Republic of South Africa (1991)
Republic of South Africa (1991)
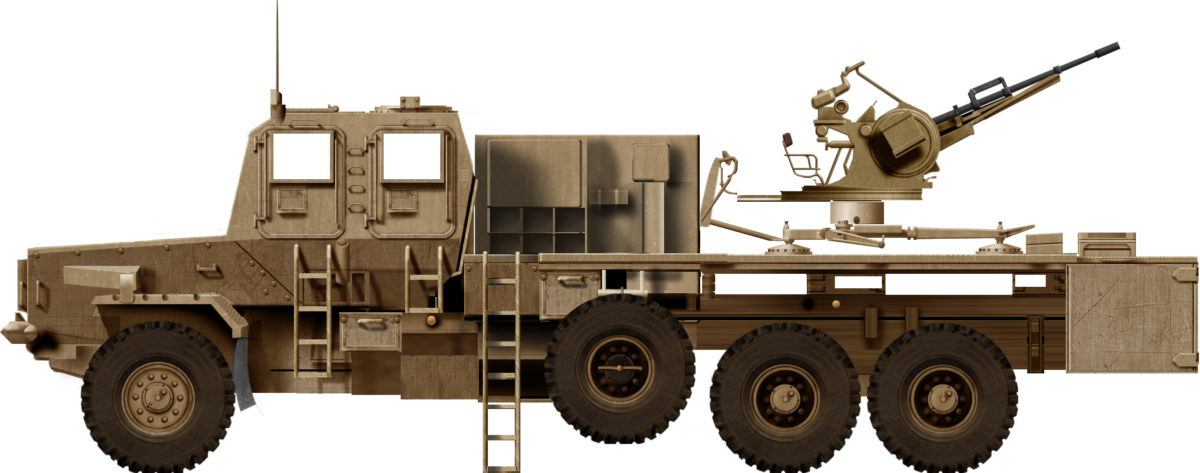
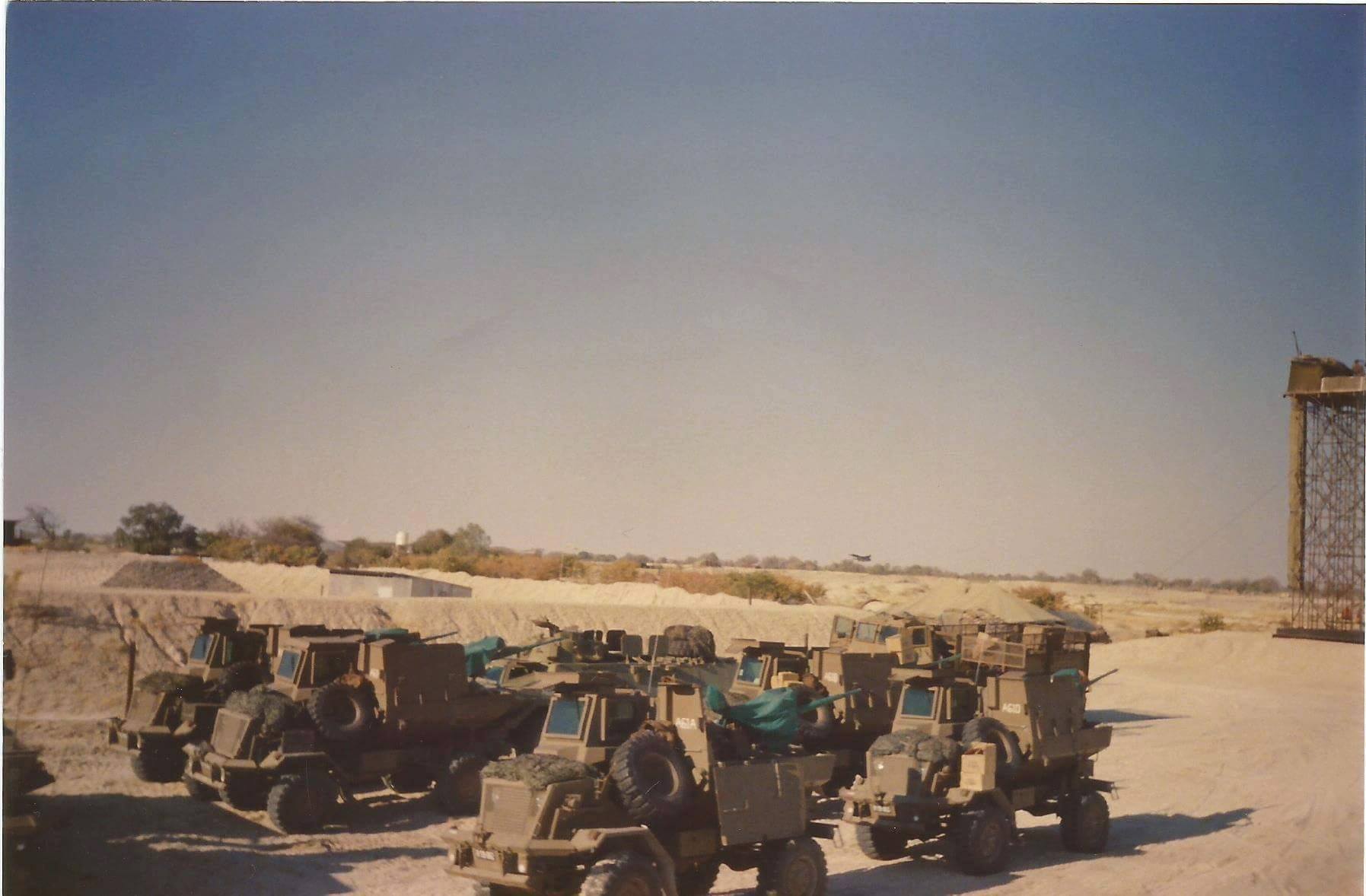
Self-Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun – ~36 Built
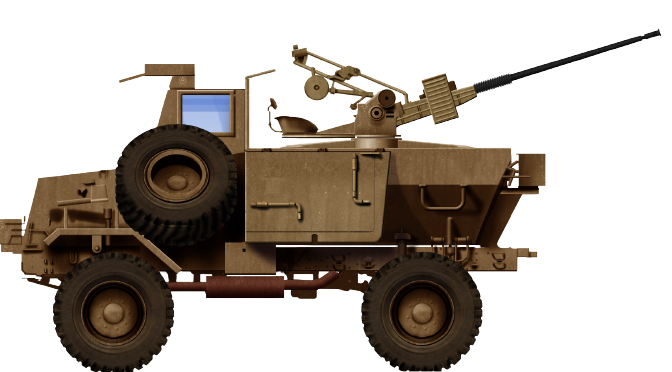
“Bosvark” The African Bushpig
The Bosvark takes its Afrikaans name from the African Bushpig, which is armed with an impressive set of tusks for digging up roots and to protect itself against predators. Like its namesake, the Bosvark self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) evolved to adapt to the harsh Southern African environment.

Development
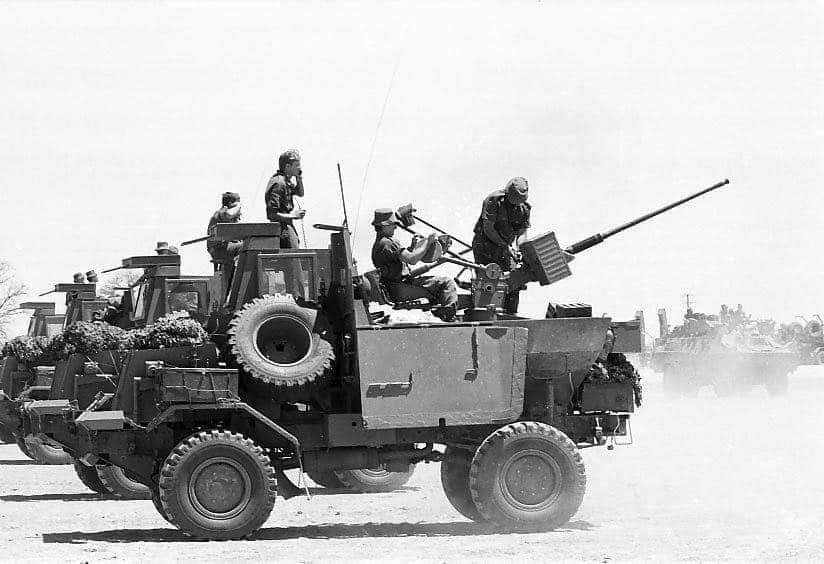
During the South African Border War (1966-1989), the South African Defence Force (SADF) captured large quantities of ZU-23-2 towed anti-aircraft defence gun systems from the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA). The MPLA had acquired these from their Cuban and Soviet benefactors. The SADF used these weapons in various roles, including ground defence of bases, makeshift weapons platforms, and training. With the war’s conclusion, those not used for training were sent for preservation and storage.


During early 1990, the Armaments Corporation of South Africa (ARMSCOR) launched a call based on end-user requirements set by the South African Defence Force (SADF) for proposals to mount a ZU-23-2 (designated GA-6 in the SANDF) on a vehicle. The primary development requirements stated that the vehicle had to be mine-resistant and be able to mount the ZU-23-2. The South African Military (SAMIL) -100 Kwêvoël cargo vehicle fulfilled the requirements with its armored crew compartment, mine-protected chassis, and spacious rear deck to mount the ZU-23-2. Nick Conradi a young engineer at Megkon Inc. came up with the concept that led to the project contract being assigned to them. Nick Contadi was entrusted with the design and engineering work.




The first prototype was completed in early April 1991 with testing of the running gear done at Gerotek testing grounds in Pretoria. All tests were successfully completed by June 1991. ARMSCOR recommended that the Bosvark be mass-produced and full-scale production followed at the end of 1991, with 36 vehicles eventually built. Surprisingly, the Bosvark was not primarily born out of the need for a SPAAG, but rather a vehicle that could mount the ZU-23-2 (designated GA-6 in the SANDF) and be used in the ground role.


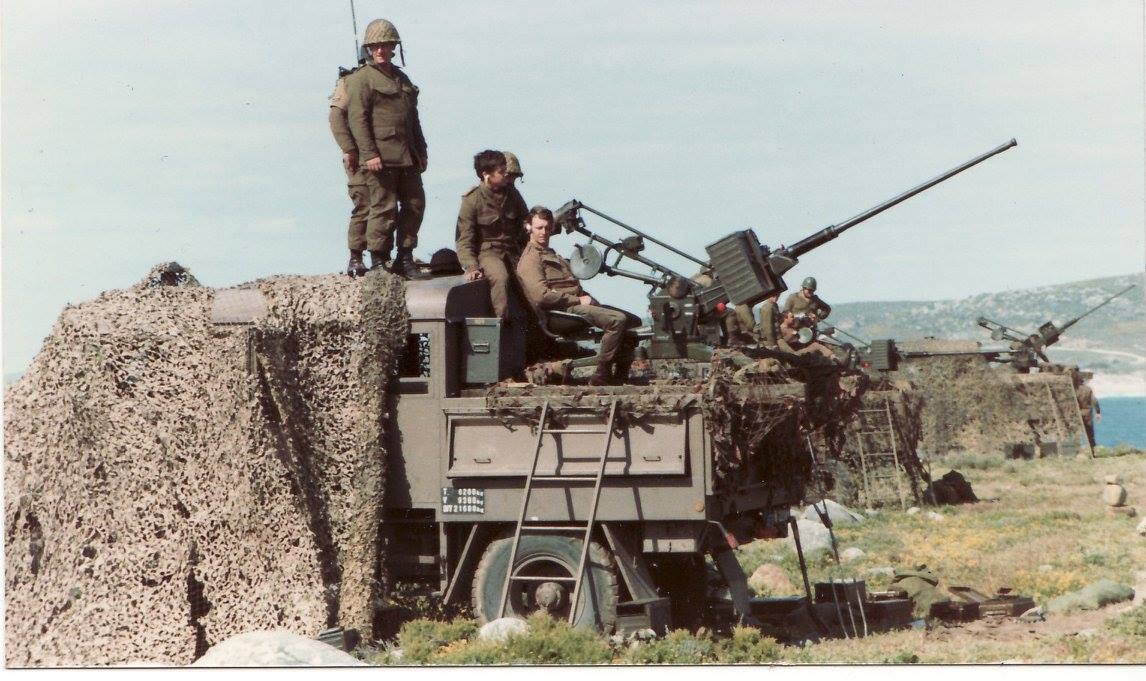
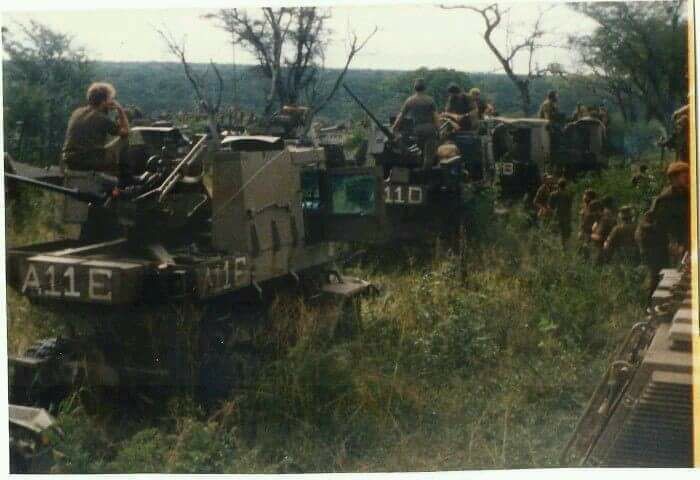
Its predecessor, the Ystervark, was withdrawn from service in 1991 and decommissioned in 1997, making the Bosvark’s entry into service critical. South Africa is the only operator of the Bosvark SPAAG, which the 10 Anti-Aircraft Regiment uses in Kimberley, the capital of Northern Cape province. At the time of writing, there are no published plans to replace the Bosvark.

Design features
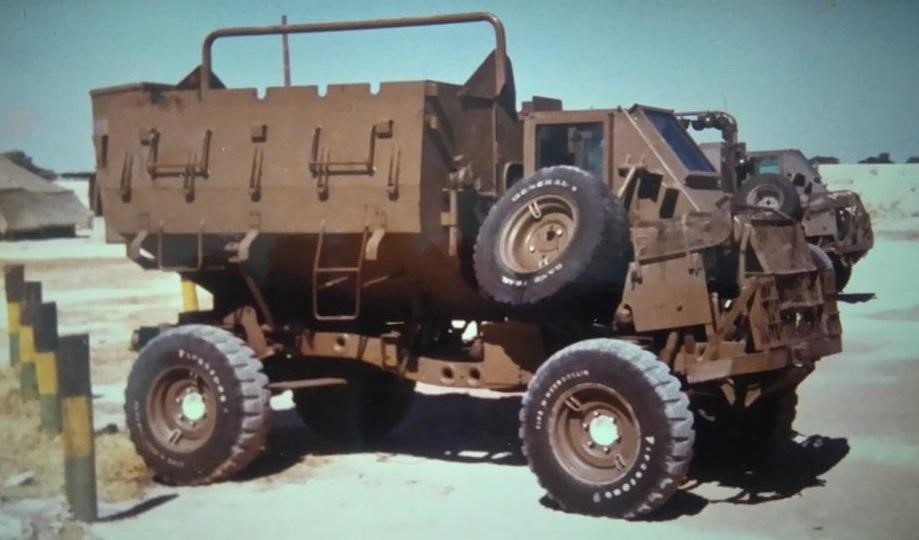
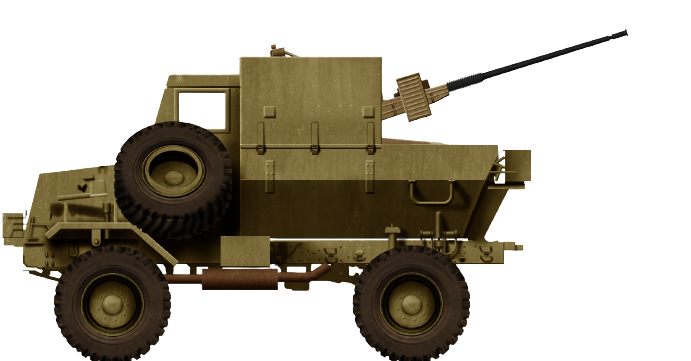
The Bosvark is a three-axle, 6 x 6 all wheel drive SPAAG based on the robust SAMIL-100 Kwêvoël mine-protected chassis. The chassis is V-shaped to deflect mine blasts from under the hull, away from the crew cabin, to maximise its crews’ chances of survival. This is achieved through several key design elements, which include high ground clearance, the V-shaped underbelly, and a purpose-built strengthened upper design which reduces the risk of shattered or buckled hull plates that could become debris. Most parts can be obtained commercially, which makes the Bosvark’s logistical train shorter and specialised maintenance support in the field unnecessary. The ability to interchange parts with other SAMIL-100 Kwêvoël vehicles simplifies and makes field repairs easier. Unlike its predecessor the Ystervark, the Bosvark crew are all located inside the crew cabin while travelling, which makes them less vulnerable to small arms fire and artillery fragments.
Mobility
The Bosvark is based on a three-axle 6 x 6 all-wheel drive chassis and the wheels are 14×20 in size. The engine is a type FIOL 413F V10 air-cooled 4-stroke Deutz diesel with direct injection, which produces 315 hp at 2,500 rpm and 1,020 Nm of torque at 2,500 rpm. This effectively provides 16.15 hp/t, which is more than adequate for its role as a SPAAG operating behind the forward elements. Power is transmitted via a single dry plate clutch with per assisted hydraulic mechanism to the ZF 56-65 synchromesh manual gearbox, with a gear selection range of six-speed (6F and 1R). The drive travels through a transfer box, providing high and low-range gear selection for on and off-road use.
The vehicle’s recommended safe travelling road speed is 100 km/h (62 mph) and 40 km/h (25 mph) cross-country (terrain dependent). It can ford 1.2 m (4 ft) of water without preparation and can cross a 0.5 m (19.7 in) ditch at a crawl. A power steering system makes the driver’s task easier, while acceleration and braking are done via foot pedals. The vehicle uses a Withings suspension with 380 mm (15 in) of ground clearance.
Endurance and logistics
To facilitate strategic mobility, the Bosvark has two 200 litre diesel fuel tanks on the right-hand side of the lower hull, which gives it an effective road range of 600 km (373 mi), 350 km (218 mi) cross-country, and 175 km (108 mi) over-sand. The vehicle is also fitted with a 200 l (53 gals) water tank underneath the armored crew compartment. The crew can access the water via a tap located above the front left wheel.
The Bosvark is equipped with two tactical radios, enabling the crew to communicate effectively with command and control. A portable radio is used for seamless communication between the crew compartment and the weapons deck.
Vehicle layout
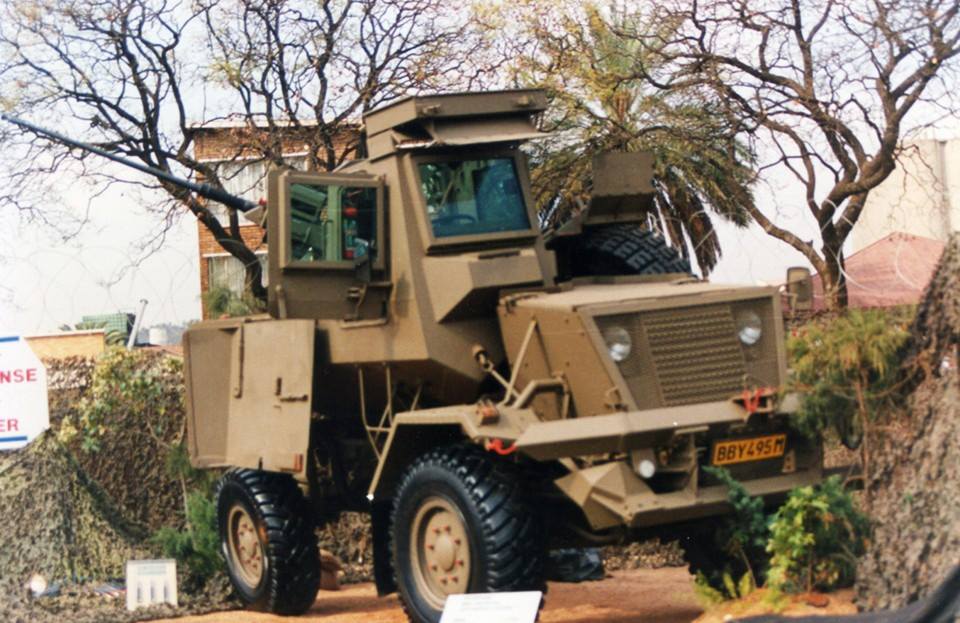
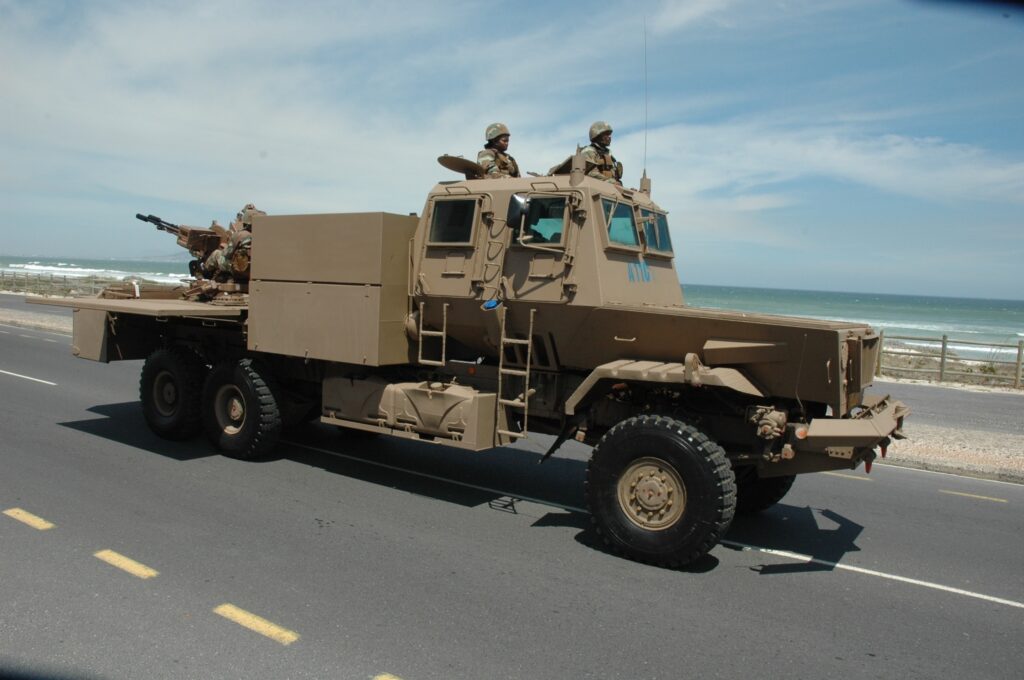
The Bosvark can be divided into three parts: the chassis; armored crew cabin at the front; and the weapons deck at the rear, where the main armament is mounted. The engine is located at the front of the vehicle, with the raised armored crew cabin behind it, the length of which is built on a V-shaped hull. The engine features a trapezoidal ventilation grid at the front of the hood and beneath it is a forward-facing V-shaped bumper to assist in bundu bashing (driving through dense vegetation). The armored crew cabin is rectangular, with two forward-facing rectangular bullet-resistant windows. On either side of the cabin are two entry and exit armored doors with a rectangular bullet-resistant window each. The roof is armored and protects against medium artillery fragments. This setup provides all-around protection against small arms fire and the V-shaped hull protects the crew from mine blast underneath the hull. Access to either side of crew cabin doors is via steel-framed ladders.
The crew’s seating is blast resistant and designed to protect the spine in case of a mine detonation under the vehicle. The driver station is located on the forward right side of the cabin, with the vehicle’s commander seated on the forward left. Behind them are three seats with the remaining crew. The vehicle’s commander is responsible for communication via the command system. The driver station has a range of mobility options, depending on terrain type, controllable through a panel to his front left.
For ease of access to the weapons deck, a removable solid steel stepladder is placed on the left side of the vehicle, between the armored crew cabin and weapons deck. The weapons deck consists of the floor on which the main armament is mounted. On either side of the weapon deck are two downwards folding side plates, which are kept upright when travelling. When stationary, these side plates are manually lowered to a horizontal position, which increases the available floor space on which magazines are placed.
To the front right of the weapons, deck is a large armored storage box, where the magazines are kept. To the rear of the weapons deck is a large metal bin in which extra barrels and related gear are stored.
Protection
The armored crew cabin structure is made of RB 390 armored steel, which is 10 mm (0.4 in) thick and offers protection against 7.62×39 mm AP fire. The roof is 6 mm (0.24 in) thick and rated against 155 mm medium artillery fragmentation. The crew cabin doors are 6 mm (0.24 in) thick. The vehicle windows are made of armored glass 40 mm (1.57 in) thick and offer the same protection rating as the cabin structure. The V-shaped hull has been tested and proven against 3 x TM-57 landmine or equivalent of 21 kg of TNT under the crew cabin. The weapons deck is exposed.
Firepower
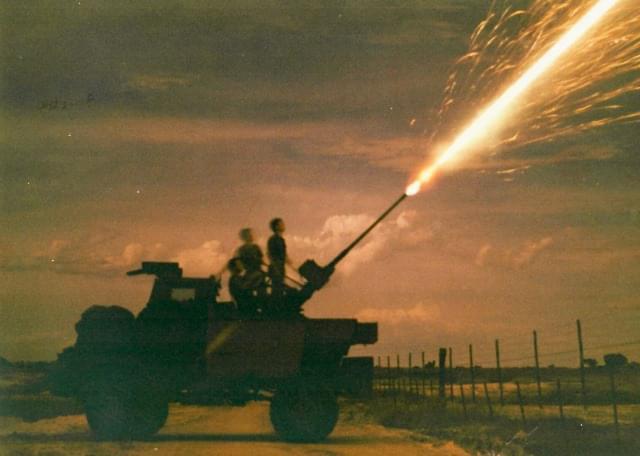
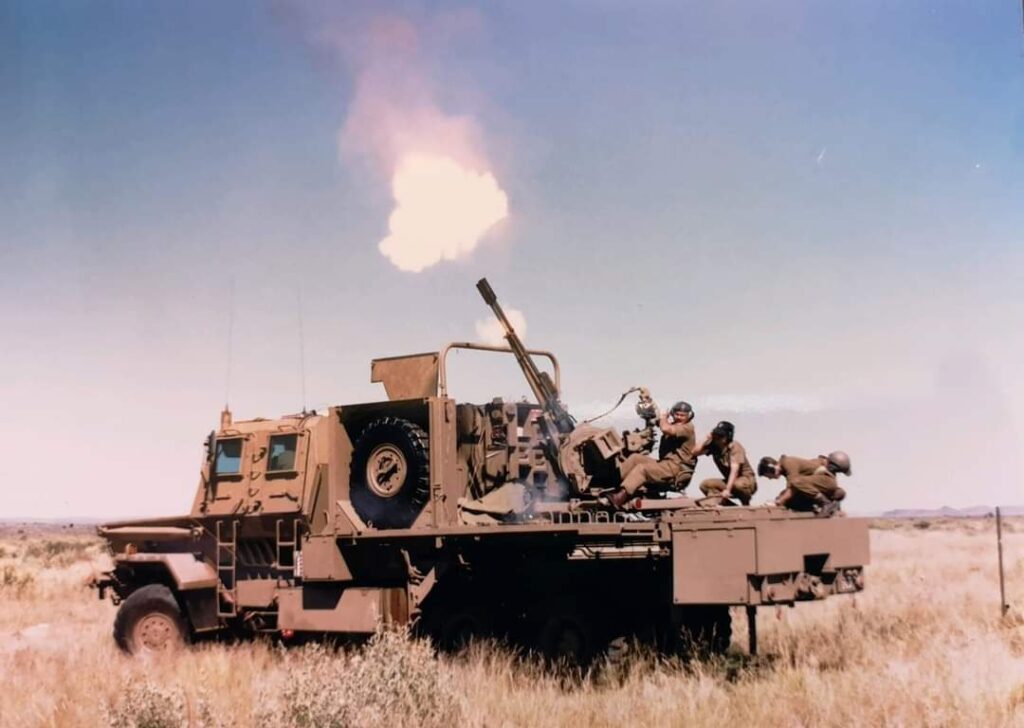
The Bosvark’s main armament is a gas-operated ZU-23-2 anti-aircraft gun system fitted to the weapons deck on three legs. It comprises two 23 mm barrels set side by side, each having an integrated ammunition box in which a single feed 50 round magazine feeds the barrels via a conveyor belt.
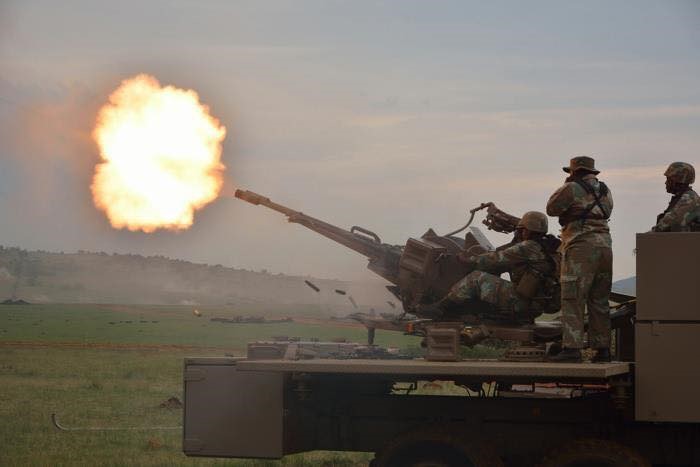
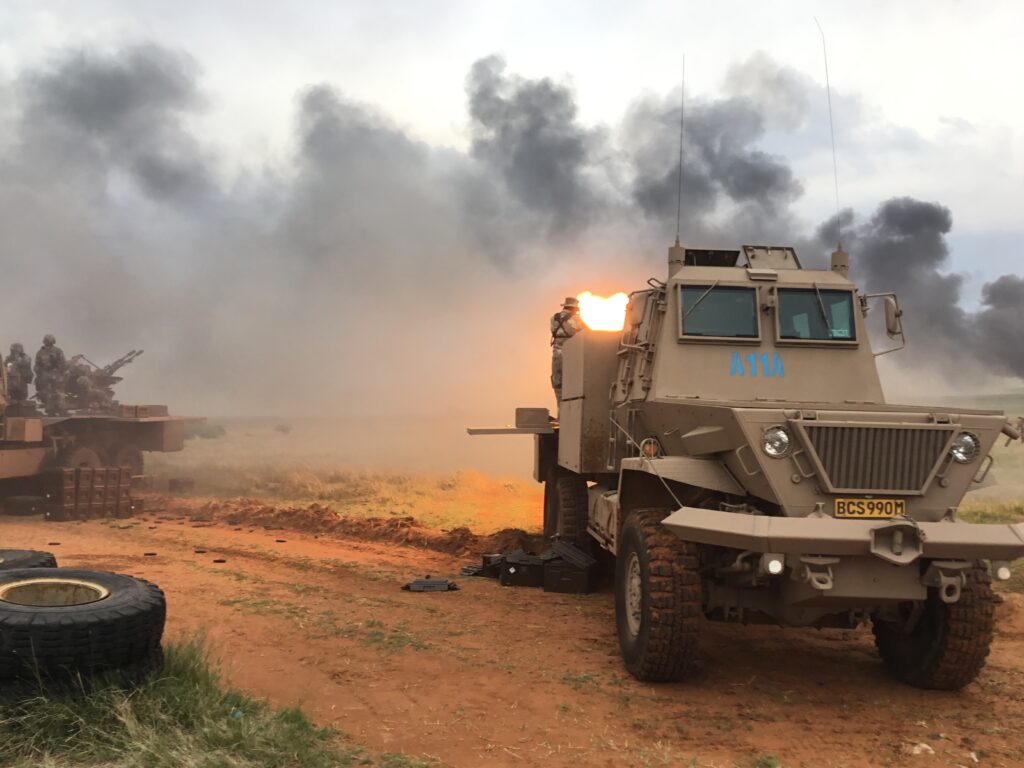


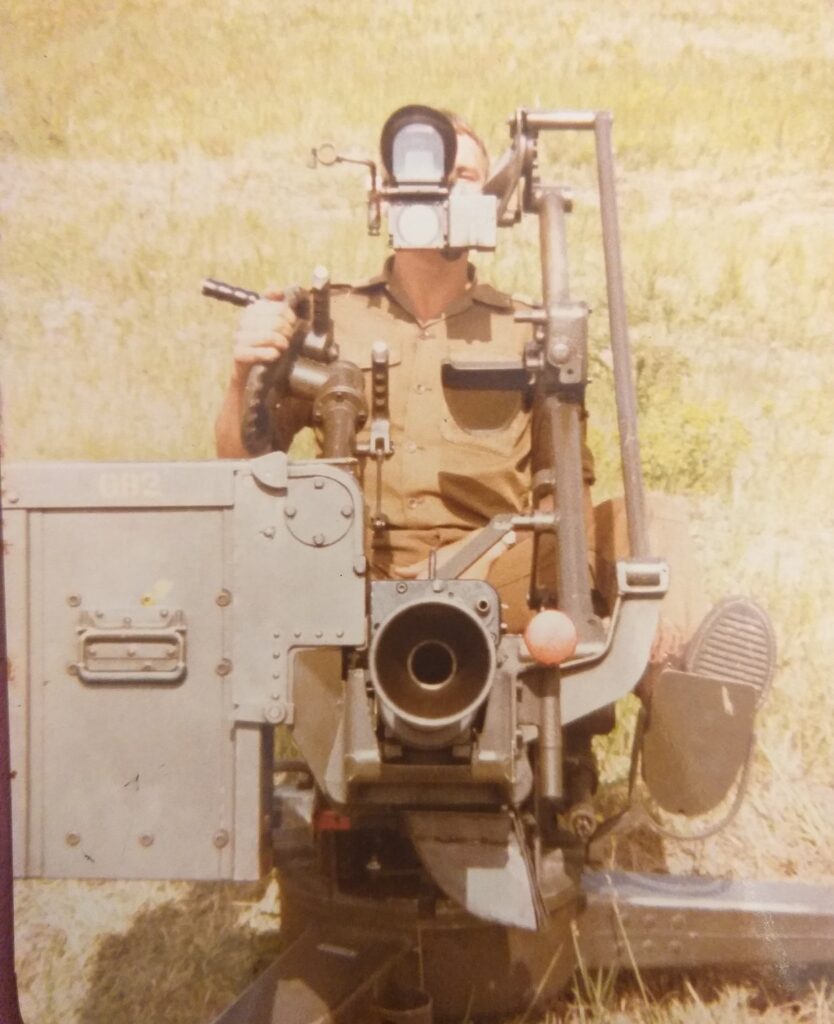
The rate of fire is between 800 – 1,000 rpm per barrel, which translates into three one-second bursts before reload for each barrel is required. Due to the heat generated by firing, the barrels need to be changed for cooling after every six bursts. Practically, this means that, with the required reload and barrel changes, the gun can fire 200 rpm. The gun is operated manually and elevation is achieved with a handwheel and foot brake on traverse, which makes it somewhat limited in engaging fast-moving targets. Although the gun can elevate between -10º to +90º and can traverse 360º, its firing arc on the weapons deck is limited to -7º to +85º. With the armored crew cabin and magazine storage bins, the weapons full range of elevation and traverse is limited to the sides and rear of the vehicle.
Available ammunition includes APC-T and HEI. The HEI and APC-T ammunition weighs 445 g and has a muzzle velocity of 975 m/s. The ammunition has an effective range of 2,500 m against air targets and 2,000 m on ground targets. The APC-T can penetrate 50 mm of armored steel at 0º at 100 m.
Some 600 rounds of ammunition are carried in 12 portable magazines. When the vehicle stops to engage, the magazines are removed from their storage bin and placed on the deployed side panels for easier access. The Bosvark primarily relies on resupply from a SAMIL Kwêvoël 100 ammunition vehicle for sustained combat operations.
For close-in protection, a 7.62 mm SS-77 General Purpose Machine Gun (GPMG) can be mounted on the roof of the crew cabin.
Fire Control System
The ZU-23-2 is equipped with the ZAP-23 anti-aircraft automatic sight. The sight consists of two optics: the straight tube 2Ts 27 telescope and the 1 OM 8 optical sight. The former is used to acquire ground targets while the latter is used to engage targets in the air accurately. The 1 OM 8 optical sight has an x3.5 magnification and 4°30′ field of view.

Conclusion
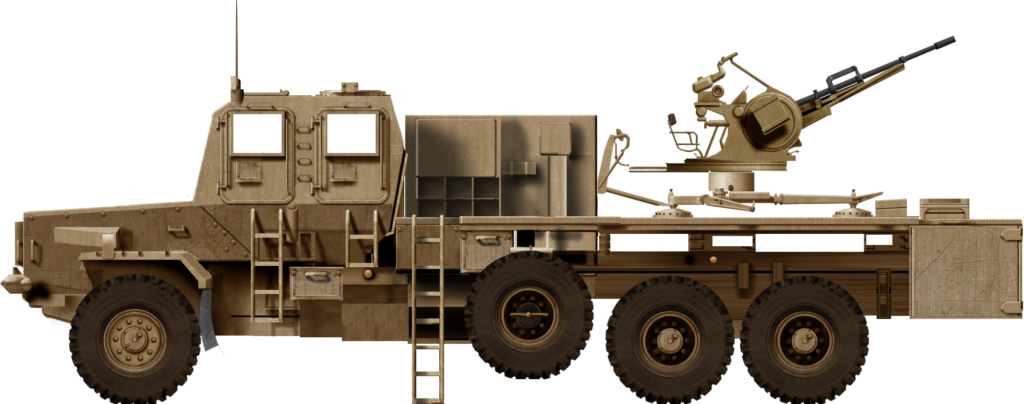
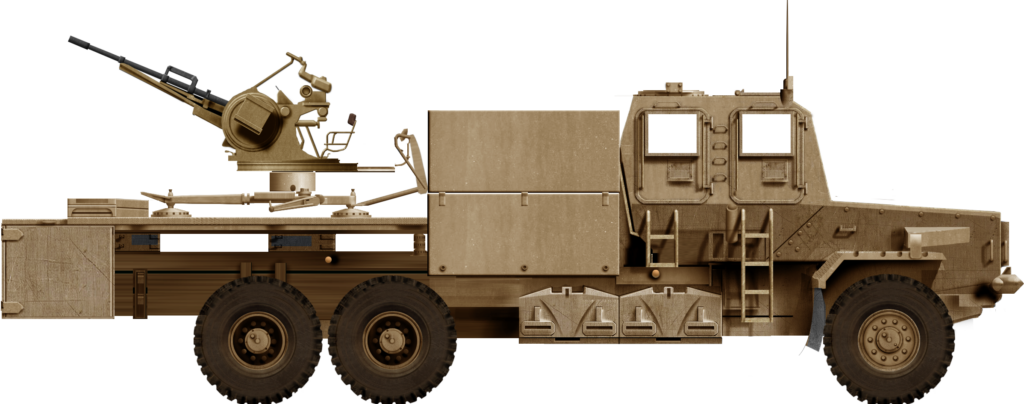


Illustration by Tank Encyclopedia’s own David Bocquelet.