
Links
Gepanzerter 8t Zugkraftwagen and 8.8 cm BuFlak ‘Bunkerknacker’On achtungpanzer.com
On panzerserra.blogspot.com
Model photos on garage-house.org
Model Photos on track-link.com
7.62cm Pak 36 (r) Auf 5t Zugkraftwagen Sd Kfz.6/3
Photos on worldwarphotos.info
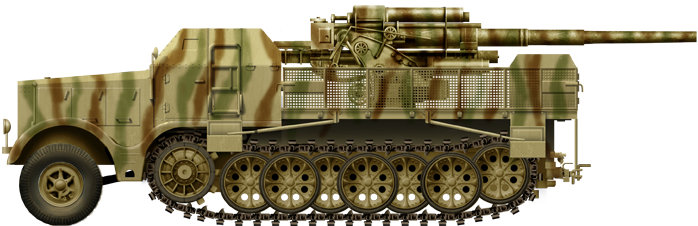
Camouflaged rendition of the vehicle in Italy, early 1944.
Gallery
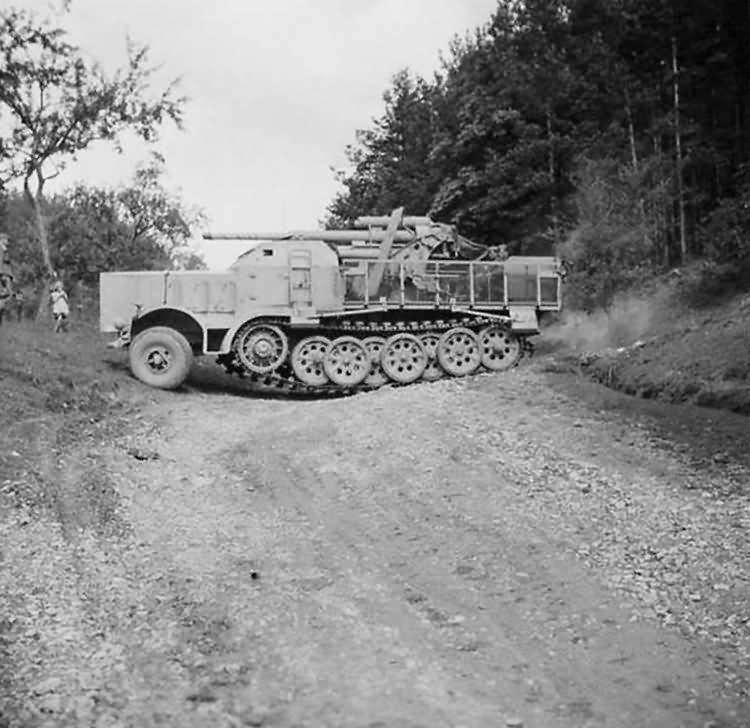


88_cm_Flak_18_Sfl_auf_Zugkraftwagen_18t_sdkfz_9. src ww2 photos
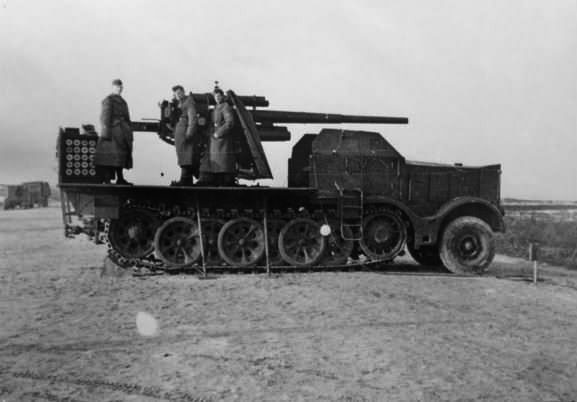

Sdkfz_9_with_88_mm_flak src ww2 photos
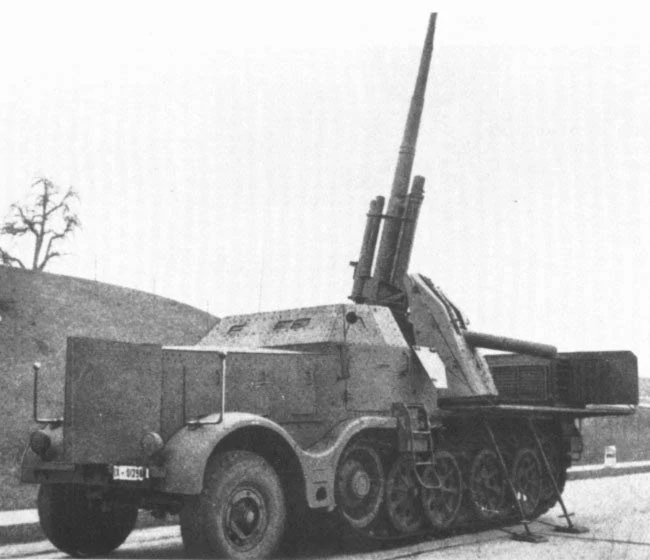

Sdk.fz.9 flak 37
_auf_Zugkraftwagen_18t.webp)
8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf Zugkraftwagen 18t

Help Support Tank Encyclopedia !

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

