The main Turkish IFV
The ACV-15 was started by FNSS Savunma Sistemleri A.Ş when it was apparent that the M113 was no longer sustainable as a first line APC. The M113 was in service with the Turkish Army to an extent of 2,813 vehicles since the 1970s. A Turkish Land Forces Command's (TLFC's) operational requirement came out in 1990 that concerned a vehicle derived from the license-built M113 and rederived from the FMC's AIFV family in the late 1980s/early 1990s. The AIFV never enjoyed a considerable influence through license production and exports worldwide, being mass-produced and exported by Belgium and the Netherlands.Development
The ACV-15 was developed by FNSS as an APC/IFV capable to follow and accompany Main Battle Tanks in armored divisions or mechanized brigades. Emphasis is put both on protection with an add-on armor and armament with a 20 mm autocannon in the turret. According to FNSS, it is designed for Multi-Missions in Mechanized/Armored Infantry units, Reconnaissance, Special Operations and Independent Infantry Operations. Production started in 1992 and spanned until 1997. It was replaced by the ACV-19 (ex.ACV-SW) or new generation IFV with one more roadwheel per side and stretched hull. Both vehicle also serves to a large family of specialized vehicles. Production records differ from 2500 (FNSS ) (probably because the integration of specialized vehicles and/or exports). According to Wikipedia however, some 650 AIFV IFV versions and 1,550 AAPC are in service, but more in detail, 2,249 in all comprising 1,380 AAPC, 650 AIFV, 48 ATV and 170 AMV.Design
Like the AIFV family of vehicles, the ACV-15 striking difference with the M113 is the beefed-up armor, sloped rear section, and of course main armament in a fully enclosed turret. The structure is made of welded reinforced ballistic aluminum plate and the rear section is given two pistol ports on each side plus one in the rear door. Protection is assured against heavy machine gun rounds (Typically the 14.5×114mm armor-piercing rounds of the Russian-built BTR and BRDM) for the whole frontal arc and small arms fire elsewhere. The internal crew compartment is protected NBC with an overpressure system, and automatic fire extinguishers are placed in the engine and crew compartment. The driver is located on the left-hand side, with the Detroit Diesel Model 6V-53T 300 hp on his left. He has four vision block with a central passive night vision system. Behind him is located the commander cupola with a rear-opening hatch and five vision blocks plus a passive rotatable periscopic sight.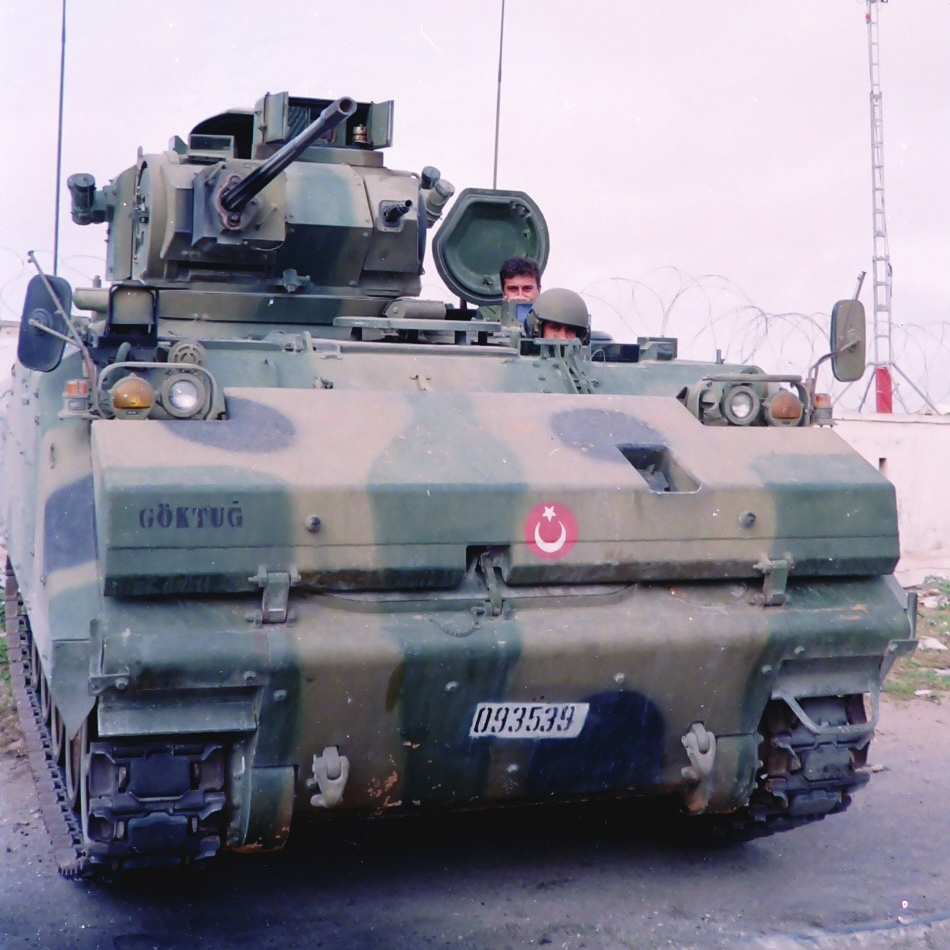
ACV-15 in Mogadisciu
At his left lays the one-man FNSS Sharpshooter turret and gunner station. He has a hatch on the turret top, four vision blocks, two per sides, plus the front gunner sight with magnification. The gun is of the standard US 25 mm type built under license (same as the M2 Bradley), which can fire either HE and AP rounds. The ACV-15 hull is completely sealed off and the vehicle is amphibious without preparation but the trim vane folded on the front being erected. When swimming at about 10 kph, the tracks are used for direction. For concealment, the ACV-15 is literally bristling with smoke dischargers, eight on the turret, seven on the front above the trim vane, and eight at the rear, on two extension of four dischargers each. With such an arrangement all angles are covered. There is also a rear hydraulic ramp.
Variants
ACV-AAPC (advanced armored personnel carrier) had a one-man turret with a 12.7 mm machine gun and 7.62 mm machine gun, carrying capacity 13 troops. It is more of an APC with the modular right section replaced by a gunner cupola and a cal.50 browning M2HB replacing the turret. The up-armored variant receives a near-complete shielding of the ACAV type.ACV-AIFV /FMC EWS, DAF Special Products turret and 25 mm Oerlikon Contraves, plus coaxial 7.62 mm LMG
AIFV /Giat Dragar turret 25 mm M811 cannon, coaxial 7.62 mm LMG.
ACV-ATV Armored Tow Vehicle, fitted with a Norwegian one-man turret, two BGM-71 TOW missiles, 4 infantry carried.
The Command variant received a large superstructure at the rear with extra radios and electric generators.
Tank Destroyer: Two versions exist, one with a TOW mount (TUA style arrangement), and the other similar to the AAPC but with a single TOW tube launcher replacing the cal.50 mount.
SPAAML variant, with two banks of four launchers and a coaxial machine gun.
ARV (armoured recovery vehicle) with an articulated arm, crane, jib and winch.
ACV-AMV Armored Mortar Vehicle The 81 mm mortar carrier version, with an open top to bear the mortar.
ACV-15 SPM 120mm The heavy self-propelled mortar version. The mortar is folded inside the rear compartment and raised through two roof doors.
ACV15 AESV: A version optimized for urban combat with slat armour, extra stowage, an RWS (remote weapon system) plus extra cameras.
Armoured ambulance with internal space for stretchers and medical equipment.
Derivatives
Malaysian ACV-300 Adnan:
The Malaysian version, and collaboration between FNSS and DRB-Hicom Defence Technologies (Deftech). Named after Adnan bin Saidi, a hero from the battle of Singapore in 1942. Similar to the ACV-15 with the difference that the 25 mm Sharpshooter Turret is assembled by Deftech at Pekan, Pahang. Also, these are given the ANVVS-2 night vision system, KVH TacNav navigation system incorporating (GPS), LWD Avimo laser warning, 76 mm Wegmann grenade launchers, and NBC filtration system. 12 were already battle-tested at Lahad Datu (Sulu) in 2013.ACV-19 (2000)
Also denominated ACV-S (the S for "stretched") it is the upgraded variant of the ACV-15 with a stretched chassis (extra pair of roadwheels). It was renamed later to ACV-19. Two prototypes were built in 1999 and 2000. It could receive extra protection and a larger turret ring, with a heavier turret of the Bradley type. Total capacity is said to be 25% greater. Air conditioning and satellite navigation are mandatory. Protection is enhanced against 30 mm rounds and RPG-7s while the floor's spall liners and 18 mm armor procure some protection against mines.ACV SW (BMP-turret)
This single experiment has been built by the Instrument Design Bureau (KBP) of Tula, fitted with a BMP-2 turret for export. None have been ordered yet.Exports & service
So far the vehicle has been exported to Jordan, the Philippines, Malaysia (211), and the United Arab Emirates (136 delivered).Links
The ACV-15 on wikipedia - The ACV-15 on army-guide - Official product page
ACV-15 specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 5.26 x 2.83 x 2.88 m (17.2 x 9.28 x 9.44 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 15 tons |
| Crew | 2 (driver, gunner/radio) |
| Propulsion | 5,2 litre 350 hp 6V-53T, 23 hp/ton |
| Suspension | Torsion Bars |
| Speed (road) | 89 km/h (55 mph) |
| Range | 450+ km (280 mi) |
| Armament | 12.7 mm gun on APC variants |
| Armor | 14.5 mm sides to 25 mm front (0.57 - 0.98 in) |
| Total production | 2945 |

Turkish ACV-15 AAPC in 1992, in plain green livery

Standard AAPC with ACAV main mount, camouflaged in the 2000s.

Turkish Army HOT tank hunter
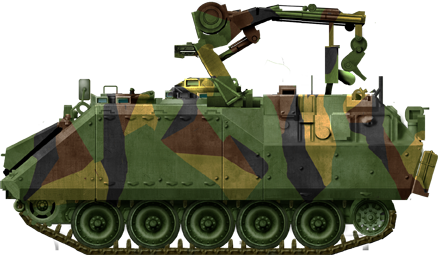
Turkish Army ARV version

Turkish Army ACV-15 IFV, camouflaged

Malaysian ACV-300 Adnan
Gallery
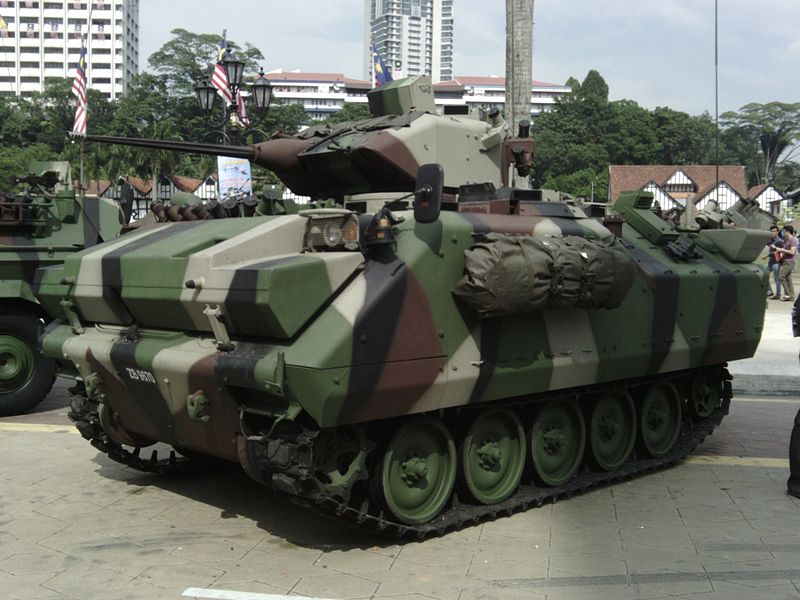

Malay locally-built ACV-300 Adnan
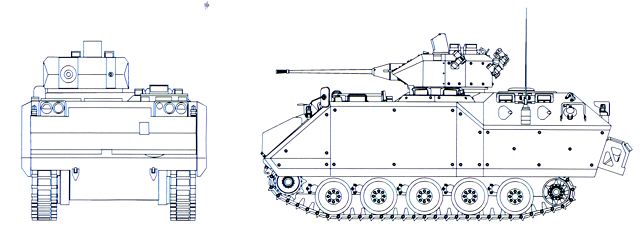
Blueprint of the ACV-15 AIFV.
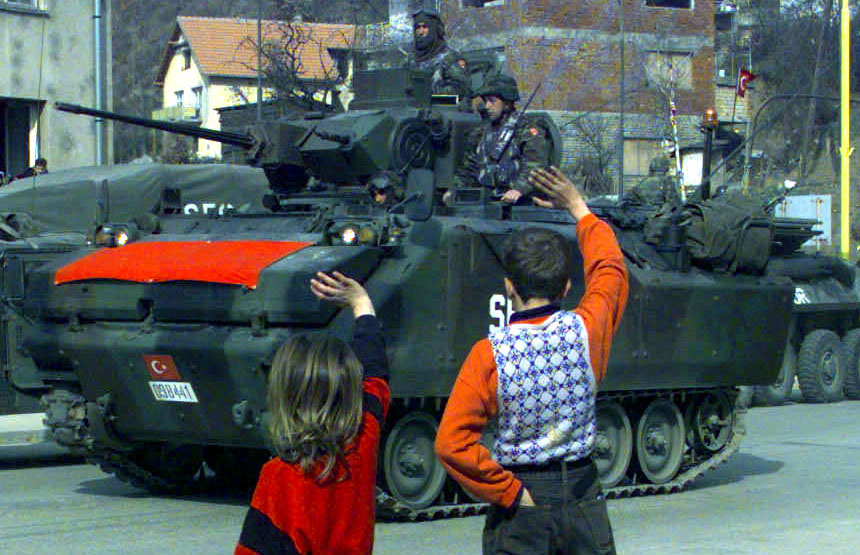

Turkish Army ACV-15 in Bosnia 1998

Modern Tanks
Modern MBTs posters

Denel Bagder (2018)

Type 16 MCV (2016)

Gepard 1A2 last rounds 2011

SANDF

Russian AFVs

Main Battle Tanks
