The 9P162 Kornet-T is an anti-tank missile carrier designed in Russia on the basis of the BMP-3 IFV, part of the 9K128 "Kornet-T" complex, and design to carry and operate the 9M133 Kornet anti-tank guided missile. It was designed to replace the older 9P149 Shturm-S based on the MT-LB, but also the 9P148 Konkurs based on BRDM-2 armored scout car. First Kornet-T anti-tank missile carriers were delivered in 2003, but tests and fixes were ongoing for many more years. A first batch of 20 were delivered to the Russian Army in 2012.
The Kornet-T has been designed to engage tanks and low-flying helicopters but also fortifications, using the right warheads. This antitank vehicle was also designed to operate and fire in day, night and all weather conditions and even tanking in account enemy countermeasures.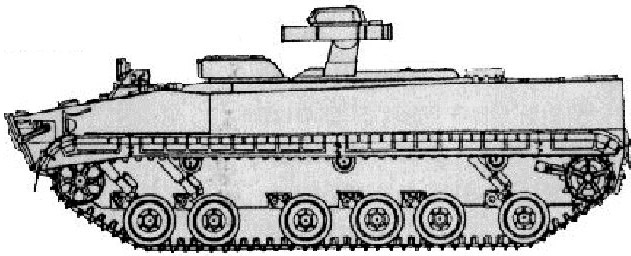
Basic blueprint
The hull is the same as the basic BMP-3 and thus, armor protection stays the same, with a welded aluminum alloy armor hull. Its front arc is however made of composite armor, providing enough protection against 30-mm armor-piercing rounds. All-round protection is down to 14.5-mm armor-piercing rounds. There are experts saying the vehicle could also be enhanced with add-on explosive reactive armor kit (ERA) but none so far has shown it on photos. NBC protection is collective, with slight overpressure. There is an automatic fire suppression system for the fighting compartment and engine compartment as well.
The drivetrain uses six simple rubberized roadwheels on torsion bar suspensions, with the addition of three hydraulic dampers on either side, two on the front two roadwheels and one of the aftmost one. Drive sprocket is at the rear and idler forward. The 18 t vehicle, 7.2 m long by 3.22 m and 2.85 m could reach 72 km/h on flat, with an amphibious speed of 10 km/h and a range estimated to around 600 to 650 km. It was test able to clib a 60% gradient, 40% Side slope, 0.8 m Vertical step and gap a 2.5 m trench.
The main lauincher arm carried two launch canisters. Both missiles could be operated against the same target for a saturation fire and better chances of hitting, but the modern radar and tracking system allows the operator to engage two targets simultaneously. In travel mode, the launcher arm rectracts inside the hull and its deployment is a matter of seconds. When on road, the vehicle looks like a turretless BMP-3.
The Kornet-T is most efficient went launching a salvo of 2 missiles in less than a second apart to the same target, intended to overcome its active protection systems. The first missile triggers it and is likely destroys or lost, but the second hits anyway. Without any active protection system the probability of first hit is increased as well as destruction chances.
It was adopted by the Russian Army back in 1994 and being developed in 1988–1998 as a universal missile, it was fitted on a large variety of platforms. At its core, it's fire-and-forget anti-tank missile, laser-guided with a practical range of 100-5,500 m and ideally 3,500 m. its strenght is to use both tandem HEAT and thermobaric warheads. The first defeats 1,200 m behind ERA, which is lethal to any modern western MBT. it was also exported many countries. The later Kornet-E was developed as a downgraded export version, first seeing combat in the Middle East, the 2003 during Invasion of Iraq, 2006 Lebanon War, by Hamas and Hezbollah fighters.
The Kornet-M pushes this range to 8 000 m, and 10 000 m for themobaric warheads (quite useful on fortifications). The missiles carried by the 9P162 could be also dismounted and fitted on a tripod launcher with its sight unit. The 9M133 missile's nose houses the guidance section, with laser beam sensor at the rear. The warhead is located behind the rocket fuel, well inside the missile body. It gives on purpose, a bit more time for the precursor charge to detonate ERA armor. However the plasma jet had to force its way through the forward components, and occasionally deforms, with a reduced penetration.
The Kornet is a subsonic missile and makes about 0.5 min (30 sec.) to reach its maximum range. Outside tripods for the indantry, it could be carried by light vehicles on a pedestal-mounted manpack rear launcher. The night sight of the dedicated tank destroyer and its autoloader as well as all-terrain capabilities and better protection are all superior to light vehicles solutions suc as the GAZ Tiger.
*Lenght, diameter, wingspan
btvt.narod.ru
vpk.name/en/520152
weaponsystems.net
globalsecurity.org
military-today kornet_t
9M133_Kornet
Design of the "Abrams Killer"
The Kornet-T is based on the BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicle and close in general design to the 9M123 Khrizantema, which is also based on the BMP-3 cassis. The later entered service way sooner, back in 2004. The Kornet-T as it seems was deployed with the motorized units, and the Khrizantema became organic to artillery units.The Kornet-T has been designed to engage tanks and low-flying helicopters but also fortifications, using the right warheads. This antitank vehicle was also designed to operate and fire in day, night and all weather conditions and even tanking in account enemy countermeasures.
Hull & Protection

Basic blueprint
The hull is the same as the basic BMP-3 and thus, armor protection stays the same, with a welded aluminum alloy armor hull. Its front arc is however made of composite armor, providing enough protection against 30-mm armor-piercing rounds. All-round protection is down to 14.5-mm armor-piercing rounds. There are experts saying the vehicle could also be enhanced with add-on explosive reactive armor kit (ERA) but none so far has shown it on photos. NBC protection is collective, with slight overpressure. There is an automatic fire suppression system for the fighting compartment and engine compartment as well.
Powerplant and Powertrain
This anti-tank missile carrier is operated by a crew of two, including gunner and driver. The latter is installed in the same locations as for the standard BMP-3, installed on the central hatch, with three sight periscopes and central IR one for night driving. The vehicle is powered by an UTD-29 turbocharged diesel engine rated for 500 hp, located at the front. There is also an optional, more modern UTD-32T turbocharged diesel engine rated 660 hp coming from the improved BMP-3M IFV. It is not known if it was fitted. The vehicle is fully amphibious, propelled while swimming by its two rear waterjets, and it has been tested fire missiles while afloat.The drivetrain uses six simple rubberized roadwheels on torsion bar suspensions, with the addition of three hydraulic dampers on either side, two on the front two roadwheels and one of the aftmost one. Drive sprocket is at the rear and idler forward. The 18 t vehicle, 7.2 m long by 3.22 m and 2.85 m could reach 72 km/h on flat, with an amphibious speed of 10 km/h and a range estimated to around 600 to 650 km. It was test able to clib a 60% gradient, 40% Side slope, 0.8 m Vertical step and gap a 2.5 m trench.
Loader and launcher system
The entire vehicle is dedicated to anti-tank purpose. It does not have any armament past the Antitank launcher, but the crew's own personal weapons (Driver and commander/missile operator). The centerpiece of the whole system if the center-mounted automatic loader, with two ready vectors at all time. A total of 16 missiles are carried inside the bay below. The entire process is automatic so there is no crew access to this part. 12 missiles total are stored in the autoloader below the launcher itself, barillet type, plus four extra ones stored inside the hull.The main lauincher arm carried two launch canisters. Both missiles could be operated against the same target for a saturation fire and better chances of hitting, but the modern radar and tracking system allows the operator to engage two targets simultaneously. In travel mode, the launcher arm rectracts inside the hull and its deployment is a matter of seconds. When on road, the vehicle looks like a turretless BMP-3.
The Kornet-T is most efficient went launching a salvo of 2 missiles in less than a second apart to the same target, intended to overcome its active protection systems. The first missile triggers it and is likely destroys or lost, but the second hits anyway. Without any active protection system the probability of first hit is increased as well as destruction chances.
About the 9M133 Kornet Missile
The 9K135 Kornet (NATO AT-14 Spriggan) was developed to replace both the Cold War era 9K111 Fagot ("AT-4 Spigot") and 9K113 Konkurs ("AT-5 Spandrel"), heavier and more expensive it became more of a supplementary system, and did not really replaced them.It was adopted by the Russian Army back in 1994 and being developed in 1988–1998 as a universal missile, it was fitted on a large variety of platforms. At its core, it's fire-and-forget anti-tank missile, laser-guided with a practical range of 100-5,500 m and ideally 3,500 m. its strenght is to use both tandem HEAT and thermobaric warheads. The first defeats 1,200 m behind ERA, which is lethal to any modern western MBT. it was also exported many countries. The later Kornet-E was developed as a downgraded export version, first seeing combat in the Middle East, the 2003 during Invasion of Iraq, 2006 Lebanon War, by Hamas and Hezbollah fighters.
The Kornet-M pushes this range to 8 000 m, and 10 000 m for themobaric warheads (quite useful on fortifications). The missiles carried by the 9P162 could be also dismounted and fitted on a tripod launcher with its sight unit. The 9M133 missile's nose houses the guidance section, with laser beam sensor at the rear. The warhead is located behind the rocket fuel, well inside the missile body. It gives on purpose, a bit more time for the precursor charge to detonate ERA armor. However the plasma jet had to force its way through the forward components, and occasionally deforms, with a reduced penetration.
The Kornet is a subsonic missile and makes about 0.5 min (30 sec.) to reach its maximum range. Outside tripods for the indantry, it could be carried by light vehicles on a pedestal-mounted manpack rear launcher. The night sight of the dedicated tank destroyer and its autoloader as well as all-terrain capabilities and better protection are all superior to light vehicles solutions suc as the GAZ Tiger.
9M133 specifications | |
| Launcher | 2 canisters 9P163M-1 Kornet-T, round internal magazine |
| Dimensions (L-d-w)* | 1,200 mm -152 mm - 460 mm |
| Total weight, battle ready | (xxx lbs) |
| Guidance | SACLOS, laser beam riding, beyond 5 m accuracy |
| Control | Automatic tele-orientation in the laser beam |
| Propulsion | Single-stage solid propellant rocket motor |
| Speed | over 250 m/s |
| Range | 100-150 m to 5,500 meters (3.4 mi) |
| Penetration | 1.000-1.200 mm RHA behind ERA and 1200–1400 mm RHA, 3-3.5 m concrete |
| Altitude | Up to 3 km |
| Warhead, TNT quivalent | 7 kg |
| Canister lenght | 1.21 m |
Types | |
| 9M133 | tandem-cumulative warhead |
| 9M133F | high-explosive warhead |
| 9M133-1 | tandem-cumulative warhead |
| 9M133F-1 | HE warhead |
| 9M133FM | HE warhead |
| 9M133M-2 | tandem-cumulative warhead |
| 9M133FM-2 | thermobaric warhead |
| 9M133FM-3 | HE warhead |
| Total production | 35,000 |
Related links
on rusarmy.com/btvt.narod.ru
vpk.name/en/520152
weaponsystems.net
globalsecurity.org
military-today kornet_t
9M133_Kornet
specifications 9P162 Kornet-T | |
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 7.2 x 3.2x 2.85 m (erected) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 18 Tons (xxx lbs) |
| Crew | 2 (driver, commander/operator) |
| Propulsion | UTD-29 diesel 500 hp Maximum road speed Amphibious speed on water 10 km/h Range |
| Speed (land/water) | 72/10 kph |
| Range (on flat) | 600 - 650 km |
| Armament | Kornet-T, see notes |
| Armor | As BMP-3, see notes |
| Total production | 20 (as for 2012) |
Operational History
Deployed in a single brigade for testing and exercizes since 2012. It has been publicly revealed further at the 2014 tank biathlon competitions in Russia. Since it has been seen at the 1000th Training Center of Rocket and Artillery Troops, Kolomna. The only place this vehicle is known to have seen combat so far is the current conflict in Ukraine. According to Oryx blog photos from a destroyed 9P163M-1 are confirming such deployment. *defence-blog.com 12/04/2022 * Oryx list of destroyed vehicles * Additional photos at Kolomna. Six 9P162 Kornet-T has been spotted on 29 January 2022 transiting also to Belarus *src.Illustrations
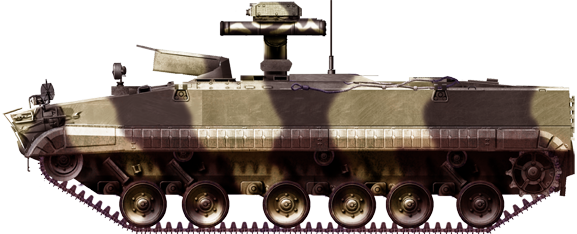
9P162 Kornet-T Camouflaged

9P163M-1 as seen in Kolumna
Gallery
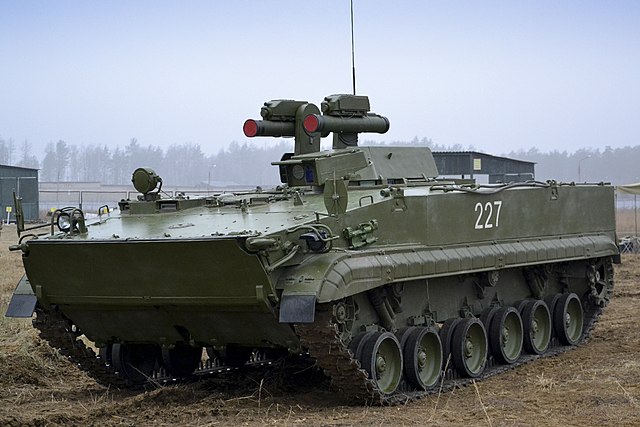
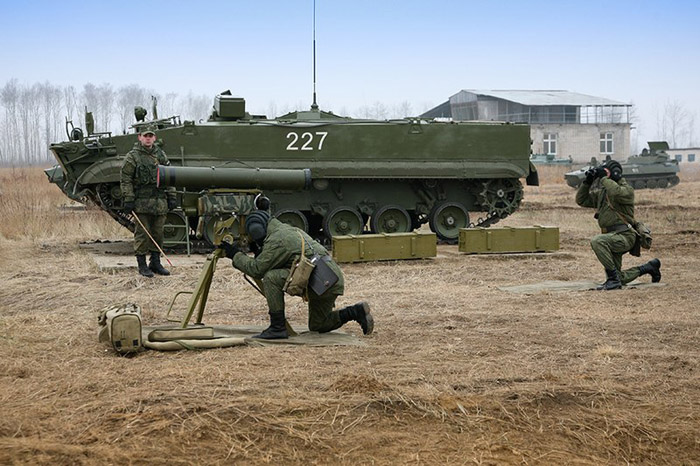


Kornet-T at the 1000th Training Center of Rocket and Artillery Troops
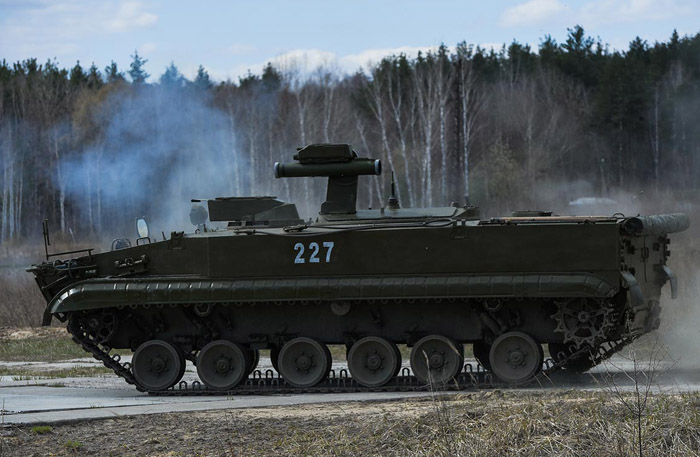

Same vehicle "227"

Modern Tanks
Modern MBTs posters

Denel Bagder (2018)

Type 16 MCV (2016)

Gepard 1A2 last rounds 2011

SANDF

Russian AFVs

Main Battle Tanks
