Tanks and armored cars – Around 250 armored military vehicles by September 1918
Armored Vehicles
- Büssing A5P
- Flakpanzer A7V
- Gruson Fahrbare Panzerlafette / Fahrpanzer
- Leichter Kampfwagen II (LKII)
- Mannschaftstransportwagen Mannesmann-MULAG
- Protos Panzerauto
- Sturmpanzerwagen A7V
- Sturmpanzerwagen A7V 506 ‘Mephisto’
Unarmored Vehicles
Anti-Tank Guns
Prototypes & Projects
- Ehrhardt Ballon Abwehr Kanone (BAK)
- Goebel Landpanzerkreuzer
- Großkampfwagen / K-Wagen
- Opel-Darracq Kriegswagen für höhere Truppenführer
- Panzerautomobil Daimler 1909
- Treffas-Wagen
Tactics
A long and difficult start
While the British and the French were prompt to build their first operational tanks, the German High Command was doubtful of their capabilities. That was until mid-1917 when came the successes that proved any well-coordinated attack using tanks in a proper way could break through and create havoc in rear lines. They had some reasons not to urge tank production. First, infantry troops, like the stürmptruppen (elite assault squads) were a simple and much cheaper way to achieve this breakthrough, as they had shown on many occasions throughout 1917 and particularly during the 1918 spring offensives.
The military blockade also played a role, limiting the abilities of an already exhausted industry to produce enough materials and manpower to build swarms of tanks, reducing the chances to launch tank offensives at full force. There was also repugnance for this new “dishonorable weapon” as stated in propaganda and newspapers, coming from the ancient and very deep traditional ways of the Aristocratic Prussian officer, that dominated both the head of staff and the Kaiser himself.
However, the Germans were also naturally fond of new technologies of war and besides this official view, an army engineering department (Allegemeine Kriegsdepartement 7, Abteilung Verkehrswesen) was quickly created to study tank designs and produce one. Under the cover of a small department responsible for road safety, it was mirroring the British unified “Landship Committee” which drove the entire British tank development. In fact, high command had already requested designs for an armored vehicle before the war.
But all designs were rejected. This was to change in September 1916, when the British Mark Is, fielded with great secrecy in France, were put in action for the first time. Their psychological effect, despite the losses and tactical failure of the entire operation, largely surpassed any other aspect. This side-effect came into serious consideration as in mid-1917 very low morale, disobedience, and even full-scale mutiny became a problem of many Allied units, the product of a three years gruesome war of attrition.
The first tank design – Sturmpanzerwagen A7V
In fact, many projects were sent to the committee during 1917 and only a few were selected. The A7V was the project of engineer Joseph Vollmer. First, the committee had to choose a suitable basis for mobility on the battlefield. The natural choice was the Holt chassis. The Germans knew they had been used by the French as a basis for their own tanks. Holt tractors were already used by the Austrian army. This was also the most proven tracked vehicle available. After trials J. Vollmer not only decided to build a lengthened version of the chassis, he also chose a twin-engine to propel the entire vehicle.
A wooden mockup was tested in spring 1917, followed by an unarmored tank. Armament and armor were fitted later. The early single-plate “Röchling” armor was relatively thick (up to 30 mm/1.18 in at the front) but made of traditional soft steel. It was inferior to French and British armor. The main gun finally chosen was the Belgian Nordenfelt quick-firing gun, short, light, and compact, with almost no recoil. It was sturdy and available in large quantities, taken from various Belgian arsenals in 1914.
The first A7Vs were ready for action in March 1918, when their advantages became clear. All were equipped with a gun, in a good, straightforward position. They had good sprung tracks, thick armor, and had plenty of ammunition for their numerous machine-guns. Plus they were tall and impressive, perfect for the desired psychological effect, and had an excellent power-to-weight ratio, being fast for their size, faster than anything the Allies could field. But their disadvantages also became clear in April, especially during the single attack at Villers-Bretonneux on the 21st, where all available machines (18 in all), were put in action together.
Several broke down at the beginning of the action, others were ditched in trenches and the muddy terrain, and only three, which were the most advanced, met enemy troops and especially the three British tanks which followed them. This was the first -and only- tank-to-tank battle of the “war to end all wars”.
But this epic duel ended in a draw. The two female British tanks retired, as well as the two other A7Vs, damaged by infantry bullets and shrapnel. However, the only which fought the British male, after taking three hits (the British 6-pdr was notably faster and more accurate), was evacuated. The British male was lost soon under heavy mortar fire. But the result of the entire commitment of the A7V was deceiving at best. The combination of very low ground clearance (20 cm/7.87 in), high gravity center, low tracks, and hull overhanging, proved definitely to the Germans, as it did for the French, the lack of capability of the “armored boxes” based on Holt chassis to cope with a heavily cratered terrain and large trenches or even muddy soil.
Other projects
The A7V-U, with full-length tracks, was designed after the capture of many Mark IV tanks. It became obvious that this concept was far more capable of dealing with the real conditions on the battlefield. In fact, around 50 Mark IVs were captured during the aftermath of the battle of Cambrai, a British failed offensive in late 1917. They were salvaged, repaired and the ones unable to be refitted in running conditions, left as spare parts reserves for the others. Most of these were refurbished by the BAKP 20, equipped with new German weapons including the freshly arrived 5.7 cm (2.24 in) Belgian QF guns in socle-mounts, repainted with new unit marks and large Maltese crosses.
Then they were sent to specially trained assault squads, operating as the “Mark IV – Beute” or Beutepanzer Mark IV (“Captured Mark IV tank”). Nearly all “females” were converted to “males” in the process, with some also equipped with a 13 mm (0.52 in) T-Gewehr heavy antitank rifle in place of their initial forward Lewis machine-gun. They also added an extra safety escape hatch to the cupola-roof. They were used in summer offensives, in batches of three, sometimes with reserve tanks, and an overall high rate of attrition. They proved slower than the fast pace of the Stürmtruppen they were supposed to cover and usually broke down often. All of the Beute Mark IVs left in the field for various reasons were blown up and their weapons salvaged. This tank had a valuable impact on German designs, notably the short-lived A7V-U.
This mid-1918 project was not operational on time. Production started in September, but no units were equipped by October as it was scheduled. By November, this was all over. The A7V-U looked like a much taller and larger version of the Mark IV. It was ten tons heavier and much less maneuverable, despite being equipped with the same engine and transmission as the A7V. However, this design was not the only one to reach the general staff.
Several other projects were tested, notably the Treffaswagen, a kind of armored tractor with massive front wheels, designed to crush barb wire. A prototype, built by Hansa-Lloyd works of Bremen was tested in February-March 1917, but the project was canceled in favor of the A7V. In May 1917, officers assisted in the first trials of a rather unconventional prototype using the “pedrail” solution.
This Orionwagen, as it was named, had a turtle-back sheet-metal protection with a small rear driver compartment over a chassis fitted with eighteen track feet on each side. The steering was assumed by a front steel wheel. The concept was not new. It was based on the prewar standard Orion produced 4-ton lorry, an unusual but potent solution that made its mark commercially. Each foot had a large spring in between the top and bottom trackpad which helped moving forward as well as assuming the role of suspension of the whole system. The 45 hp (33.6 kW) engine soon proved not up to the task because the finished prototype was heavier than expected. It failed in some tests like crossing trenches and passing various obstacles. The concept however had strong supporters inside the OHL and development continued as a field transport.
The second prototype was more successful. It was developed in late 1917, had no steering front wheel, was more compact, and propelled by a more powerful engine. It was also covered by sheet metal and was projected to have a rear fully traversed turret equipped with up to four machine-gun or a 2 cm (0.79 in) Tankabwehrkanone Becker M.11. But as the OHL was now set on the A7V, no order came. The team behind decided however to produce a new design for 1919, hoping for further orders. This Orionwagen III was an enhanced version of the latter, equipped with two turrets, one carrying the 20 mm (0.79 in) Becker M.11 and the other two Mauser machine guns.
WWI German super-heavy tanks
– K-Wagen (1918)
Two uncompleted prototypes. Final version specifications: 120 tons, 13 x 6 m (42.6×19.7 ft), 4×77 mm (3.03 in) guns.
WWI German heavy tanks
– Sturmpanzerwagen A7V (1917)
20 built total.
– Sturmpanzerwagen A7V-U (1918)
Full-length track version of the A7V with guns in sponsons. Prototype only.
WWI German medium tanks
– Sturmpanzerwagen Oberschlesien (1918)
Two prototypes planned. 19 tons, 1×37/57 mm (1.46/2.24 in) gun.
– Orionwagen (1917)
Two pedrail prototypes built.
– Bremer Marienwagen Gepanzert (1916)
Single tracked prototype derived from an Ehrhardt armored car.
WWI German light tanks
– Leichter Kampfwagen LK.I (1918)
Two prototypes only. No turret, fixed superstructure with a single 7.7 mm (0.3 in) machine-gun.
– Leichter Kampfwagen LK.II (1918)
Two prototypes only. Fixed superstructure with 37/57 mm (1.46/2.24 in) gun. 10 Stridsvagn m/21 bought by Swedish government after the war.
WWI German armored cars
– Ehrhardt E-V/4
43 built, three Mauser 7.7 mm (0.3 in) machine guns.
– Büssing A5P
1 built, three Mauser 7.92 mm (0.31 in) Mg08 with no less than eleven hatches and a crew of ten.
Links about German WWI armor
https://www.militaryfactory.com/armor/ww1-german-tanks.asp
https://www.awm.gov.au/about/our-work/projects/mephisto
https://landships.activeboard.com/f318871/german-tanks/
https://the.shadock.free.fr/Surviving_WW1_Tanks.pdf
https://encyclopedia.1914-1918-online.net/article/tanks_and_tank_warfare
Bass, Eric (2006). German Panzers 1914-18. Osprey Publishing. p. 232. ISBN 1-84176-945-2.
Foley, John (1967). A7V Sturmpanzerwagen. Great Bookham, UK: Profile Publications.
Foss, Christopher F. (2003). The Encyclopedia of Tanks and Armoured Fighting Vehicles. Staplehurst, UK: Spellmount. p. 232. ISBN 1-86227-188-7.
Cutaway drawing of the interior of a Stürmpanzerwagen A7V.

The Stürmpanzerwagen A7V-U. Designed by the same bureau which signed the A7V, the A7V-U (U stands for Umlaufende Ketten, or “full-length tracks”), this 40 ton monster was designed to have better trench crossing capabilities and was to be ready on time for the winter offensives. While the prototype was ready by June 1918, the production was delayed until September and none were delivered before the armistice.
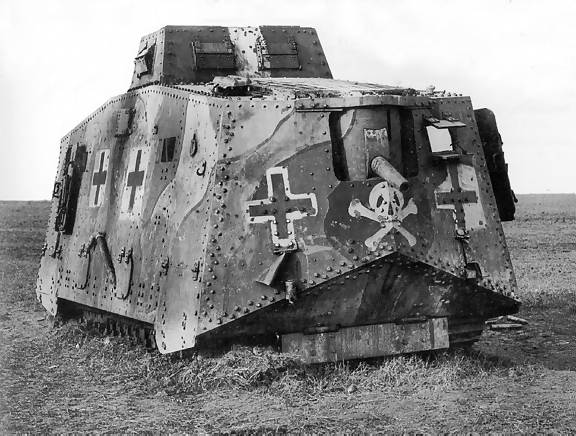

A disabled A7V shown here after the war, perhaps in 1920. Weighing more than 30 tons most of these tanks were scrapped in situ rather than being towed away.
The K-Wagen mockup, profile. This armored giant would have been the biggest tank ever built, if the war would have lasted enough.
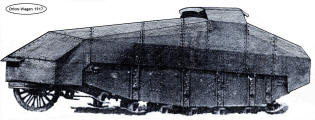
The Orionwagen, the first prototype of a pedrail tank.

The second prototype of the Orionwagen, which was to be equipped with a machine-gun turret. Production was planned for 1919.
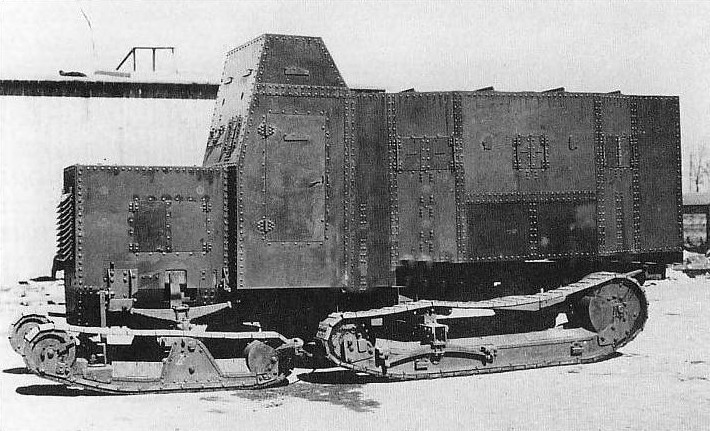
Bremen Marienwagen Gepanzert, a prototype based on the Ehrhardt armored car. One was built in 1916 for evaluation.

The Leichter Kampfwagen II, a gun armed version of the LK I. Only two prototypes were built, but a small production run was realized after the war for Sweden.

The Büssing A5P, one of the three designs ordered by the German head of staff. Only one A5P was built. It was a massive vehicle, weighing 10 tons, with a crew of nine and propelled by a truck engine.
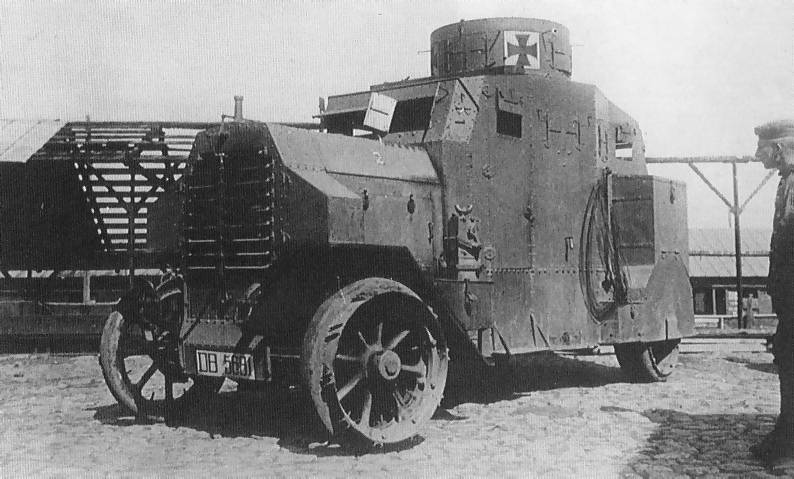

Only 43 Ehrhardt E-V/4s were built (three prototypes and two series of twenty units). The last series was built in 1919 and participated in the German Revolution.
Illustrations

Panzerwagen Ehrhardt 1915 on the Eastern front, in 1916.
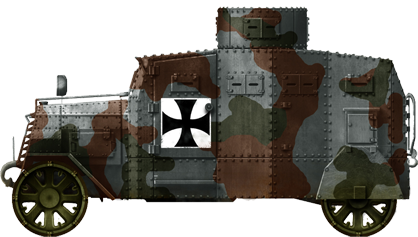
Camouflaged Panzerwagen Ehrhardt model 1917 in 1918.

Ehrhardt EV/4 model 1918 with the Freikorps, Berlin streets, 1919.
By Craig Moore
The First World War’s fierce battles saw the need to develop military technology beyond anything previously imagined: as exposed infantry and cavalry were mowed down by relentless machine-gun attacks, so tanks were developed. Stunningly illustrated in full colour throughout, Tank Hunter: World War One provides historical background, facts and figures for each First World War tank as well as the locations of any surviving examples, giving you the opportunity to become a Tank Hunter yourself.




9 replies on “German Empire”
A ball tank called the Treffas-Wagen is brought up on the Kugelpanzer article. Is there enough information on this Treffas-Wagen to get its own article?
There is good amount of info on it, and pictures, an article may well be released in the future.
– TE Moderator
ohh yea you should look up the wepons of war hitler wanted to create but never saw mass production
Any plans for a LK II page? Love your guises illustrations, and more so would love to see an LK page with illustrations.
Hello Pruss,
The LK tanks are in our sights, however, they have not been worked on as of yet.
Any change there will be an article on the k wagen
Becker Tankabwehrkanone M.11 or M.2?
I would like to purchase a tank
Will we get an A7V-U article anytime soon?