The first Panhard Armored Car
The Panhard company was no novice on the military vehicle stage, having had already produced parts for armored cars prior to the Great War. The 1930 Panhard 165 and 175 armored cars were derived from the 16 cv X46 car chassis of 1926. They were designed especially for the TOE (Théâtres d'Opérations Extérieurs) or Foreign Theaters of Operations (overseas, colonial service).North Africa was foremost in the minds of the designers, the terrain there requiring decent off-road capabilities. Other "theaters" included Syria, Palestine, Constantinople, Morocco, and AOF-AEF (West and Equatorial Africa) in the interwar. Two models were designed, the first called 165 (used during the Rif War, against Moroccan tribal warriors), and the second 175, completely overhauled with better suspensions and used in WW2, exclusively in North Africa.
The Panhard 165
The story of the Panhard 165 starts in 1929. The Panhard AM20 and "new" Laffly AMD 50 failed the tests of the Armored Cavalry Bureau. The harshness of colonial service imposed new requirements linked to the lack of spare parts and maintenance facilities. The new Panhard 165 prototype was still largely based on the AM20, but with some modifications, like the armor plates and a more powerful 4-cylinder Panhard 86 hp engine instead of the previous 20 hp one. The engine radiator was protected by narrow horizontal plates.The tall 4x2 vehicle had a crew of four (driver, assistant driver/mechanic, commander/radio and gunner). 60 such vehicles were built in total, but 30 were of the modified 175 type. The overall weight was 6750 kg, with a length of 5.43 m (17'10'') and a height of 2.76 m (9'1''). The vehicle had a good ground clearance. Its most striking visual characteristics were its uneven roadwheels, the rear pair being massive, supported by leaf springs. The armor was riveted, 6 to 9 mm thick (0.2-0.35 in).
Propulsion was assured by a Panhard, 4-cylinder 86 hp gasoline engine, procuring a power to weight ratio of about 7.31 hp/t. It was coupled to a mechanical type gearbox, with propeller shaft, manual handling and reverse gear. The top speed (shown on trials) was 75 km/h (47 mph) on road and 31 km/h (20 mph) off road. The maximum range was 600 km (380 mi) and 385 km (240 mi) respectively, thanks to a fuel capacity of 170 liters. The fuel tank was mounted close to the engine. It could climb a 0.3 m (1') vertical obstacle or manage a 40% gradient, gap a 0.7 m (2'4'') trench and ford 0.6 m (2') of water. The front wheels measured 8x36 dm and the rear ones were 10x40 dm, with bulletproof tires manufactured by Veil-Picard and leaf spring suspensions.
Its main armament was the standard-issue Puteaux short barrel 37 mm (1.46 in) SA 18 L/21 gun meant to deal with fortified buildings at moderate range, or lightly armored vehicles at less than 200 m range. The muzzle velocity was 367 m/s or 388 m/s (400-425 yd/s) depending of the charge. It came with an ammo supply of 194 rounds (94 AP mle 1898 and 100 HE Mle 1916 according to some sources) and had a secondary armament comprising a Chatellerault FM 24/29 7.5 mm (0.29 in) or MAC 31 machine gun, with 2400 rounds of ammo. The rear fighting compartment housed the vehicle commander, tasked with gun maintenance, and machine gunner. Boxes with tools, spare parts and regular entrenching tools were located on the side steps.
The Panhard 175
This model was overhauled by Panhard, taking into account the lessons of the Rif War and interwar service. It is quite hard to have a precise detail of the modifications list which seems to revolve around the reinforced suspension and the addition of a rear mounted driver post. However, the model was in "competition" with the more modern Berliet VUDB. It seems that some vehicle had their 37 mm (1.46 in) gun replaced with antitank 25 mm (0.98 in) guns during the wartime period.Another model was derived for the chassis, the Panhard 179. This armored personal carrier had a completely new rear compartment replacing the turret and fighting compartment, large enough for 6 infantrymen. Its armament was a single FM24/29 machine gun and about 30 to 60 units were manufactured in all.
Radios: Squadron commanders (GAM) received models equipped with an ER 26 ter radio set intended for internal communication within and between cavalry units. The captain's vehicle was fitted with two ER 26 ter radios, one for communication with the platoon leaders and the other for keeping in contact with the squadron's colonel. The crew wore flexible helmets equipped with headphones, one under the cap and the other under the helmet, specific to the on board radio sets. The ER 26 had a wavelength of 40-110 m and 100 watts of power. Its range was 60 km (37 mi) when stationary and 30 km (19 mi) (in graphic mode only) when moving. It had two 2 m antennas at each end of the vehicle.
Lineage of Panhard Armored Vehicles
WW1: Panhard-Genty 24 HP (1911), Panhard 103 (1914 - partially armored), Panhard 105 (1913). Interwar: Panhard 138 (1926) cavalry type, from which the Panhard 165 was derived. The single vehicle was converted into an armored command car.In 1932, the Panhard 179 appeared, derived from the same chassis as the 165 and 175. In 1935, they were overshadowed by the Panhard AMD 178 (AMD 35). In 1940, the Panhard 201 prototype was hidden from the Germans and after liberation, and used for the design of the famous EBR in 1951.
Coldwar: In 1956, the rare Panhard ETT appeared. The Cold War years saw the arrival of the AML 60/90 (1966), M3 (1969), VCR (1977), ERC-90 Sagaie (1979), VBL (1990). After the fall of the Iron Courtain, the Panhard PVP appeared in 20o2 and in 2005 the VPS was derived from the Peugeot P4. In 2010, the SPHINX prototype was unveiled at Satory, with the CRAB following a year later. None were ordered yet.

Panhard 165 squadron command variant - Source: Unknown
The Panhard 165/175 in action
The first use of the 165 was during the Rif War (1920-26). The French started their intervention when the country passed onto their control as a protectorate. Their intervention lasted just one year, between 1926 and 1927. The Rif was a mountain range in Northern Morocco, 150 km long. The Rif tribal warriors used very efficient guerilla tactics.The Panhard 175 saw action in WW2 against the Axis, in Morocco, Syria then Tunisia. They were used alongside Panhard 179s that acted like APCs, generally placed at the head of the column, three vehicles. The French used these until the spare parts stock was exhausted. By 1944, American and British vehicles had replaced all the French built armored cars. None survived to this day. Its legacy had been overcast by the excellent Panhard 178.
Links
Panhard 165 on Chars-Français.netOn the turret difference (forum)
Interesting photo of the camouflaged 3th RCA -coll AVZ94
Another reference on Armoredgun.org
About the battle of Gembloux, French AFVs
Model on Warpains.net Same on Minitracks
Panhard 165/175 specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 4.79 x 2.01 x 2.31 m (15'7'' x 6'6'' x 7'5'') |
| Total weight, battle ready | 8.2 metric tonnes (17,000 lbs) |
| Crew | 4 (driver, rear driver/radio, commander, gunner) |
| Propulsion | Panhard 4-cyl SK, gasoline, 105 hp |
| Speed | 72 km/h (46 mph) |
| Suspensions | 4 x 4 leaf spring suspensions |
| Range/fuel capacity | 300 km (186 mi)/140 l |
| Armament | 37 mm (1.46 in) SA 18 Reibel M1935 7.5 mm (0.295 in) machine-gun |
| Armor (max) | 20 mm (0.79 in) |
| Total production | 1143 A+B versions |

The basic Panhard 165 of 1933, here with a wartime modification, the replacement of the 37 mm (1.46 in) Puteaux by a 25 mm (0.98 in) antitank gun.

A camouflaged Panhard 175 TOE of the 3rd BCA (Bataillon de Chasseurs d'Afrique) - Click for the HD version.
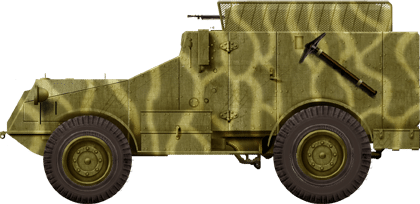
The closely derived Panhard 179, also with the 3rd BCA (Bataillon de Chasseurs d'Afrique)
Gallery
 Panhard 165/175 - Source: Unknown.
Panhard 165/175 - Source: Unknown. Panhard 179 seen from the rear in North Africa
Panhard 179 seen from the rear in North Africa
Panhard 165/75 TOE - Source: Panhardclub.nl

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

