From the "universal tank"
The postwar "Universal Tank" concept was derived from the 1944 A45 Infantry Support Tank concept, an attempt to create, right after the Centurion, a successor heavy tank to the Churchill. However both projects were fused as the FV200 universal tank series that was to have the mobility of a cruiser but the level of protection and firepower of a heavy tank as well as a versatile chassis for other purposes (ARV, SPG...). The heavy tank variant Fv201 (55 tonnes, 20-pounder gun) was chosen for development to respond to the Soviet IS-3. It was to be armed with a 120 mm, however the delay to create such massive gun and the turret led to the transitional F221 Caernarvon, fitted with the Centurion Mk.2 turret. Eventually, the definitive FV214 was built in 1955 in two series; and deliveries lasted until 1959.Design
Protection
The Conqueror was the last British Heavy Tank in service. It was largely a product of ww2 thinking about tanks, and unlike first generation MBTs, put the typical emphasis on firepower and protection over mobility. They were tailored to defeat the Soviet IS-3 when the cold war was at its hottest and would have been surely up to the job (see later). The hull made of RHA was all-welded and relatively low, with a well-sloped glacis nose and cast turret design. The armor level was particularly high, with 178 mm nominal thickness front plates (7 inches), but equivalent to 250 mm (10 inches) LOS (line of sight). The lower beak was 78 mm at 60°, the rear part of the front glacis, connected to the turret ring, 21 mm at 83°, and rear engine deck 17 mm, the rear plate 51 mm (flat), the rear lower plate 31 mm at 70° and the bottom, 13 mm. The upper and lower side walls were 51 mm thick, flat, and the protective side skirts 6 mm.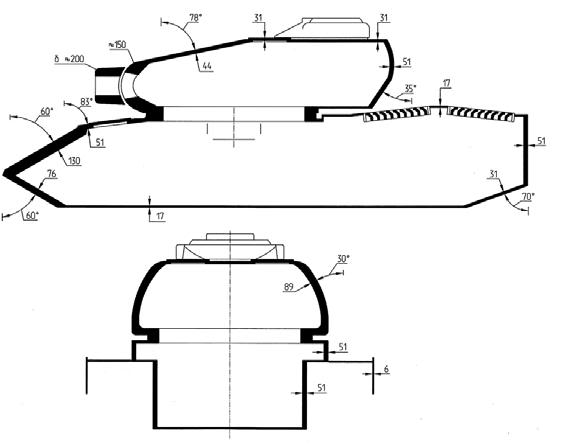
Conqueror Armour scheme
The cast armor turret had a similar front thickness and even superior on the mantlet (200 mm). The front was 150-170 mm thick, the front slope was 44 mm at 78°, the roof 31 mm, the rear 31 mm, and the rounded sides walls 89 mm. The general profile of the tank stayed relatively low, slightly higher than the IS-3.
Mobility
The hull and chassis of the FV 200 series were designed for a wide variety of duties, and sturdy enough for the heaviest loads. It was composed of a typical "heavy tank" drivetrain, in two 8x2 roadwheels groups per side, for 64 roadwheels in total, resting on double pin, large track links to reduce ground pressure. Reinforced and sturdy Horstmann units instead of torsion bars assumed the suspension. The paradox was only light tanks and the heaviest in service in the UK were given these, like, until the Chieftain in the 1960s. By the 1980s, the Challenger adopted hydropneumatic units. Based on coil springs bogies, they had a relatively long course, were 100% external and easy to replace and maintain, while the torsion bars were partly internal.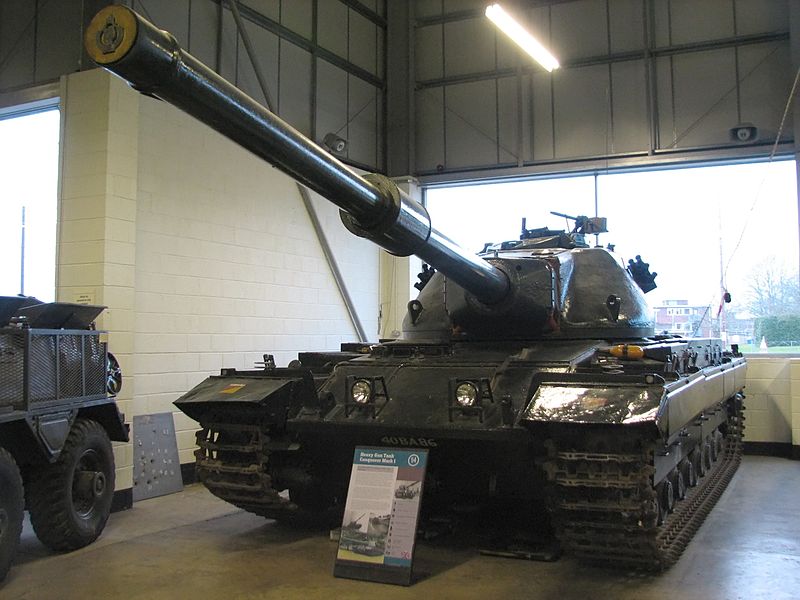
Conqueror mk.I at Bovington
All this armor made it for an exceptionally heavy tank, at 64 tons compared to the Centurion's 51. The only source of power available was the proven Rolls Royce Meteor, in a souped-up version of the ww2 Cromwell and Centurion 650 hp, coupled with a 5-speed Merrit-Brown Z51R Mk. F gearbox. Its top speed and range were consequently severely limited, and the stress both on the engine, transmission (only 800 hp), and suspensions took its toll, making it mechanically unreliable. Tactical mobility in addition was limited by the few bridges capable to handle it weight. However the small roadwheels resting on many bogies and wide tracks had the effect of giving similar traction and mobility performances as the Churchill, if not better. It could climb and go in some places the centurion couldn't, despite the latter was 13 tons lighter.
Armament
The IS-3 main gun indeed was ill-designed for accurate long-range fire, fast rate of fire or was limited in its ammunition capacity due to old-fashioned two-stage rounds. On the contrary, the British Royal Ordnance L1 120 mm rifled gun was tailor-made and much more capable gun than the IS-3 at long range. In fact, all studies shown that it was capable to out-range the IS-3 by a generous margin. That, in theory, would have rendered heavy armor unnecessary, but experience showed that engagements rarely occurred in optimal distances and terrains. The secondary armament comprised two cal.30 Browning machine guns, one coaxial and the second placed on the roof, manned by the tank commander.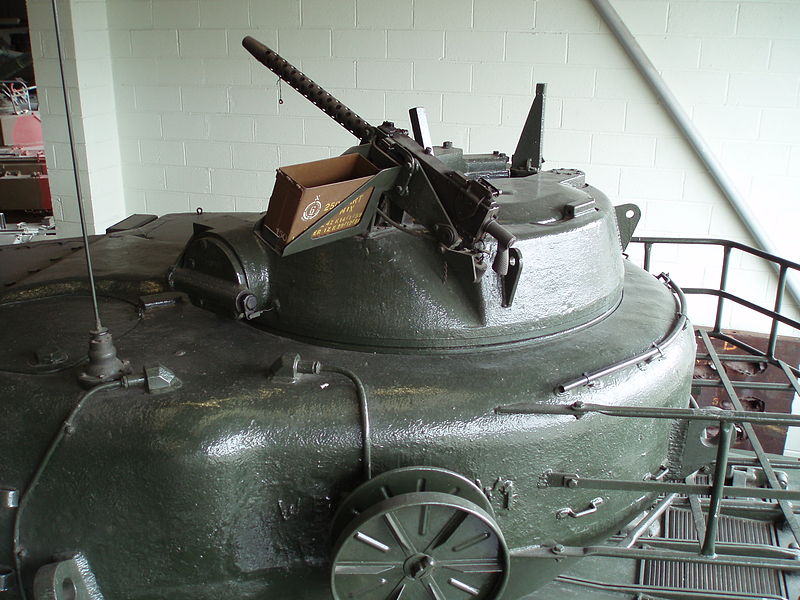
Conqueror Mk.I rotatable Tank Commander Cupola at Bovington
It should be noticed that the commander had an advanced rotating cupola, providing an equally advanced fire control system as he could align it on a target independently of the turret, to measure the range with a coincidence rangefinder. He could then direct the gunner on the laying and azimuth parameters which were mechanically indicated in the cupola. This was a very early "hunter-killer" mode allowing to rapidly engage several targets. At the same time, the Soviet TPKU-2 and TKN-3 did not use a rangefinder.
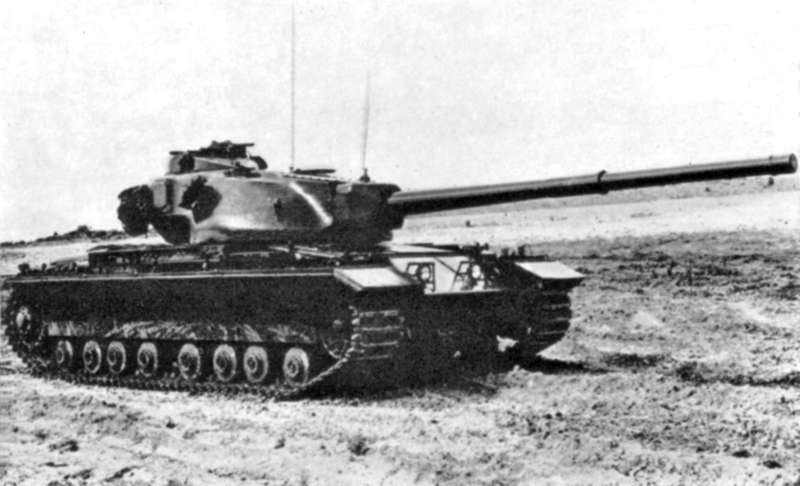

Conqueror Mk.I on trials in 1956
Evolution
FV214 Conqueror Mk I This first version (20 built) had three periscopes for the driver. FV214 Conqueror Mk II This second, more produced version (160) had redesigned frontal armour plates joins but a single rotatable periscope for the driver, and a modified, improved exhaust system.FV215: A semi-SPG design with a FV200 chassis mounting a limited traverse turret armed with a 183 mm gun. Only a wooden mockup was produced. More information can be found HERE.
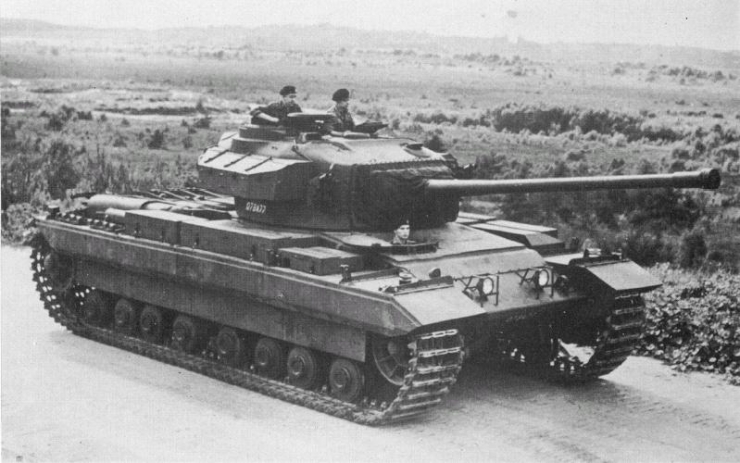

Caernarvon mark II
The FV221 Caernarvon
Considered as a stopgap tank before the heavy turret was ready, it was nonetheless part of the FV 200 lineage. At the end, the Centurion was found better. Only the Caernarvon mobility was judged satisfactory, as its turret was far lighter and its engine at least on paper (800 hp vs 650 hp) much more capable. But in terms of speed and range, it lagged behind. They were given the Mk III 20 pounder turret of the Centurion mark II but never really hit their mark as main battle tank and after a single prototype Mark I, only a short experimental serie (21) Mark II was released.FV219 & FV222 Conqueror ARV
This was the heavy Armoured Recovery Vehicle (ARV), still used years after the retirement of the main type. The FV219 Mk.I (8 produced) was succeeded by the Mk.II, with 20 produced.In action
All the 180 Conqueror ever built were stationed in Germany, in the northern British sector, facing the possible Soviet onslaught. Their rôle was also to provide a long-range cover for the early, 20-pdr armed Centurions. They would have been also directed against Soviet heavy tanks units, on par with the American M103s. They stayed in service in Germany only seven years, nine given to each tank regiment, and usually grouped in three tank troops. They Participated in rare exercises (due to their poor tactical mobility). In the early 1960s, the arrival of the Centurion armed with ROF's L7 gun made the last British heavy tank obsolete and they were retired. Surviving vehicles could be found at the Bovington Tank Museum, and the Land Warfare Hall of the Imperial War Museum Duxford. Another is on display in France, at the Musée des Blindés, Belgium at the Royal Museum of the Army (Brussels) and Kubinka in Russia. The American Littlefield Collection also counts one. In Germany, several training target hulks could be seen at the Haltern Training area. ARVs also survived, two at the Military History Museum on the Isle of Wight, and the REME Museum of Technology.Sources/Links about the Conqueror
The Conqueror on WikipediaConqueror and various concepts on Henk of Holland
Conqueror specifications
Illustrations

FV 221 Caernarvon. It has to be the main battle tank of the ubiquitous FV 200 serie, but the success of the A45 Centurion made it obsolete. Only 21 were built.

FV 214 Conqueror Mark I based in West Germany in the early 1960s.

FV 214 Mark II based in West Germany.
Gallery
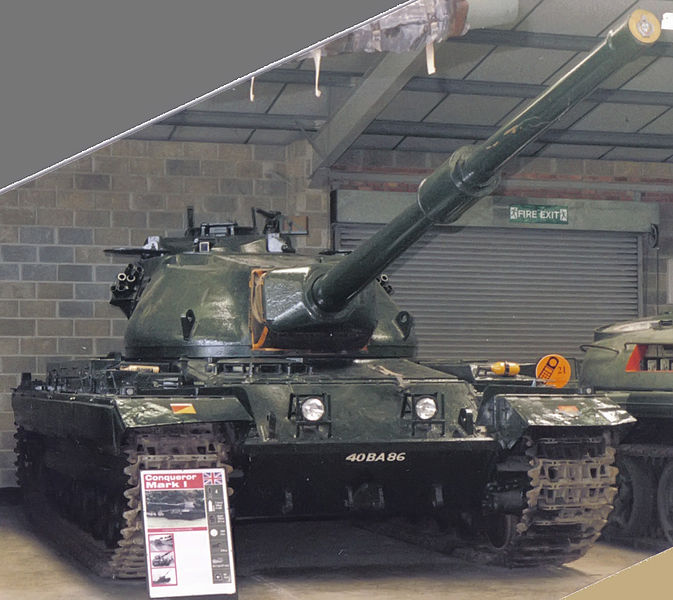

Conqueror Mark I in Bovington
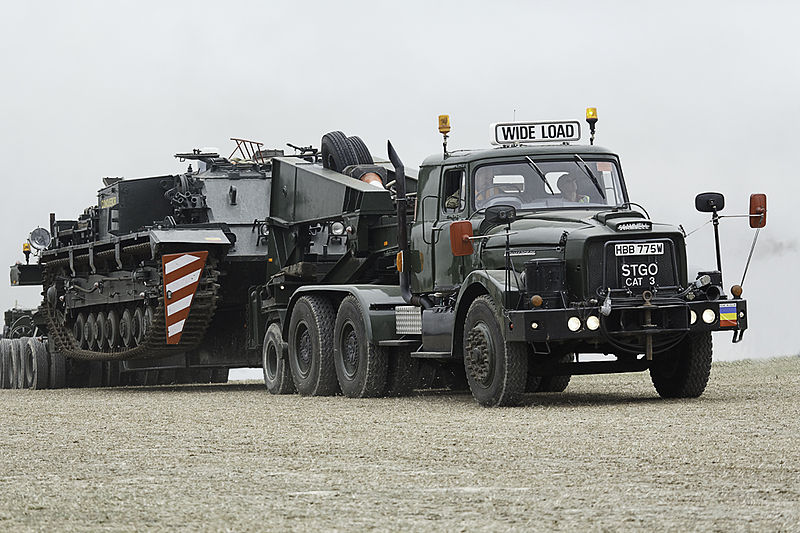

Conqueror on a Scammell 28 Transport
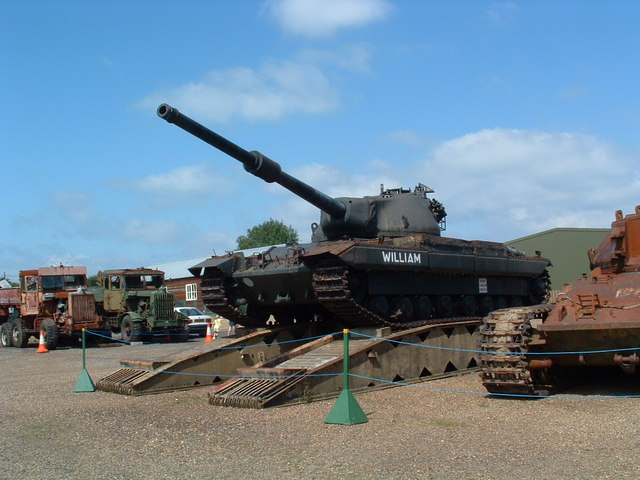

"William" Gate gardian
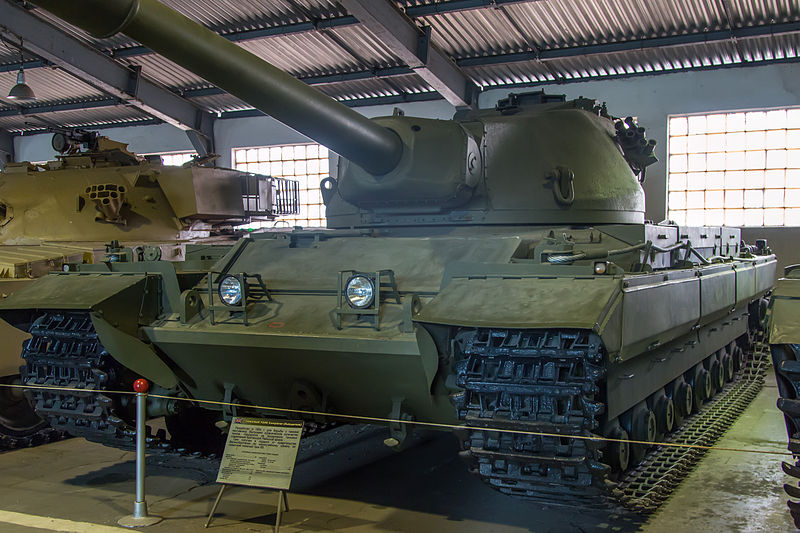

Conqueror in the Kubinka Museum

FV2015b Self Proplled Gun

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

