Other Vehicles
Prototypes & Projects
- Begleitpanzer 57
- Carro da Combattimento Leone
- Indien Panzer
- Jank One Man Tank
- Kanonenjagdpanzer 1-3 (Kanonenjagdpanzer HS 30)
- Spähpanzer 1C
- TH-301
Deutschland Jahre Null
Germany emerged from the war in the summer of 1945 as a broken and devastated country. “Deutschland Jahre Null” as written and photographed on a ruined vestige of a wall and recalled by Rosselini’s 1949 eponym movie. A country in disarray, military occupied by foreign nations, with an ongoing hunt towards Nazis on the run.
The fate of Germany was kept in balance between USSR and the western allies, and the question of rearming its demobilized forces was raised as tensions rose on the Berlin question and occupation zones by some American and British officers alike, fearing the communist takeover of Europe. As these tensions crystallized with the blocus of Berlin, the question was raised once more, and eventually led to the cold war as we know it. From now on, Germany would became for NATO and the Warsaw Pact alike the object of most scenarios of a “hot” war between the two giants, a virtual battleground where most forces were deployed and multiplied excercizes.
NATO’s 1950s manoeuvers in West Germany (British Pathé Archives)
A country split in two
The split between the GDR (German Democratic Republic) and FRG (Federal Republic of Germany) in 1949 was in some ways, inevitable, as only a war could have persuaded Stalin to leave East Germany, but the price paid in blood for the territory made some legitimation of this occupation. As Churchill stated with his famous “iron curtain” the creation in Berlin of a wall in 1961 symbolized in itself the very nature of the tensions and drama that unfold in Germany. A people divided -by force- for 43 years.
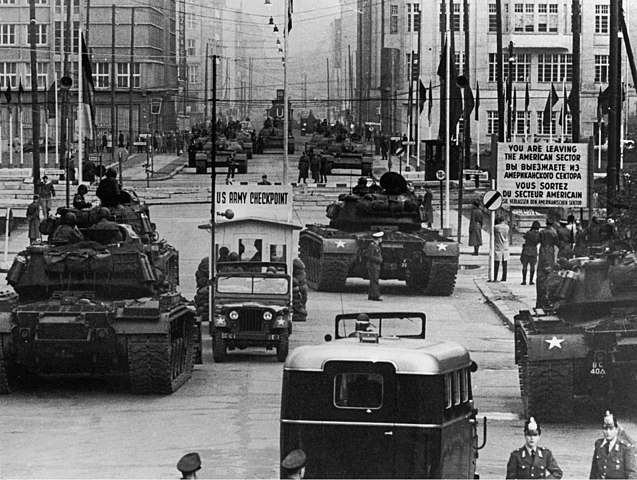

Berlin 1961: US and Soviet tanks facing off at Check Point Charlie
Two countries antagonized by the very fracture that divided two sphere of influence and visions of the world. And on the borders were massed untold numbers of divisions, of infantry, tanks. Military airbases and garrisons dotted the landscape, ready to get on one another’s throat in the shortest notice.
Thought frightening, it was only the conventional aspect of this cold war. Over everybody in Germany loomed the dark spectre of nuclear annihilation, targeted precisely on these allied German bases. So Germany was in the very heart of the cold war, and Berlin the symbol-city of it all. In the years following the raising of the wall, entire families were divided and two countries gradually emerged, with vastly diverging way of living and cultures.
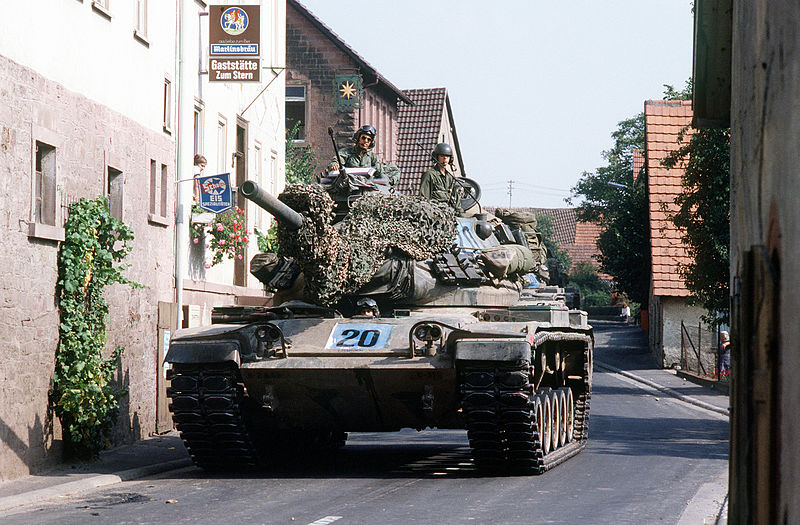

M60 Patton on the streets of a West German village, NATO exercize Reforger ’82
West Germany and NATO
Soon after the signature of the treaty that led to NATO, the question of West Germany incorporated inside it was raised again. Prior to that era, the rearmament of Germany was perceived as a threat both by the Soviet Union and French Gaullists and communists. However after the 1949 split, both sides were to be rearmed as it was seen the most logical choice. After all, German engineers were known to be possibly among the best in the world, and the German army although badly led on top, proved to be a formidable fighting force.
The baby-boom also was to provide the manpower for a new, defensive army, deeply embedded in strong constitutional and democratic principles, eradicating the old specter of German militarism.
It was also seen as a practical way to gradually reduce the military presence of the allies (and the financial burden associated) on the territory, although local authorities alleged the financial benefits of such presence in their area.
Konrad Adenauer also led his country resolutely on the western side rather than seeking any form of neutrality. So West Germany joined NATO on 9 May 1955 and soon the Bundeswehr was born.
The Bundeswehr
The creation on November, 12, 1955 of the Bundeswehr was accompanied by a split between the ground forces (Heer), the Luftwaffe and Bundesmarine, but also the Streitkräftebasis (Joint Support Service) and the Joint Medical Service or Zentraler Sanitätsdienst. The symbol associated was the old Maltese cross, partly associated with the past Teutonic Knights and Prussian nobility, rather than the straight Balkan cross, for obvious reasons. Needless to say the swastika was banned from any display in any forms or shapes.
This army was equipped predominantly American equipment, soon partly produced locally under licence. To start with, the Bundeswehr were equipped with American tanks such as the M41 Walker-Bulldog light tank and the M47 Patton medium tank.
These formed the basis of most of West Germany’s panzer divisions. These would be followed by the M48 Patton. Soon, West Germany had both the experience, the will and the industrial basis to design and produce a new, indigenous tank. It was decided to pursue the development of the “Europanzer” in the 1950s, together with France and later joined by Italy. The M48, however, would go through numerous upgrade programs in the Bundeswehr, ultimately culminating in the M48A2GA2, and was not removed from service until the early 1990s.
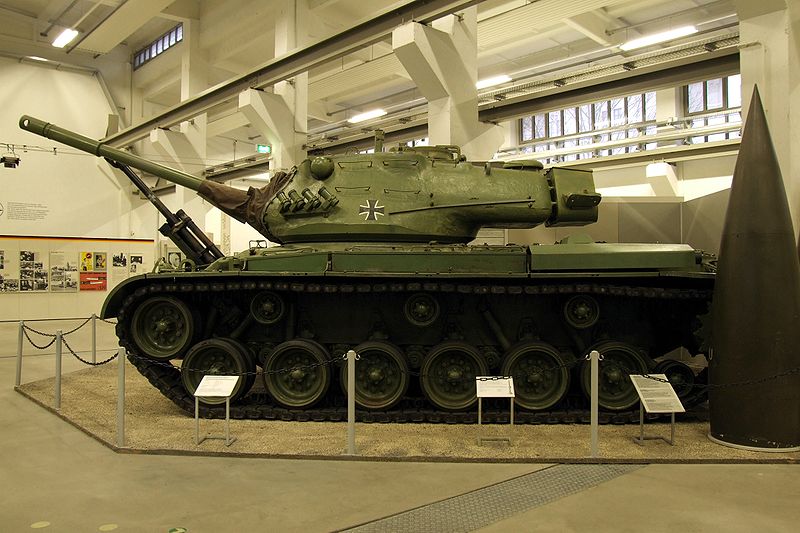

German M47 Patton now on display at the Dresden museum
The “Europanzer” project
The European Standard Tank was at first a joint Germans/French project started in 1955 to replaced their American models and fit more precisely their collective requirements. The whole program was dubbed the Europanzer (but was later called the “Standard panzer”) and the design emphasised mobility and firepower as both countries estimated that modern rounds rendered heavy RHA armour useless. Superior range and accuracy combined with a better speed and manoeuvrability were to compensate for a lack of protection.
In June and July 1957 both Germany and France gave their the final requirements to the companies involved in the project. Officially Italy joined the project in September 1958 and contracts were signed for the production of 2 groups of German prototypes and a single French prototype. The latter began testing at Satory in march 1961, followed by the German prototypes in Meppen.
In 1963 the French prototype was evaluated in Germany. These were refined in 1963 as the Standard-Panzer and the AMX-30 when both countries eventually decided to built their own tanks due to too much specification divergences and other considerations. The Standard-Panzer became the blueprint for the following prototypes of the Leopard in 1964.

Porsche version of the Europanzer (A group), which differed from the French one by a commander’s rangefinder.(credits:www.jedsite)
The Leopard: The European Feline
Being an the forefront of tank design during ww2, the world saw with great attention a brand new model, especially if it renewed with the “feline” tradition of its ancestors. The name reflected agility, speed and ferocity, and also proved a marketing success.
It was tested virtually by all European nations previously equipped with American tanks, and purchased in droves, as well as former UK supplied countries like Canada and Australia. The United States themselves evaluated the vehicle in Germany, which left such an impression that in 1965, the Army decided to embark on their first joint German-American tank project ever, better known as the MBT-70.
The Leopard was armed with the standard (licence-built by Rheinmetall) 105 mm L7 main gun and featured an excellent mobility with an advanced suspension system. Protection was constantly improved in the 1970s and 1980s, until the release of the Leopard 1A5, the last version, and was one of NATO’s most prolific tank.
At that time the new standard gun was to be inspired the 120 mm L11 manufactured by the Royal Ordnance Factory and also purchased for licence production by Rheinmetall.

The second prototype of the Leopard, now preserved at the Munster Museum.


American made tanks such as this M41 Walker-Bulldog (entering service in Germany in 1955, the first tank to be adopted by the Bundeswehr, top) and M48 Patton III (also entered service in the mid-1950s, only retired in the early-1990s, bottom) formed the backbone of the Bundeswehr’s armoured units after the Second World War until West Germany began producing its own tanks. The M47 Patton II was also used by the Bundeswehr.

Entering service in 1965, the Leopard 1 is one of the most famous tanks to come out of the Cold War. Thinly armoured but highly mobile, and armed with the powerful 105mm L7 gun, the tank was extremely successful. It was used by multiple countries around the world, such as Canada, Australia, Belgium and Turkey. Turkey is one of the many countries that still operates the Leopard 1. The vehicle has also spawned a number of variants, including anti-air and recovery vehicles.

One of the most successful derivatives of the Leopard 1 was the Flakpanzer Gepard. Entering service in the mid-1970s, the Gepard was equipped with two 35 mm Oerlikon KDA auto-cannons with radar assisted target acquisition. The Vehicle was used by multiple countries including The Netherlands and Belgium. This Self Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun (SPAAG) was only removed from German service in 2010, but remains active in countries such as Brazil.
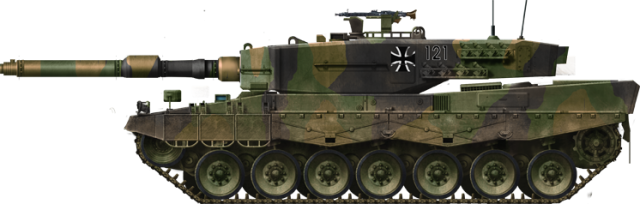
The Leopard 2, like its predecessor, is one of the most successful tanks of its era. This Main Battle Tank (MBT) entered service in 1979. It is armed with the 120 mm Rheinmetall L/55 smooth bore gun, and is equipped with composite armor of high-hardness steel, tungsten, plastic filler and ceramics. Like the Leopard 1, the 2 is used by various militaries across the globe.

The Spähpanzer RU 251 was a proposed design for a light tank. It used shared the same chassis as the Kanonenjagdpanzer 90 and Raketenjagdpanzer. It also used the same 90mm main gun as the Jagdpanzer. It was only ever a prototype, however.
The Leopard 2: An enduring legacy
The long development of the joint MBT-70 project, revealed itself to be a failure, with the separation of both armies. Too diverging specifications on the long run and the associated costs led the Bundestag to refuse to fund the project anymore in 1969 (it reached 1.1 billion DM), but data was reused for the Keiler, code name for the future Leopard 2.
The latter reused many of the advanced technologies featured by the prototypes series, married with as many parts of the actual Leopard 1 to bring the costs down. Eventually, the Leopard 2 entered service in 1979, just one year after the M1 Abrams, also born from the MBT-70.
In all, throughout all versions manufactured and exports, 3480 were built. The Leopard is recognised today as one of the very best MBT in the world, often rated #1 by military experts. Despite being thirty-six years old, it was proved modular enough to evolve with the latest technologies, and like the Abrams, is not scheduled for a replacement anytime soon.
Other Vehicles
KMW Marder IFV (1968)

Marder 1A3 (cc)
The first true German IFV: The Marder project was developed as early as September 1959 during the early phase of production of the HS 30. The aim was to develop an equivalent to the Leopard 1 armored infantry fighting vehicle. The ATV staff (training, technique, experiments) of the Panzertruppenschule Munster created the military demands with the following characteristics:
– Increased attendance of 12 men
– High protection potential for the crew
– High mobility, driving range of a Leopard 1 on a par
– A reliable 20mm on-board machine gun
– Uncomplicated switching between combat and dismounted combat
– NBC protection
It was also intended to create a whole armored infantry vehicle family, with a modular armament, ranging from AT rockets, to antitank mortars, medical armor, transportand supply, anti-aircraft and FlaRak plus SPAAML. However it was intended for the Panzergrenadiere, which had their own way of fighting, leading to refine further the concept. In fact, two lined of development started, one of cannon-armed tank hunter and another of ATGM tank hunter separately. They were concluded successfully in 1967.
Development history
In January 1960, the Rheinstahl group which comprised Rheinstahl-Witten, Hanomag, and an engineering office at Warnecke and Henschel AG (Thyssen Industrie AG at Kassel) were contacted as well as MOWAG to develop seven prototypes each. Immediately Henschel presented a derivative of the HS 30, soon followed by the other two groups that used the same blueprint. These first gen. prototypes were the RU 111, RU 112 and RU 122 (Rheinstahl), 1HK 2/1, 1HK 2/2 (Henschel) and HM 1/2 (MOWAG).
They all respectd the combat limit of 16 tons. Meawnhile, NATO started to be interested and made some proposals and the US Army made some proposals, itself looking for a beter armed replacement for the M113, which would eventually led to the development of the Badley. The one-time US-German partnership for a common armored infantry fighting vehicle failed, just as the next MBT program will. After a serie of comparative tests with these early two-three prototypes In 1963, demands for a second generation led to redefine a model weighting about 20 tons.
Rheinstahl built and sent the RU 214, 261,262 all larger, with front engine and upgraded features and a 20mm automatocannon turret plus ATGM. MOWAG released soon the 2M1/1, 2M1/2 and 2M1/3, all with a mid-mounted transverse engine. New tests were performed this year, leading the staff to create new demands. The 1964 batch of third generation IFVs meant the vehicles has to be longer and wider, with rear-mounted MG and pistol ports for the infantry and better protection overall.

But at least previous tests secured the solution of a combined one-man autoannon turret with ATGMs and there were no changes, at first, until it was asked to develop a two-man tower with a crest-mounted machine gun whereas the vehicle’s armament module remained the same. In 1967, the fourth generation IFVs represented another combined batch of ten prototypes, extensively tested with troops in the field and in all conditions. MOWAG retired in 1968, not capable of providing a satisfying ATGM solution.
In 1969, a contract was awarded for the supply of 2136 IFVs and the first production vehicle was scheduled to be delivered on 7 May 1971. The Panzergrenadiere had their new IFV, a real step up compared to the earlier HS.30. For production, Rheinstahl AG and Maschinenbau Kiel (MaK) were contracted both.
Author’s illustrations

Basic Marder 1A0

Marder 1A1

Marder 1A3
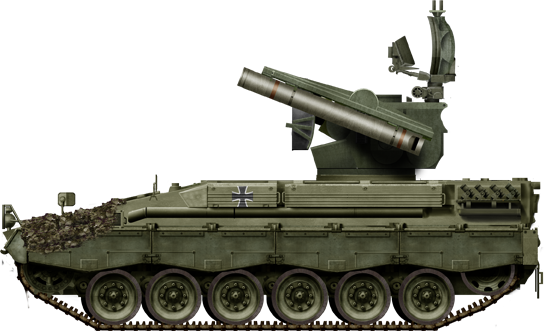
Flugabwehrpanzer Roland
Marder 1A1 specifications
Dimensions: 6.79 m x 3.24 m x 2.98 m
Overall Weight: 28.5 t (1A1/A2) 33.5 t (1A3) 37.4 t (1A5)
Crew: 3+7 (driver, cdr, gunner, 7 infantry)
Propulsion: MTU MB 833 Ea-500 diesel engine 441 kW (591 hp)
Transmission: RENK HSWL 194
Suspension: Torsion bars
Speed (road, 1A2): 75 km/h (47 mph)
Range: 520 km () 652 L (172 US gal)
Armament: 20 mm MK 20 Rh 202, MILAN ATGM, 7.62 mm MG3
Armor: VS. 20-25 mm protection ()
Total production: Circa 2,136 1961-1975
Src:
http://www.panzerbaer.de/types/bw_spz_marder_1a5-a.htm
https://www.zeit.de/politik/ausland/2016-12/jordanien-panzer-ursula-von-der-leyen-bollwerk-terror
Schrottreife „Marder“. – Der Spiegel. 5. August 2000.
Verbesserter Schützenpanzer MARDER ausgeliefert. In: bwb.org.
Rheinmetall integriert Panzerabwehrlenkflugkörper MELLS in Schützenpanzer Marder. In: Pressebox.de. abgerufen am 21. März 2018.
Siehe Bild am Artikelanfang.
Strategiewechsel: Mit dem „Marder“ in die Offensive
Afghanistan: Deutsche Patrouille nahe Kundus beschossen, 21. Feb. 2011.
Marcel Bohnert & Andy Neumann: Panzergrenadiere im Kampfeinsatz in Afghanistan
(To be completed in a future dedicated post)
Future plans for the Bundeswehr section of Tank Encyclopedia
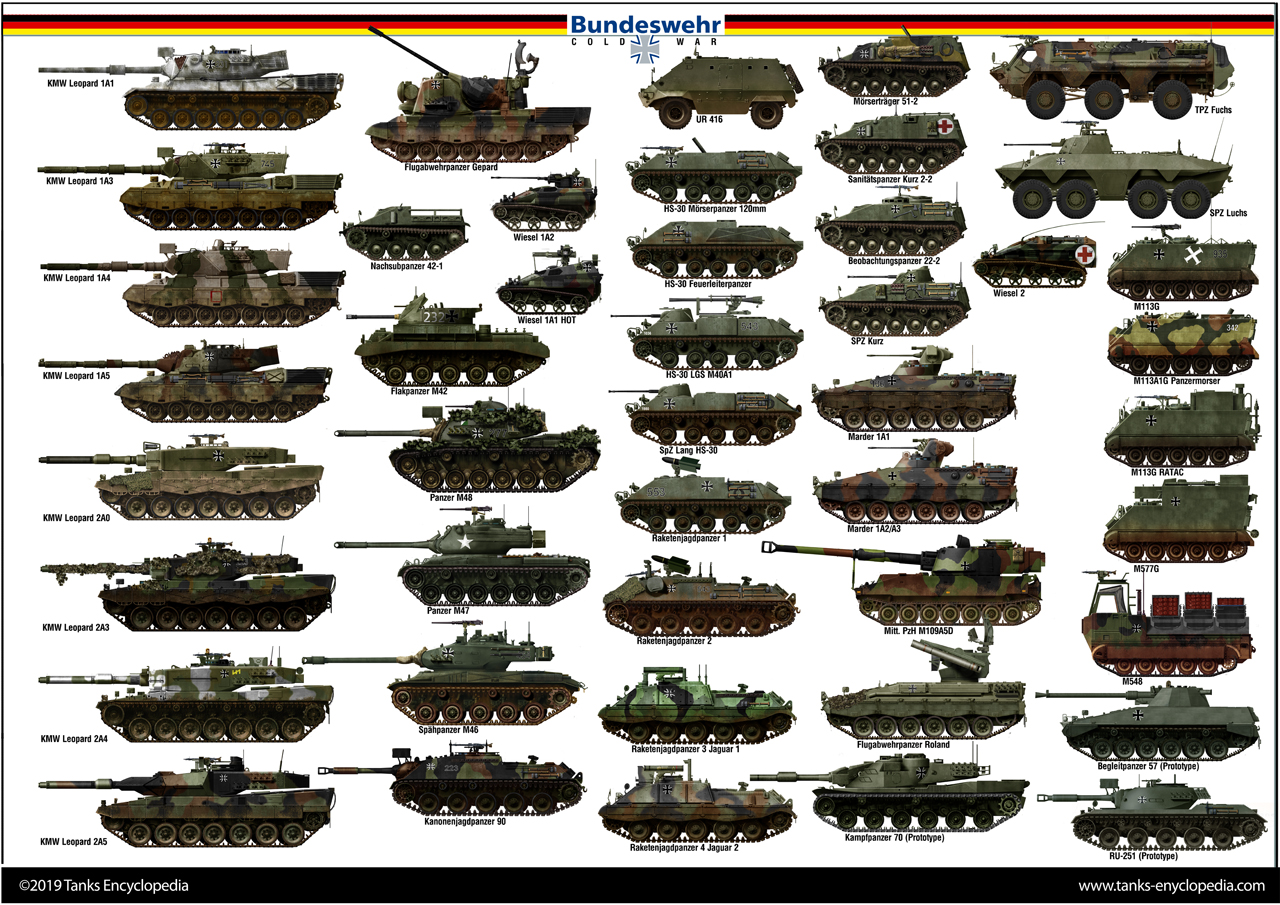

There is nothing like a good poster to show the vehicles that has been done and those which will have their own post in the future.
The most urgent ones should be the following:
-KWM Marder 1A1-A3
-Spz Luchs
-Flugabwehrpanzer Roland
-Raketenjagdpanzer 3/4
After which, we will probably go through the M113G and the M113 variants in service with the BDW, the M48A5G, M109A5D, UR416 and other export vehicles, and individual variants.
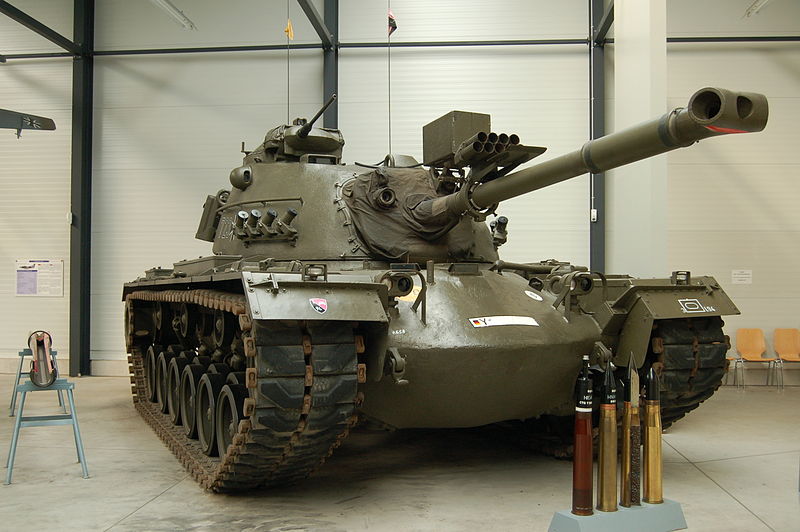

German M48A2C Patton in German Service, preserved.
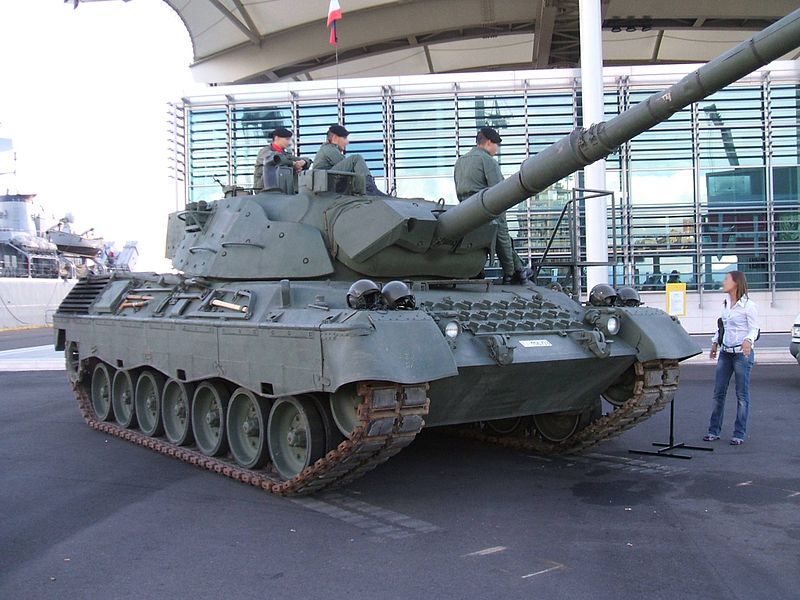

The upgraded Leopard 1A5, an export success (here in Italian service).

The Bergepanzer II ARV, based on the Leopard I chassis.
Links
The German Heer official website
The bundeswehr on Wikipedia
Panzerbaer
Equipments of the Bundeswher (West Germany)
Cold War Tank Formations
Illustrations

Prototype A (Porsche), 1961.

Prototype B (Rheinmetall), 1962.

Leopard I of the first production version, 1965.

Leopard I, 193rd C2 Panzer-Battalion, Kampftruppenschule 2 Munster, winter 1965-66.

Leopard I (Norway) Stridsvogneskadron, 6th Division, NATO winter exercises of 1988.
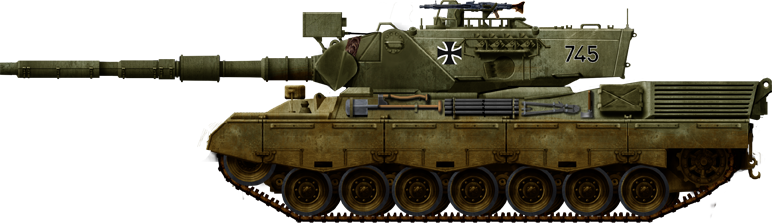
Bundeswehr Leopard 1A3, 1980s.

Norwegian Leopard 1A3, 1990s.

Danish Leopard 1A3.

Australian Leopard 1A3, 1990s.

Australian Leopard 1A4, 4th Trp. Cmdr, B-Squadron, 1st Armoured Regiment.

Danish Leopard 1A5, UNPROFOR, Tuzla, Bosnia, January 1995.

Greek Leopard 1A4, 1990s.

Leopard 1A4, AS-1 “Assassin”, 1st Australian armoured regiment, Puckapunyal, Victoria.

Leopard 1A3 (C1 late) from “A” Squadron, 8th Canadian Hussars, stationed at Lahr, March 1990s.

Turkish Leopard 1A5, 1990s

Leopard 1A5, 2nd Panzer Division, 354 Kompanie, 2nd Battalion, Exercise REFORGER FTX “Certain Challenge”, September 1988.

Netherlands Army Leopard 1-V, 2nd tank battalion, 13th Panzer brigade FTX, Operation “Field Lion” September 1988.M

Leopard 1A5, 2nd Kompanie, Panzer Battalion 14, 1st PanzerGrenadier Brigade, FTX “Sharfer Bohrer” March 1990.

Flakpanzer Gepard or Flugabwehrkanonenpanzer Gepard SPAAG (1969).
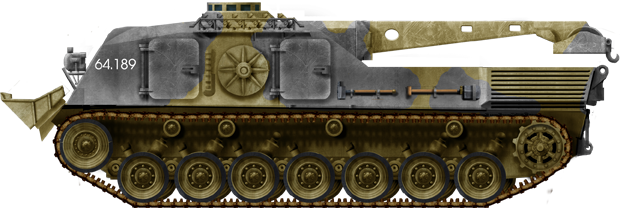
Danish 1A5 ARV, 1st Gulf War, 1991. Previously published in June 2014.

Jagdpanzer Kanonen 90, 1970s.

2nd Panzerjägerbatallion 44, Göttingen 1980.

Beobachtungspanzer 6/Panzergrenadierlehrbatallion 152, Schwarzenborn.

Raketenjagdpanzer of the first series in 1961.

Another vehicle used for tests in the 1970s.

Raketenjagdpanzer 2 in service in the early 1960s.

Another one with a camouflaged net, in the 1970s.

Upgraded Raketenjagdpanzer Jaguar-1, in the late 1980s.

Spz Kurz with bare hull (without tooling), early production by Hotchkiss-Brandt, 1960.

Schützenpanzer SPz 11-2 Kurz in service in the 1960s.

German-built Spz Kurz in the 1970s in manoeuvers, with camouflage.

Beobachtungspanzer 22-2 command/forward artillery observation tank

Sänitatspanzer Kurz 2-2 (armoured ambulance)

Nachschubpanzer 42-1 supply tank, derived from the Hotchkiss TT-6

Mörserträger 51-2 (mortar carrier) in the early 1980s, one of the rare vehicles camouflaged.

Early SPZ 12.3 Lang Gruppe, closed roof panels, 1960.

Late SPZ HS.30 Gruppe IFV in the 1970s. Smoke pots, additional racks and open roof panels.

SPZ HS.30 in provisional winter livery, 1960s. Notice the front MG3 shield manned by the front soldier, behind the driver’s hatch.

HS.30 antitank with the recoiless M40A1 LGS 106 mm cannon.

HS-30 Feuerleiterpanzer forward artillery observation vehicle.

Mörserpanzer 12 cm Brandt (F), self propelled mortar carrier.

Standard APC version (transportspanzer) – Bundeswher

Chemical recon APC Budeswehr GECON ISAF Afghanistan 2005

The ABC Abwehr Btl7 Operation Enduring Freedom, Kuwait, 2003

TPZ1A1 Bundeswehr NBC GECONISAF Afghanistan 2004

TPZ1A1 Fuchs NBC recon with the Norwegian Army, 2005

Algerian Fuchs

Wiesel-1 Mk20.

Wiesel-1A1 ISAF, Afghanistan

Wiesel-1A1 HOT tank hunter, .5/FschJgBtl – Fallschirmjägerbatallion 263

Wiesel 2 Ambulance, 1990s.

KampfPanzer 70 in 1970. The German version of the joint and ambitious US-German MBT-70 was cancelled due to skyrocketing costs.

Erprobungsserie (pre-serie), 1st batch, first three tanks. These were never fielded to any operational units but kept for tests at KMW.
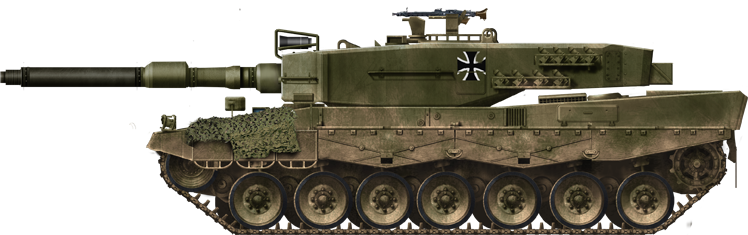
Leopard-2A0 of the first batch in 1979. Notice the PZB 2000 image intensifier mounted over the mantlet. There was also a wind sensor but not yet any thermal imager.
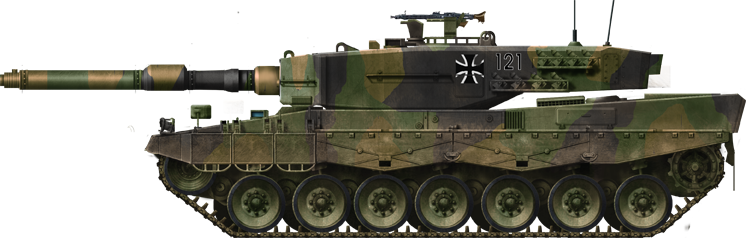
Camouflaged Leopard 2A1 in the 1980s.

Bundeswehr’s Leopard 2A2, first modified batch, 4th kompanie, 33th batallion.

Canadian Leopard 2A2.
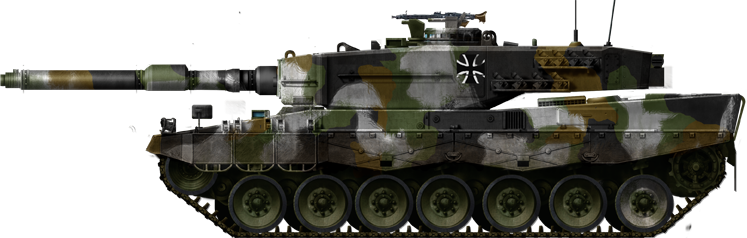
Bundeswehr Leopard 2A3 in winter manoeuvers with provisional winter paint.

Leopard 2A3 of the Bundeswehr, Panzerbattalion 123, Panzerbrigade 12, October 1990.

Danish Leopard 2A4DK. Some actively supported British troops during various operations in Afghanistan from 2008 to 2013.

Leopard 2A4 of the Bundeswehr (7th batch), 214th Panzer Batallion, 7th Panzer Division, CMTC Hohenfels, October 1990.

Swiss Panzer 87 (This version includes a Swiss-built 7.5 mm Mg 87 LMG, specific communications equipment, improved NBC. Up to 380 are in service as of today.

Polish Leopard 2A4, from the 10th Armoured Cavalry Brigade based in Świętoszów.

Leopard 2A4 of the 41 NL TankBataljon, 41 lichte brigade Weser-Emsland june 1993.

Leopard 2A4NO, Norwegian Leopard in winter manoeuvrers.
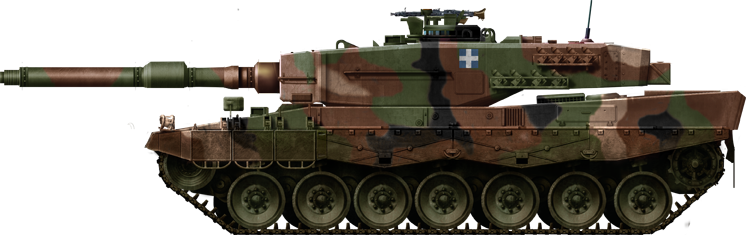
Leopard 2A4 HEL, Greek Army Leopard.

Finnish Leopard 2A4

Leopard 2A5 of the Bundeswehr. Released in 1990, right at the end of the cold war, its tank-to-tank armour capabilities were far superior to any design worldwide at that time. In addition from 1998, 225 former Leopard 2s were upgraded to this new standard. Both the Rheinmetall L44 and FCS are widely improved.

Polish Leopard 2A5

Swedish licence-built Strv-122

Danish Leopard 2A5DK. This version is upgraded to the 2A6 level but retained the same gun.

Leopard 2A6 of the Bundeswehr. Unveiled in 1998 but entering service in 2001, it is equipped with the long barrel Rheinmetall L/55 120 mm smoothbore cannon, and received an improved FCS, updated protection, battle management systems, and a modern hunter-killer capability. The new gun helps to improve both accuracy and range through muzzle velocity, and is a significant advantage over the Abrams. Experts agrees that this version outperforms the latter, but also beats the Challenger and Leclerc in all three summits of the “magic triangle” and therefore could be considered as the world number one MBT.

Spanish Leopard 2E, a locally-built version (2010)

Greek Leopard 2A6HEL as of 2014.

Canadian 2A6M, improved for urban combat, as tested in 2008 to 2013.

Krauss Maffei 2A5PSO (Peace Support Operations) optimized for for urban combat, as desmonstrated at Eurosatory 2008.


17 replies on “Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany)”
I hope I can see an article about the Panzerspähwagen Lüchs soon.
Are you going to be creating an article about the VT tank. A double barreled tank destroyer that only made it to the prototype stage. It is quite interesting.
It shall be added in the future for sure.
– TE Moderator
No articles for the Luchs or Marder?
Not as of yet unfortunately.
when are you gonna do east germany
The page actually just started writing stage, after gathering enough data.
Got something about the “Borgward-Kampfpanzer” of the 1950s? I cannot find much about this project.
I wanna hear more about spahpanzer RU 251, actually, i have been looing for its datum for a long time, i wanna build the digital model. Would somebody give me a hand?
Why is the Leopard 1 & 2 Pages on archive ??
If the Kanonenjagdpanzer is part of the raketenpanzer TD project, I’d love to see it included, along with something for the RU 251, which is a cool tank
We may have an article coming soon… Keep an eye!
Gareth (TE Manager)
Is there any chance if you making East Germany? Whould be fun to see what tanks they had.
Yes, that’s something we would love to add to our website in the future, but not something anybody is currently working on.
Thanks
Gareth (TE Manager)
Ok keep up the job i love it
Nice I love German tanks btw it would be nice if you guys could add the Swiss leopard 2 and 1 or ,at be a winter camp of these tanks
I know it is nitpicking but dutch forces use the MAG in stead of mg3