Tank Encyclopedia®: The destination for tank enthusiasts since 2014
The Four Eras We Cover:
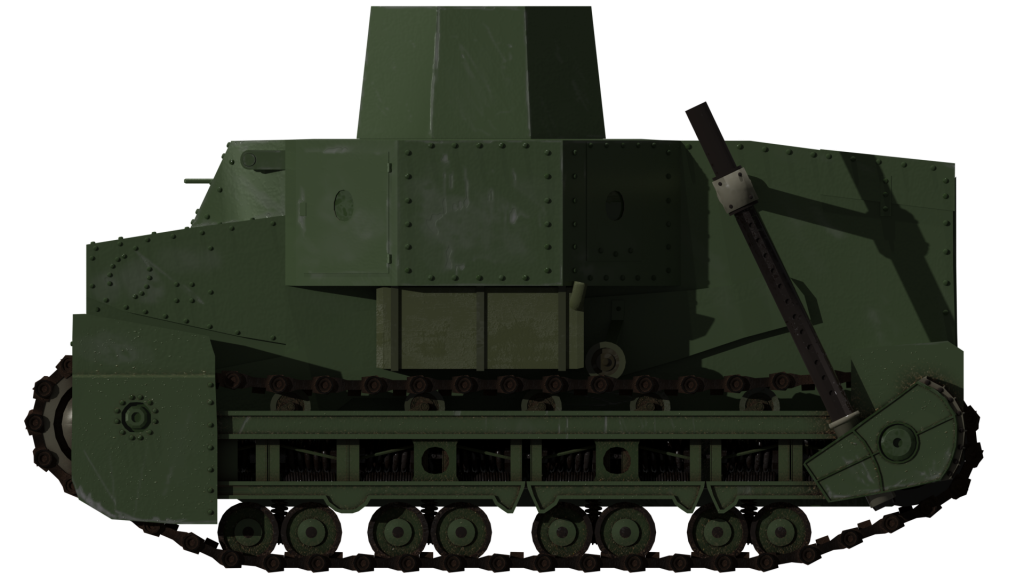
 WW1 – Mud, Barbed Wire, and Trenches: The United Kingdom and France started development of tanks in order to break through enemy lines. However, many pioneers had envisioned the use of armored vehicles in the decades prior to the Great War. Soon after its introduction, the tank quickly became a killing machine integrated into combined arms operations.
WW1 – Mud, Barbed Wire, and Trenches: The United Kingdom and France started development of tanks in order to break through enemy lines. However, many pioneers had envisioned the use of armored vehicles in the decades prior to the Great War. Soon after its introduction, the tank quickly became a killing machine integrated into combined arms operations.
 WW2 – The Tank Goes Global: The Interwar period saw the tank go on a worldwide tour, from Bolivia to China, every corner of the globe and all seven continents felt the tread of heavy armor. Even so, many were unconvinced by this new weapon of war. World War Two would change these perceptions, and see tanks used in unprecedented numbers across all theaters of war.
WW2 – The Tank Goes Global: The Interwar period saw the tank go on a worldwide tour, from Bolivia to China, every corner of the globe and all seven continents felt the tread of heavy armor. Even so, many were unconvinced by this new weapon of war. World War Two would change these perceptions, and see tanks used in unprecedented numbers across all theaters of war.
 Cold War – East vs West: In a period dominated by nuclear weapons, two opposing superpowers led to the splitting of the world into East and West. Although the USA and USSR never fought each other directly, almost all proxy wars of the period saw extensive usage of their tanks.
Cold War – East vs West: In a period dominated by nuclear weapons, two opposing superpowers led to the splitting of the world into East and West. Although the USA and USSR never fought each other directly, almost all proxy wars of the period saw extensive usage of their tanks.
 Modern Era – Are Tanks Still Relevant?: Despite numerous prophets heralding the demise of the tank, armor is still an important part of all the world’s militaries. The modern battlefield shows no signs of this changing soon, with the development of tanks continuing to adapt to it.
Modern Era – Are Tanks Still Relevant?: Despite numerous prophets heralding the demise of the tank, armor is still an important part of all the world’s militaries. The modern battlefield shows no signs of this changing soon, with the development of tanks continuing to adapt to it.
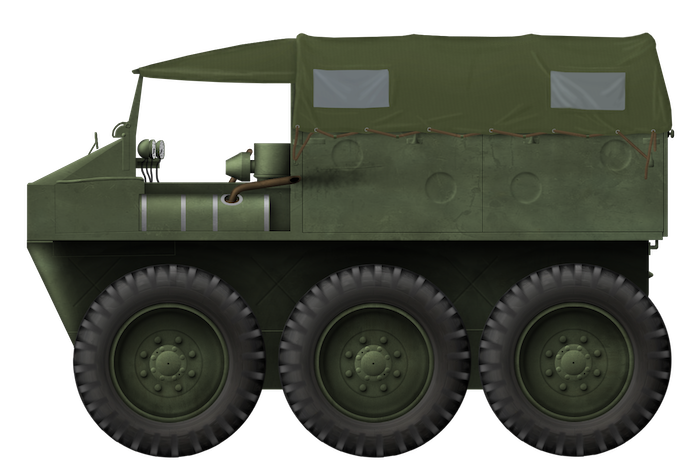
⚠ About Illustrations on this site: You are free to use and share tank illustrations from this site for personal use only. For any commercial use, including on YouTube (since most videos run ads) please contact us via the contact form. Tank Encyclopedia can offer licenses for one-time use or global licensing for larger, long-term use.