D-442 FUG (1964)
 Armored Reconnaissance/Personal Carrier - Circa 900 built
Armored Reconnaissance/Personal Carrier - Circa 900 built
The Hungarian BRDM-2
The Soviet BRDM-2 was a simple and versatile vehicle that draw attention of Warsaw Pact countries as a good candidate to be copied, or emulated by their own industries. Hungary was one such country. The D-442 FUG (Felderítő Úszó Gépkocsi "amphibious reconnaissance vehicle") and its main variant, the D-944 PSZH (Páncélozott Személyszállító Harcjármű – "armored personnel carrier") were both product of Hungarian domestic development, for a vehicle that was even cheaper, and amphibious, exported to Czechoslovakia, East Germany and Poland among others.This post will be split in two, the APC being signifuicantly different to motivate a separate entry. Variants are also to be respresented over time, if solid reference ar found. Production of the FUG and SPZH are ellusive to say the least. Hungary did not have the mass-production facilities in Soviet Union and this went with pros and cons. On one side a limited delvery rate barely sufficient to cover the needs of Hungary, and just enough for export as a complement to Soviet hardware. On the pros, a greater attention to quality and manufacturing standards than in USSR, although it was still cheap enouh to compare favourably to the BRDM. Contrary to Soviet Vehicles, the confidential FUG/SPZH was mostly used inside the Warsaw Pact, the only real foreign export being Iraq for the SPzH.
Development
After independentist aspirations (Hungarian Revolution of 1956) were brutally crushed, Hungary nevertheless, like other Warsaw Pact countries tried to reassess some independence from USSR through its own industry, which was also seen as a source of income. Hungary operated a number of domestic tanks designs during WW2 and was still capable of delivering its own domestic military vehicle. One such inspiration was the BRDM-2 in 1960, just introduced in USSR. It was asked to create an equivalent to cover the needs of the Hungarian Army, as the latter was proposed the BRDM but declined it.The first prototype, manufactured by the state factory, was tested in 1962 and accepted after some modifications by late 1963 for production. The latter was setup in early 1964 and ran until replacement by the heavier SPzH in 1968-69. Production numbers are ellusive.
The D-442 is essentially a light multifunctional scout and personnel armoured carrier intended for reconnaissance. Variants are used as an artillery observation post, mobile command/observation post and for radiological and chemical reconnaissance (NBC) plus simultaneous mapping and marking of contaminated areas.
Other specifics includes an engine at the rear, troop compartment in the center, no partition between the driver and troop compartments, two waterjet units and port covers.
Design
The D-442 had several differences with the BRDM-2. It has a lower profile and modified upper armor scheme, has two waterjet ports for amphibious propulsion instead of one. Like the BRDM it also was given two auxiliary belly wheels on each side the driver can lower to cross obstacles and gaps. This reduced top speed to a crawl at first gear, 5-8 kilometers per hour. Its hull was 5.79 meters long, 2.50 meters wide, 1.91 meters high, with a 3.3 meters wheelbase, and a ground clearance of 0.34 meters, weighting between 6,500 kg and 7,000 kg.The FUG a light multifunctional wheeled armored personnel carrier. It is primarily intended for reconnaissance activities, particularly in the rear of the adversary. It is also used as an artillery observation post, a mobile command/observation post, or for radiological and chemical reconnaissance and simultaneous mapping of contaminated areas. It can be fitted with a pintle-mounted 7.62 UK machine-gun (model 59) with electromagnetic release. The vehicle is powered by a Hungarian-made CSEPEL six-cylinder Diesel engine. To cross obstacles, it uses auxiliary hydraulically steered belly wheels which are located between the basic axles. The vehicle is equipped with a winch, intended, among others, for self-recovery when stuck in difficult terrain. To improve cross-country capability, central tire-pressure regulation system can also be used to decrease the pressure in all tires before crossing an obstacle and to increase it to the required level after the obstacle has been crossed. The tire pressure can be reduced and controlled by the driver from his post by the means of valves and a pressure indicator. Water obstacles can be crossed by swimming. In water, the vehicle is driven by two water jets controlled by the driver. Stability of the vehicle in water is improved by a trim vane which is erected at the front before entering the water.
Powerplant & performances
The vehicle is powered by a Hungarian-made CSEPEL six-cylinder Diesel engine. To cross obstacles, it uses auxiliary hydraulically steered belly wheels which are located between the basic axles. The vehicle's top speed is about 80 kph on road, 30 kph off-road, even 5-10 kph with lowered auxiliaries wheels. It is amphibious and for swimming the front trim vane is erected, bilge pumps activated while the driver engage the water propulsion at the rear. When swimming it is able to reach 8-10 kph.The FUG is able to cross a 1.2-meter trench, climb a 32 degree slope, ford any water surface, climb a vertical obstacle 40 cm high, 125 cm gap, and gradient up to 60%.
Armour
It is 13 mm strong, sloped (so able to resist 14 mm rounds) on the frontal arc, but down to 7 mm (0.3 in) on the sides of the hull and top superstructure. For passive protection, the vehicle is amphibious, so resonably tight for NBC, but not proof, to the exception of specialize Recce chemical vehicles, which has sealed hatches, and overpressure system. There is no smoke projectors for active concealment. To provide an autonomy of 600 km, the vehicle is equipped with a main 200 liters tank and/or two 75 litre tanks depending of the version.Armament
The basic D-442 FUG can be fitted with a pintle-mounted 7.62 UK machine-gun (model 59), with electromagnetic release to be fire from inside. It is placed forward of the main top hatch. Otherwise, armament is limited to what the scout team carries, AK-47 Kalashnikovs and Tokarev or other models of pistols.FUG/OT-65A: This Czech/Polish version was given a miniturret fitted with an external 82-mm recoilless gun, and an internal 7.62-mm light machine gun. Rate of fire for the recoiless rifle dependended on availability of the outside loader, abour 5-10 per minute. Practical rate of fire for the 7.62-mm MG was 200 rds/min, with a total in store of 1,000-2,000 rounds. The Hungarian reconnaissance vehicle has a standard 7.62-mm light machine gunnormally unmounted with an optional pintle mount.
Variants
- D-442 FUG: Early Hungarian Production
- D-442.00 FÚG, basic scout car.
- D-442.01 PK-FÚG. Command vehicle with add.
- D-442.03 VS-FÚG. NBC reconnaissance vehicle
- D-442.01 MRP-FÚG. Forward air controller post
- D-442.02 MÜ-FÚG. Engineer reconnaissance vehicle
- FÚG-66 (1966). 4 prototypes built for D-944 PSzH
- FÚG-70 (1970) - Pre-series built prototypes
- D-944 PSzH: Armoured Car derivative
- OT-65: Czechoslovakian Designation
D-442.00 FÚG (1963)
(early 1960s) - Basic armoured scout car without the turret. It had an R-113 or R-114 radio.D-442.01 PK-FÚG
D-442.01 PK-FÚG (parancsnoki) - Converted into a command vehicle with R-113 or R-114 and an additional R-114M or R-112 radio for platoon and company commanders. Later a R-403 or R-407 relay was built in for company and battalion commanders.D-442.03 VS-FÚG
D-442.03 VS-FÚG (vegyi sugárfelderítö úszó gépkocsi) - NBC reconnaissance vehicle based on D-442 FÚG with specialized radiation, chemical and biological detection devices as well as flag dispensers used to mark the contaminated areas.D-442.03 VS-FÚG
D-442.03 VS-FÚG (vegyi sugárfelderítö úszó gépkocsi) - NBC reconnaissance vehicle based on D-442 FÚG with specialized radiation, chemical and biological detection devices as well as flag dispensers used to mark the contaminated areas.D-442.01 MRP-FÚG
D-442.01 MRP-FÚG (páncélozott repülőirányító pont) - Forward air controller post, based on D-442 PK-FÚG with an R-114 and an R-159 radio.D-442.02 MÜ-FÚG
D-442.02 MÜ-FÚG (műszaki) - Engineer reconnaissance vehicle with special equipment.FÚG-66 (1966
FÚG-66 (1966) - Four prototypes built for D-944 PSzH without turret in 1966.FÚG-70 (1970)
FÚG-70 (1970) - Pre-series built prototypes for D-944 PSzH (Wheeled Amphibious Armoured Personnel Carrier) able to carry six fully equipped soldiers, who exit the vehicle through small two-part doors on the each side of the hull. The turret was different from the D-944.00. The main weapon was a 20mm caliber aircraft machine cannon, cannibalized from Il-10 aircraft in the middle 1950s. Only 7 were built.Main Variant: D-944 PSzH
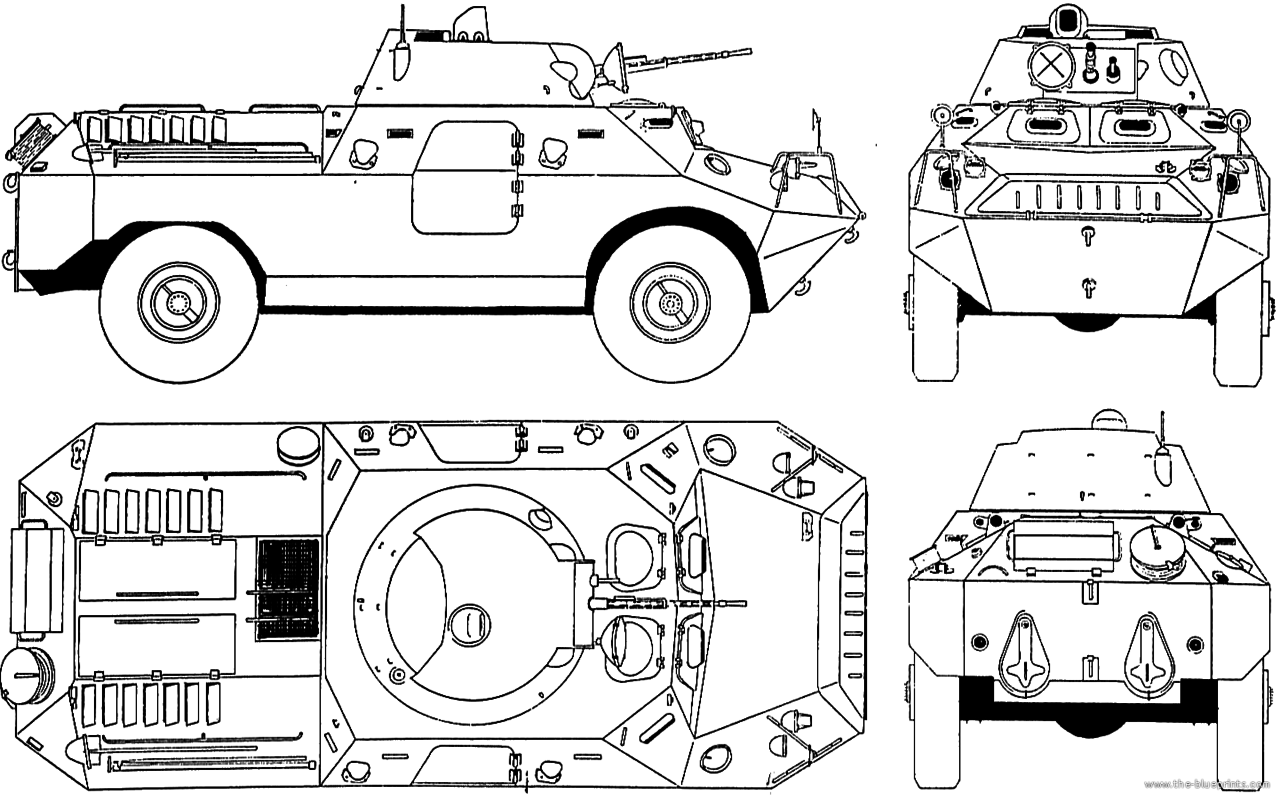
PSZH IV
This vehicle (which will be studied in a next post) was a response to some drawbacks of the FUG, and need for a more heavily armed vehicle leading to the development of the D-944 PSZH, developed in late 1960s. It was a heavier, main armoured personnel carrier for the Hungarian Armed Forces but whioch could be used by the border guard and internal security services. It had a two-part side door, removed auxiliary belly wheels and the same turret as the BRDM-2 but modified and improved, armed with 14.5 mm KPVT heavy MG and coaxial KPT 7.62 mm. Armor was the same as the powerplant.
The D-944 PSzH carried 6 troops in addition of a crew of 3 men. Commander and driver sat at the front, gunner sat in the turret. Protection was a bit better at 14 millimeter and it also introduced NBC protection and infrared night-vision equipment. Unlike the BRDM-2 it did not have its flaw related to entering and exiting the vehicle, unlike the roof hatches of the D-442 FÚG, leaving those dismounting very exposed to enemy fire. Buoyancy was also degraded slightly due to the weight of the turret.
OT-65: The Czechoslovakian Version
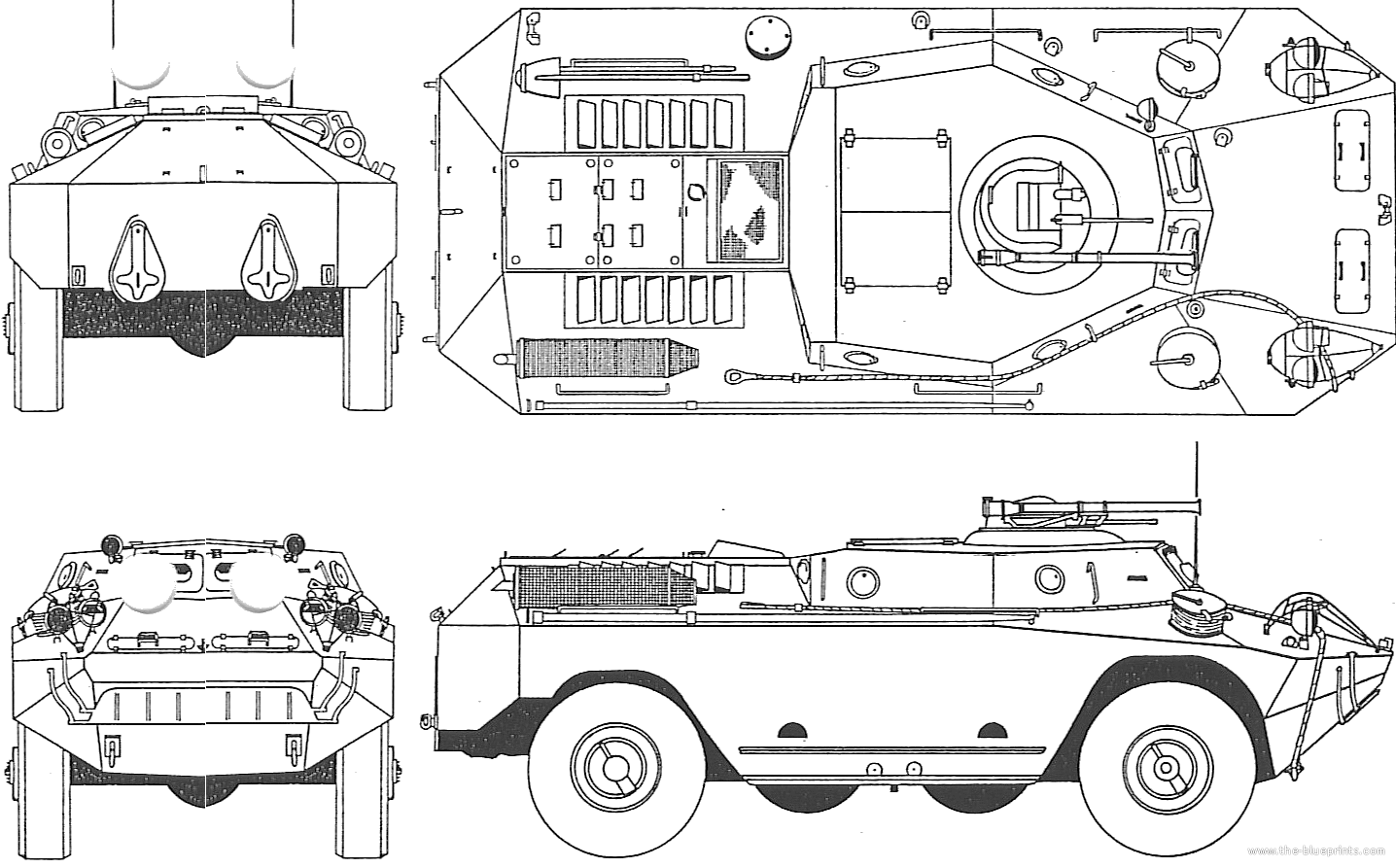
OT-65 Otter/Vydra
Czechoslovakia adopted the D-442 FUG, but not East Germany. OT-65 meant (Obrněný Transportér vz. 65). The OT-66 was the D-944 PSzH. Variants of the former included:
- OT-65ZDR (zdravotní): Armoured ambulance.
- OT-65A "Vydra" (Otter): OT-62B TOPAS turret, hatches moved behind the turret, additional protection on IR driving lights.
- OT-65Ch (chemický): NBC recce variant with detection devices, flag dispensers to mark contaminated areas.
- OT-65ChV (velitelsko-chemický): Electro-Chemical variant of the NBC vehicle.
- OT-65DP: Armoured artillery forward observation post.
- OT-65DPP (pohyblivá dělostřelecká pozorovatelna): Same vehicle, other denomination.
- OT-65 R-2: Communication vehicle with extra R-2 set.
- OT-65 R-112: Same with R-112 radio set.
- OT-65RL: Battlefield surveillance radar PSNR-1.
- OT-65VP: Equivalent to the Hungarian MRP-FÚG radio vehicle.
Active service
Production allegedly started in early 1964 and is likely to have been swapped in 1969 for the PSzH. Production figures are ellusive with various records. Hungarian deliveries are likely to have been around 900 vehiclces, with 275 ordered by Czechoslovakia in 1965, received by 1968 as the OT-65. Poland obtained 100 OT-65A Otter, making a total of 375 vehicles for export alone. According to militaryfactory, the vehicle was also operated by Romania and Bulgaria, but it is likely only to have been restricted to evaluation only. The Hungarian vehicles were withdrawn from military service in 1980s, but the Czech and Polish were maintained in service in the 1990s ad early 2000s.Battle records within the Warsaw Pact are reduced but included the "praque spring", or 1968 Operation Danube, invasion and repression of the revolution in Budapest under Soviet lead. Hungarian vehicles participated, included the D-442 FUG. Outside, the only vehicles engaged in actual combat were some 200 Iraqi PSzH-IV, but this does not concerns the D-422 FUG which was never exported outside the Warsaw Pact.
Sources/Links about the D-442 FUG
www.armyrecognition.comwww.globalsecurity.org
tvd.im/land-systems/
archivum.mtva.hu
wiki
On militaryfactory.com
D-442 FUG specifications | |
| Dimensions | 5.79 x 2.50 x 1.91 m (19ft 2in x 8ft 2in x 6ft 3in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 6.3 tons (6.2 LT) |
| Crew | 2 (Driver, commander, 4 scouts) |
| Propulsion | Csepel D414.44 in-line 4-cyl. OHV 5.5 l diesel 101 hp (75 kW) |
| Suspension | 4x4 Independant torsion bars |
| Speed (road) | 81 kph road, 45 kph cross country, 9 kph water |
| Range | 600 km (370 miles) |
| Armament | 7.62 mm UK light LMG, personal weapons |
| Armor | 13 mm max front, 7 mm sides (0.5 in) |
| Total production | circa 900 1963-1969. |
Illustrations

Hungarian D-442 FUG with its secondary wheels, Operation Danube 1968

Hungarian D-442 panels open

Polish D-442 (OT-62)

Sand Khaki OT-62
Gallery

FUG Chem, Chemical variant
OT-65
FUG D-442
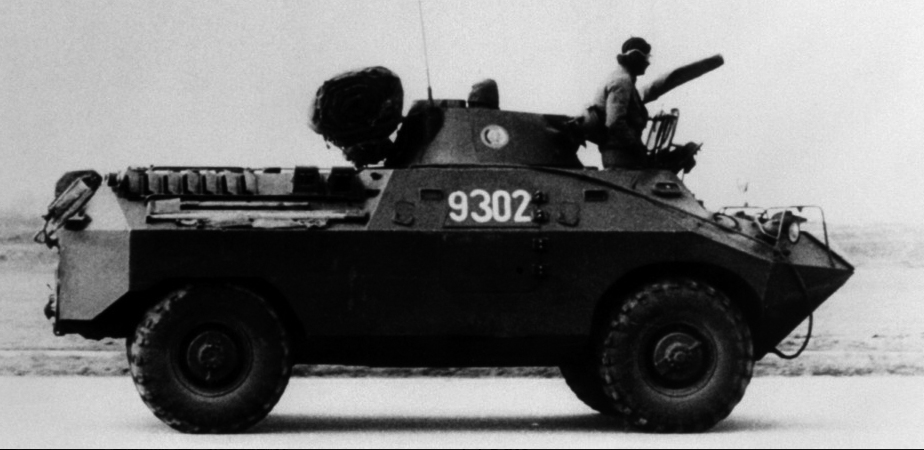

Experimental FUG-70, later D-944
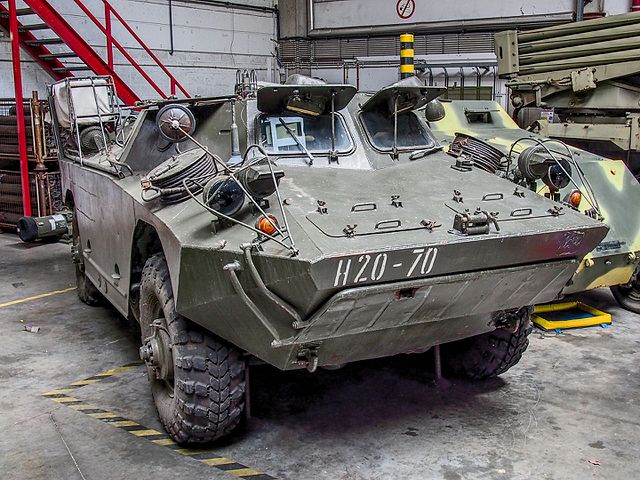

OT-65 at Brasschat Museum
Polish OT-65 Otter
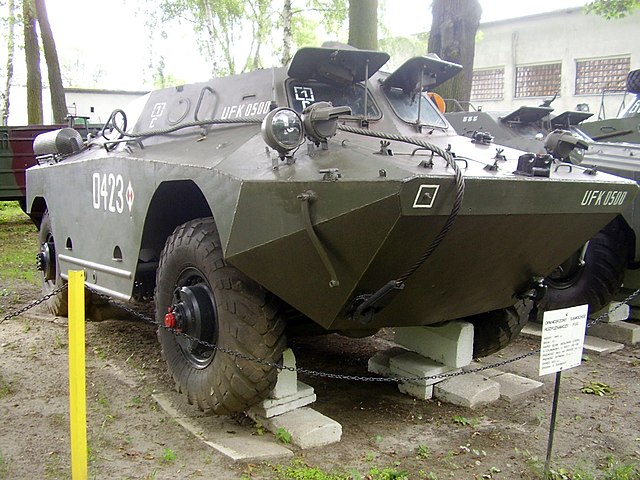

Polish OT-65

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
