






 United Kingdom/Republic of Singapore/State of Kuwait/Republic of Indonesia/Argentina/Republic of Ghana/Republic of Mauritius/Kingdom of Norway/Kingdom of Saudi Arabia/Ukraine (1988-Present)
United Kingdom/Republic of Singapore/State of Kuwait/Republic of Indonesia/Argentina/Republic of Ghana/Republic of Mauritius/Kingdom of Norway/Kingdom of Saudi Arabia/Ukraine (1988-Present)
Armored Personnel Carrier/Internal Security Vehicle – Approximately 340-354 Built + Prototypes
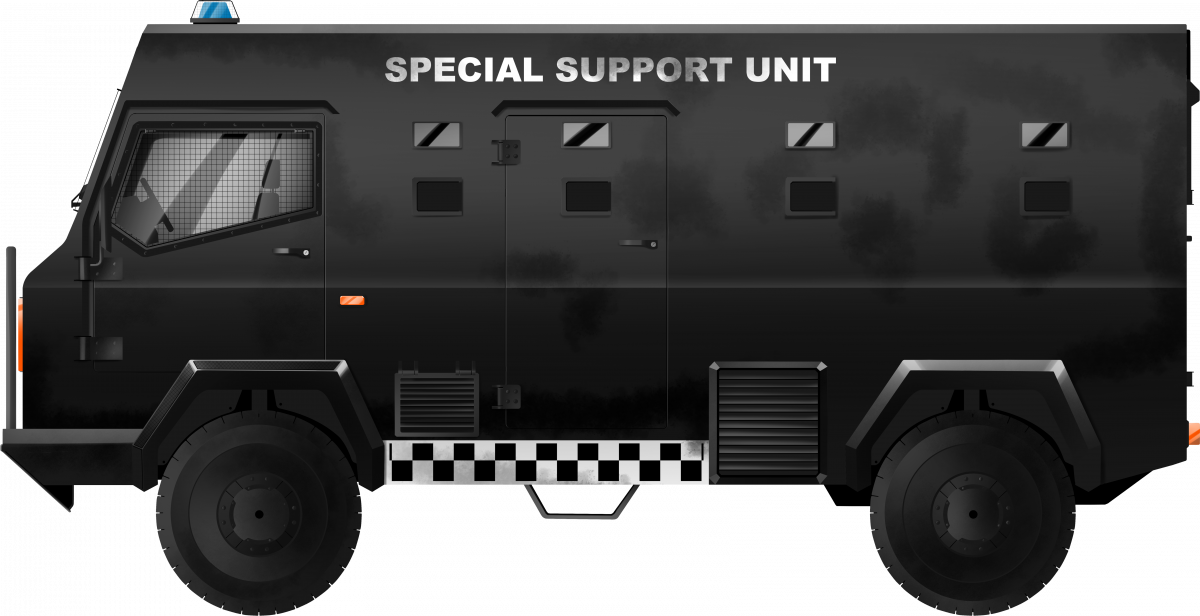
The Tactica, consecutively produced by Glover Webb, GKN Defence, Alvis plc, and BAE Systems, is an armored personnel carrier designed for internal security duties that was introduced in the late 1980s. It saw a considerable production run and has been adopted by nine countries. Two main versions were produced, an armored patrol vehicle with a bonneted design, and an armored personnel carrier with a cab-over-engine design. The latter has seen the most production in various configurations. Notoriously, the Tactica has been in the center of several heated weapon export policy debates. Two of the customers, Indonesia and Saudi Arabia, have been widely accused of having used the vehicles in human rights abuse. Simultaneously, the Tactica has also been used in three separate UN missions to good effect.

Glover Webb & Development
The Tactica started off as a private development by the company Glover Webb from Hamble, Hampshire (United Kingdom). The company used its privately developed semi-monocoque frame as a basis on which the new armored body was developed. Two main versions were built, one vehicle with a cab-over-engine [abbr. COE] design, and one version with a conventional bonnet. Furthermore, specialist variants were developed using the COE design as a base. In 1988, the vehicle was officially introduced to the commercial market and had its first customer at the end of 1989, when several were sold to Singapore. In early 1993, a series was sold to the British Army, which used them mainly in Northern Ireland in specialized roles. Additionally, Patrol Tacticas were sold to Kuwait.
GKN Defence & Alvis plc & BAE Systems
At the end of 1994, Glover Webb was taken over by GKN Defence, but remained in service as a subsidiary until it was closed down in late 1997. The business and production of the Tactica series was relocated to GKN’s main facility in Telford, Shropshire (United Kingdom). It was marketed under GKN’s name for just a very short time, as GKN Defence merged with Alvis-Vickers in 1998. Just before all this happened, in mid-1997, a new order was secured from Argentina, for use with the UN mission on Cyprus. Furthermore, GKN showed off their two models at the British Equipment Exhibition of 1997, held at Farnborough Airfield, Hampshire. The APV version was shown in mock-up MOD police markings, while the APC stood next to the GKN Simba.
In addition to Singapore, the UK, Kuwait, and Argentina, further deals were consecutively concluded with Ghana, Indonesia, Mauritius, and Norway. In 2004, Alvis was taken over by BAE Systems. Under their management, the largest Tactica deal was signed, concerning an additional 200 vehicles for Saudi Arabia. As of October 2021, the Tactica is still listed as a product on the BAE Systems website, but the official sale brochure was taken offline before 2017 and the Tactica is no longer on offer.

Design
The forward-control vehicle with the COE configuration was introduced as the basic vehicle in 1988. It had its engine mounted centrally between the driver and commander, who were seated at the front. Depending on the customer, the driving position was either on the left- or right-hand side. Their compartment was separated with half a bulkhead from the troop compartment that extended to the rear of the vehicle. There was enough space for at least ten men, but there were other configurations available for fourteen, sixteen, or eighteen men.
Although the first prototype was based on a commercially available Gomba Stonefield P5000 4×4 truck chassis, later, a new chassis was developed. This new semi-monocoque hull was made with certified high-hardness armor, providing protection against 7.62 mm AP rounds. Reportedly, the actual thickness used to achieve this was around 25 mm. The vision blocks were purported to offer equal protection, while the belly also protected against fire bombs and IEDs. The armored glass of the windscreen and windows was 50 mm thick, with a 6 mm thick anti-spall liner. The vision blocks were 73 mm thick. The armor was supplied by Sleeman Engineering and the glass by Romag. The wheels were standard equipped with AL1-DCSR high-speed shoot-through tire systems.
For propulsion, a range of diesel engines were provided, depending on the customer’s needs. Gearboxes were also choosable, with either automatic or manual options. When equipped with the Mercedes-Benz OM 906LA diesel, the Tactica could reach a speed of 120 km/h with a range of 650 km. Another known engine option was the Perkins 180Ti.
Other standard features of the Tactica were powered steering and a permanent 4×4 drive with selectable ratios and three lockable differentials. The driver’s compartment could be reached through a door on either side, and the troop compartment through four doors, one in each side and a double door at the rear.
Armament
The regular APC version featured ten firing ports, while additional armament could be deployed on the roof. A small machine gun-armed turret was also optional, but only sold to Ghana. The turret could be armed with either a 7.62 mm machine gun or a heavier 12.7 mm [.50 cal] M2 HB machine gun.

The Armored Patrol Vehicle
In essence, the Patrol vehicle was identical to the forward-control vehicle, although having a completely different hull, with less room inside and a less aggressive appearance. The Patrol also has eight firing ports, instead of ten.
Variants
- APC
- APC with ten-, fourteen-, sixteen-, or eighteen-man configuration
- Armored Command Vehicle with a higher roof
- Armored Ambulance with a three-man crew and four stretchers
- Armored EOD vehicle
- Armored Water Cannon
- Patrol
- Armored Patrol, high-speed, ten-man crew
- Armored Patrol, APC, ten-man crew
- Armored Assault, five- or ten-man crew
Tactica 2000
Some twelve years after its first introduction, an improved version of the Tactica was presented, which featured a more powerful Mercedes-Benz 906 series diesel engine, coupled to a new ZF Ecomat automatic transmission. In addition, the axles and suspension were upgraded, increasing the maximum vehicle weight significantly. The Tactica 2000 was bought by Saudi Arabia and Norway. The Saudi vehicles were based upon chassis developed by the Belgian/Flemish company Mol.

The Tactica as an ISV
As far as classifications go, internal security vehicles can broadly be separated into four categories, based upon the level of protection [Fulvio Bianchi, 2003]. The first class has very limited protection, not more than the addition of bulletproof glass, bars, and add-on armor plates no thicker than 2.5 mm. Often, these are converted vans or light trucks. The second class provides enough protection against small arms fire with ball rounds. To achieve this, a new body has to be built, but use is still made of vans and the like. The third class are considered to be protected against 7.62 mm fire and even small explosions. This level of protection is pursued by most police forces, as it offers a good balance in weight, protection, and agility. Examples for this class are the Shorland S600 and the RG-12.
The fourth class features protection to a military level and are less common to encounter, as it is easier and cheaper to adapt an already existing military vehicle to the police role, than to have to develop a dedicated ISV, although this can cause some drawbacks, like the potential lack of internal space. The Tactica was one of the few vehicles built in this class, offering protection similar to the German Thyssen TM-170, for example.
Operators
Confirmed Sales Overview
| Country | Quantity | Order | Delivery | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore | 2-10 | 1988 | 1989 | |
| Kuwait | 20 | 1993 | 1993 | |
| United Kingdom | 35[+4*] | 1993 | 1993-1996 | |
| Indonesia | 33 | 1994, 1995, 1996 | 1994, 1995, 1997 | |
| Argentina | 9 | 1997 | 1998 | For UNFICYP |
| Ghana | 20 | 2000 | 2000-2002 | For UNAMSIL |
| Mauritius | 9-12 | ~2002 | 2003 | |
| Norway | 12 | 2002 | 2003 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 200 | 2006/2007 | 2009-2012 | |
| Total | 340-355 | 1988-2006/2007 | 1989-2012 |
* It is unclear if the four vehicles of the British Atomic Weapons Establishment were included in the official government figure of 35 owned vehicles.
Singapore [>2-10]
After the Tactica was introduced in 1988, Singapore was the first customer and placed an order for an unspecified number for the police. They were delivered in 1989, which made Singapore the first operator of the Tactica. A basic police version was acquired, painted in a typical British police style; dark blue with a blue-white checkerboard pattern stripe running along the sides.

The vehicles are rarely seen and appear to be last photographed around 2013 or early 2014 during riot control training with the Special Operations Command [SOC] and the Gurkha Contingent. The police mainly relies on locally-built tactical vehicles, which are painted red and therefore known as “Ang Chia” [Eng: Red Vehicle]. The current [2022] status of the Tacticas is unknown. They are either in storage, only to be used during a major emergency, or have already been disposed of.

Kuwait [20]
Kuwait received Tacticas for use by the Special Forces, under the Ministry of Interior [MOI]. According to Jane’s, 20 Patrol Tacticas were delivered after an order from 1993, but any details on their use, including photographs, are unknown. It is known that they were serviced by the company Ali Alghanim & Sons Automotive Co.w.l.l. which also services the other armored vehicles of the MOI, such as the Condor, TM-170, and Soframe.
United Kingdom [35]
In early 1993, the United Kingdom took its first deliveries of Tactica vehicles. They were acquired in specialized roles to be deployed in Northern Ireland, especially in the EOD configuration. Others were delivered to security services of the Ministry of Defence [Ministry of Defence Police, abbr. MDP or MOD Police]. In 1997, the Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Defence, John Spellar, confirmed that a total of 35 Tacticas had been acquired.
Not much is known about the MDP vehicles. They did not serve very long either, as they were replaced in 2010 by MacNeillie Protected Escort Vehicles. The EOD vehicles were used in Northern Ireland, in light of the unrest and threats posed by the Provisional Irish Republican Army. However, after a ceasefire in 1997 and an official dissolution in 2005, stability mostly returned and the EOD Tactica’s became redundant. They have since then been disposed of. Most if not all of the decommissioned Tacticas have been sold on the civilian market, with vehicles finding their way into private collections or museums. Several have been sold abroad too, with at least two going to the USA, and another two to the Netherlands.



Atomic Weapons Establishment
In 1996, the British Atomic Weapons Establishment [AWE] based in Aldermaston and Burghfield, Berkshire (United Kingdom), placed an order for four Patrol vehicles. These were intended to provide terrorist attack intervention at Aldermaston and high speed support response to Burghfield by the Aldermaston MOD Police Response Force. They could also be used for convoy duties, in which case they would have carried eight armed personnel to protect nuclear warheads and nuclear fission material during transport in the United Kingdom.
These four vehicles were built in a unique configuration, with a dual 12 and 24 volt electrical system, two-wheel drive instead of the regular four-wheel drive to allow for higher speeds and road tractability. The chosen engine was a high pressure turbocharged 6-l Perkins engine, coupled to an Allison automatic 5-speed transmission. They carried the registrations ‘N855 GBK’, ‘N856 GBK’, ‘N857 GBK’, and ‘N858 GBK’.
One vehicle, with the new civilian registration ‘HI 90 AA’ passed to the collection of the RAF Hack Green Nuclear complex in 2010. Another also came in private hands and was later sold as an ambulance to Ukraine. The status of the other two is unknown.

Indonesia [33]
In 1994, Indonesia placed an order for three water cannon vehicles, which was approved by the British government. A second order for six water cannons was also approved next year. On 9th December 1996, it was announced that new export licenses were granted for a large number of vehicles, including two Tactica Patrols, two APCs, five EOD vehicles, seven water cannons, and eight command and communication vehicles, totalling 24 Tacticas. The license was granted in advance of the contract, which was signed later. All were delivered before the end of 1997. The company Procurement Services International Ltd acted as a mediator between the Indonesian government and Glover Webb.
Tactica Deliveries to Indonesia
| Order | Types |
|---|---|
| 1994 | 3x Water Cannon |
| 1995 | 6x Water Cannon |
| 1997 | 2x 4-seater Patrol, 2x 10-seater APC, 5x EOD, 7x Water Cannon, 8x Command & Communication |
The deal was not without controversy. At the time, older British armored vehicles were already used against protesters and, in one notorious incident, three students were killed in South Sulawesi in April 1996. This fueled larger protests in June, in which the new Tacticas were used in Bandung. Eye witnesses stated that the water was mixed with teargas. These matters led to outrage among the British public and human rights activists when the new export license was granted in December 1996. It also led to questions in the House of Commons and, on 21st January 1997, a motion was signed by 75 members calling for the licenses to be revoked. However, the British government stated that they found the evidence inconclusive so the licenses remained effective.
In May 1997, the factory’s security was breached by a group of eleven protesters who heavily opposed the sale to Indonesia. At the site, twenty unfinished armored vehicles were decorated with the slogan: “not for export to Indonesia”. The protestors were later detained by the police.




Tactica Deployment
Once delivered, the Tacticas were taken into use by the Korps Brigade Mobil [English: Mobile Brigade Corps, abbr. BRIMOB], which is the combined tactical, paramilitary, and special forces unit of the Indonesian National Police [abbr. POLRI]. The BRIMOB consists of two branches, Gegana, which is responsible for more specific operations, such as EOD, counter terrorism, and intelligence, and Pelopor, with tasks like riot control, SAR, and guerrilla operations.
The new Tacticas were extensively used to quell any anti-government protests, of which the June 1996 deployment in Bandung is a prime example. In early August 2005, two Tacticas, normally stationed in Aceh, were transferred to Jayapura, the capital of West Papua. This was done in light of heightened tensions between the government and Papuans. The police were instructed to prevent people from participating in public protests and actions. The Tacticas were deployed on a number of occasions, for example, against a large demonstration on 12th August and another one on 31st October, which was a protest against the establishment of the Papuan People’s Assembly. Instead of pure water, the Indonesian police added a mixture of salt or liquid soap to achieve the same effect as teargas. In other instances, a color was added to the water, enabling protesters to be identified later, and consecutively arrested or even tortured.


On 14th April 2010, a riot broke out in Koja, Tanjung Priok, Northern Jakarta, over a land ownership issue. In the heavy clashes between the mob and the police, three members of the municipal police were killed. Some 130 to 231 people, including police, sustained light to heavy injuries. Many police vehicles were destroyed, but it was the first time an armored vehicle was set on fire too, namely a Tactica water cannon.

Argentina [9]
In the summer of 1997, it was disclosed that nine vehicles were under production for the Argentine United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus [UNFICYP]. In late 1997, these were finished and directly delivered to Cyprus and attached to the United Nations island Mobile Force Reserve [MFR]. The MFR was a multinational infantry company of five officers and a hundred soldiers. The vehicles were stationed at Airfield Camp to the west of Nicosia, but small sections were sometimes sent to other patrol bases in the west [Sector 1] or east [Sector 4].



UN Registrations
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 |
| UN 524 | UN 525 | UN 5?? | UN 528 | UN 529 | UN 530 | UN 531 | UN 532 | UN 5?? |
After twenty years of service, Argentina decided to pull the vehicles out of Cyprus in 2018. On 21st June 2018, the vehicles arrived in the harbor of Buenos Aires. They were then overhauled and repainted by the Batallón de Arsenales 601 [Eng. Arsenal Battalion 601] and attached to the Compañía de Comandos 603 [Eng. Commando Company 603]. The new registrations range between ‘EA 437330’ to ‘EA 337338’.


Ghana [20]
In 2000, a Ghanese contingent was active in Sierra Leone with UNAMSIL [United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone]. To reinforce this contingent, the UK government agreed to sell 17 Tacticas, divided over 12 APC 14-seaters, armed with a 12.7 mm machine gun; 3 APC 10-seaters armed with a 7.62 mm machine gun; 1 Command APC; and 1 Ambulance. The vehicles were planned to be shipped in four batches to the Sierra Leone capital of Freetown. On 9th July 2000, the first shipment left for Freetown, while the others were planned to leave in September 2000, April 2001, and October 2001. In addition to these 17 vehicles, another 3 Tacticas were shipped to Ghana itself, where they arrived around 13th March 2002 in the city of Tema. These three were all 10-seaters with turrets, but where two had a day/day sight, the third had a day/night sight.


Reportedly, the whole deal was worth GBP£9 million. It is unknown if any of the vehicles were damaged during the deployment in Sierra Leone. Presumably, all returned with the Ghanese contingent to Ghana after the mission was concluded. The Tacticas remain in service with the Ghanese Army, but any details about their distribution among the troops are lacking.


Mauritius [9-12]
Sometime in the early 2000s, the government of Mauritius placed an order for a small number of Tacticas of both variants, which were delivered in 2003. The specific number is unclear, as various sources give numbers ranging from seven up to twelve or even fourteen vehicles. Based upon the vehicle registrations, which are known thanks to the various photographs, at least nine Tactica’s have been identified, including four APCs and five Patrol vehicles.



Norway [12]
In November 2002, the Norwegian Ministry of Defense placed an order for 12 Tactica 2000s in the Explosive Ordnance Disposal [EOD] configuration. They were to be used by the Air Force’s air base security units, with each air base receiving one vehicle. Final assembly, modifications, and training were undertaken by Alvis’s subsidiary in Norway, Alvis Moelv [which existed between 1989-2004].
The local final assembly and various specific requirements gave the Norwegian Tacticas some unique features. The lights were differently designed and placed, additional rear-view mirrors were installed, the number and the size of the windows was changed, and a winch was mounted on the front, below the grille. The ‘Tactica’ nameplate was not mounted on the bonnet, but above the front window.


All vehicles were delivered throughout 2003. In December 2002, the Norwegian Defense Logistics Organization/Land had signed a contract with Kongsberg for the delivery of weapon control systems for armored vehicles. Eight of these new weapon stations, known as RWS-N, were to be installed on Tacticas. The systems would be used for the destruction of mines and other explosives from a distance, by firing on them.
The fact that eight weapon stations were bought for twelve vehicles is explained by the reforms undertaken by the Norwegian Air Force at the time. The total number of air bases was reduced, so only eight vehicles were required. Of the remaining four vehicles, at least three were reconfigured into armored ambulance versions. The other eight were stationed at the air bases. However, soon after, the demining groups of the air base security units were reassigned to wartime groups, meaning they would be inactive during neutral periods. Since then, the Tacticas have been reassigned from active duty to mobile assets and subsequently stored in military depots, in Romerike in the south, and in Bjerkvik in the north. Therefore, the vehicles are rarely spotted and remain some of the obscurest vehicles in use by the Norwegian Air Force. The vehicles received registration numbers ranging from ‘89001’ to ‘89012’.

Norse Tacticas In Chad With MINURCAT
Three of the vehicles that were converted into ambulances saw more use, as they were deployed to Chad with the Norwegian contingent participating in the UN MINURCAT [United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad] mission between 2009 and 2010. The mission was established in September 2007 as an EU-led operation consisting of military and police forces that were meant to protect civilians, refugees, and provide a safer environment in Chad and the Central African Republic, countries which had been destabilized following the civil war in neighboring Sudan. The mission lasted until 31st December 2010.
From the spring of 2009 until May 2010, Norway contributed a field hospital and a well-drilling team to the mission, totalling some 400 people. The field hospital was set up in Abéché in Chad and was staffed by roughly 150 people, as well as additional Serbian personnel. Among the used materiel were the three armored ambulances which allowed safe travel for wounded and sick people. In Chad, the vehicles received special UN registration numbers. The only two observed numbers are ‘UN 01023’ and ‘UN 01024’. Presumably, the third registration number ended with either ‘22’ or ‘25’. It is unknown which original Norwegian registration corresponded to which UN registration.
After the Norwegian contingent returned home, an ambulance with the Norwegian registration ‘89011’ was put on display at the Armed Forces Museum in Oslo. The others have remained in service after deployment, but their status, as of May 2022, is unclear.



Saudi Arabia [200]
During the late 1990s, Saudi Arabia wanted to acquire many new armored vehicles, mainly for use to protect facilities near Islamic holy sites, such as Mecca and Medina. They were to be operated by the National Guard, also known as the White Army, which consists of active-duty soldiers, but is not attached to the regular army. Its main task is the protection of the Royal Family from internal rebellion or military coups. The initial demand was broadly set for 60 up to 700 vehicles, but potentially up to a 1,000. Comparative tests between the Tactica and the Tenix Shorland S600 in September 1998 had resulted in the decision to acquire Tactica vehicles. According to both companies, their vehicles had been chosen as they offered a versatile chassis that was and could be adapted to many roles. Due to a lack of information, it is unknown if any vehicles were actually delivered. It is likely that, due to financial problems caused by long-term low oil prices, the order was canceled completely.
Since tensions with Iran and the threat of terrorist attacks kept rising, the National Guard of Saudi Arabia announced a new competition in 2005 regarding a large amount of military equipment worth US$900 million. Four companies were invited: General Dynamics Land Systems, Australian Defence Industries [Bushmaster], Steyr-Puch [armored Pinzgauer], and BAE Systems. The original requirement called for 144 armored personnel carriers, 52 armored command & control vehicles, 36 platoon command vehicles, 17 ambulance and evacuation vehicles, and 12 water cannon vehicles, totalling 261 vehicles.
A year later, in 2006, BAE Systems won the tender, although the number of vehicles was reduced to 200, including 108 APCs, 39 command & control vehicles, 27 platoon command vehicles, 17 ambulances, and 9 water cannon vehicles when the final contract was signed in 2007.

To fulfill this order, BAE largely relied on the Flemish company Mol Cy for production and assembly. The Flemish export license, worth €56 million, was granted in December 2007, and production could commence on 116 armored vehicles and 84 assembly kits. A few vehicles were almost completely assembled, but most were only partially assembled, with the chassis receiving components such as axles, engines, brakes, and similar equipment. After this, they were shipped to the United Kingdom for assembly of the armor.
Delivery to Saudi Arabia began in 2009, and in 2010, 157 vehicles had already been delivered and accepted into service. The other 43 were expected to be delivered in the first quarter of 2011, but it appears the last vehicles were only accepted into service in 2012. In Saudi Arabia, the vehicles first went to the Aircraft Accessories and Components Company Ltd. [AACC], where final testing and quality control took place.
In 2010 training was provided by a Short Term Training Team of the Training Wing of the King’s Royal Hussars. For three weeks, personnel of the 1st Crowd Control Battalion received training in Riyadh, and the 2nd CCB received two weeks training after that in Jeddah. The 2nd CCB is involved in the security of the yearly Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca and Medina and proved more experienced than the 1st CCB.


Deployment to Bahrain
The export of armored vehicles to Saudi Arabia quickly turned into a sensitive and highly criticized sale, both in the United Kingdom and Belgium, mainly because they were not solely used for domestic law enforcement and protection. In March 2011, in light of the Arab Spring, protests broke out in the small state of Bahrain, in the Arabian Gulf. The Bahraini police forces were quickly overwhelmed, and help was called in from the Gulf Cooperation Council. In response, the United Arab Emirates sent some 500 police, while Saudi Arabia sent some 150 armored vehicles, including a large quantity of Tacticas, on 14th March. The next day, a state of emergency was declared and the armored vehicles saw use in the brutal quashing of the protests. Over two months later, on 1st June, the state of emergency was lifted, but the Saudi National Guard maintained a presence in Bahrain.


Ukraine [1-4]
Following the 2022 invasion of Ukraine by Russia, Ukraine received large amounts of military equipment through its allies and special organizations. Since several former-British Alvis Tacticas were available on the market, it was just a question of time when the first of this type would be sent to Ukraine. Indeed, one former MDP vehicle, registered ‘170 HYP’, was outfitted with a stretcher to serve as a medevac vehicle. It arrived in Ukraine around September 2022.
Furthermore, in January 2023, the “Together to the Future UA” charity organized a fundraiser to acquire multiple Alvis Tacticas from a Dutch company called Ex US Army Auction. They were intended as protected ammunition carriers for an artillery unit of ВЧ А4100. It is unclear if the fundraiser reached it goals, but the Tactica(s) was sold. Given its appearance, it was likely one of three Tacticas, earlier offered by a Dutch company called D. van Dam. Therefore, it is possible that these three Tacticas have since gone to Ukraine.

Other Evaluators
Belgium
Since the late 1970s, the Belgian Gendarmerie [NL: Rijkswacht, a paramilitary police force] had been operating 80 BDX armored vehicles. After the Gendarmerie became a civilian police organization in 1992, the number was drastically scaled-down and, near the end of the 1990s, it became clear a replacement was needed. After evaluating a variety of options, the Alvis Tactica, Vickers OMC RG-12, and the Shorland S600 were selected as potential successors, with the S600 eventually winning.
Türkiye
In May 1995, a temporary export license was granted to deliver Tacticas to Türkiye. However, the vehicle, or possibly vehicles, were returned within approximately three months, suggesting an unsatisfactory trial. A second license was granted in October 1996, but appears to not have been used, suggesting Türkiye eventually did not buy any Tacticas.
Notable Former UK Vehicles in Private Hands



Conclusion
The Tactica was a successful armored vehicle, both regarding its potential in the internal security role, and as a commercial venture, with approximately 350 vehicles sold to nine countries. During its production run, the Tactica changed producers four times, a feat not achieved by many, but this did not hinder its production. As one of the first recipients, the United Kingdom was also the first to retire all their Tacticas from service, but all the other users retain nearly all in service and will likely remain to do so in the foreseeable future.





Specifications (BAE Systems Tactica 2000 APC variant) |
|
|---|---|
| Dimensions (LxWxH) | 5.9 x 2.4 [2.6 including wing mirrors] x 3.0 m |
| Crew | 2+12 (driver, commander + personnel) |
| Empty Weight | 12.6 tonnes |
| Gross Weight | 14.1 tonnes |
| Fording depth | 50 cm |
| Turning circle | 15.4 m |
| Wheelbase | 3.3 m |
| Angle of approach | 30º |
| Angle of departure | 35º |
| Ground clearance | 34 cm |
| Max grade | 60% |
| Fording depth | 50 cm [max. angle of entry 19º] |
| Obstacle | 30 cm |
| Engine | Mercedes OM 906 LA turbo-charged intercooled diesel, 6,370 cc, 180 kW @ 2,200 rpm, 900 Nm torque @ 1,200 rpm. |
| Max. speed | 120 km/h on-road |
| Fuel | 205 l |
| Transmission | ZF HP 502 automatic 6 forward and 1 reverse speeds |
| Brake system | Fully air powered with 4-way protection valve and split system |
| Differential locks | Independent inter axle and cross axle differential lock capability |
| Blast protection | STANAG level 1 |
| Ballistic protection | B7 |
| APV | |
| Crew | 2 + 6 (driver, commander + personnel) |
| Range | 650 km |
| Fuel | 167 l |
| Protection glass | 5 cm armored glass + 6 mm Polycarbonate |
| Accessories | 2 x 4 CN-gas/some launcher |
| Weight | 6,500 kg |
| Indonesian water cannon | |
| Dimensions (LxWxH) | 5.020 x 2.045 x 2.320 m |
| Water tank capacity | 4000 l |
| Crew | 4 |
| Engine | Perkins Phaser 180Ti diesel, 6-cylinder, 134 kW @ 2,600 rpm, max torque 618 Nm @ 1,400-1,600 rpm |
Sources
Special thanks to Dave Mckay, the former MOD police driving instructor at AWE Aldermaston, for sharing invaluable information regarding their use by the MOD police.
Tactica Brochure, BAE Systems.
Tactica Brochure, Alvis Vickers.
Sipri Trade Registers. 2002. “Appendix 13C. Register of the transfers and licensed production of major conventional weapons, 2002.” https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/476-534%20App.13C.pdf
Sipri Trade Registers for UK.
UNROCA registers.
Kraft, Andrej. 2018. “Самый секретный норвежский броневик.” andrej-kraft.livejournal.com, 22nd August 2018. https://andrej-kraft.livejournal.com/141495.html
Phythian, Mark. 2000. The Politics of British Arms Sales. Manchester: Manchester University Press, p.168.
https://undocs.org/pdf?symbol=en/S/2000/730
https://undocs.org/pdf?symbol=en/S/2002/498
https://www.thefreelibrary.com/Fired+from+under.-a0136078071
https://www.kongsberg.com/fr/newsandmedia/news-archive/2002/expansion-of-contract/
Brown, Peter. New Armored Vehicles Debut At British Equipment Exhibition ARMOR January-February 1998 https://man.fas.org/dod-101/sys/land/docs/1baee97.pdf
Jane’s Armour and Artillery, 2002.
http://kementah.blogspot.com/2014/01/a-look-at-riot-police-from-singapore.html
Korea Science. August 1999. Saudi Arabia may delay purchase of armored vehicles. http://www.koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO199941548495409.pdf p.52.
https://vlaamsvredesinstituut.eu/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/Report-business-as-usual_web.pdf
The King’s Royal Hussars Yearly Journal 2010 https://www.krh.org.uk/uploads/4/5/0/9/45090939/krh_2010.pdf
Made in Flanders: The end-use of Flemish military equipment, 2012, Nils Duquet, https://www.academia.edu/4276719/Made_in_Flanders_The_end-use_of_Flemish_military_equipment
https://www.linkedin.com/in/mohammed-shahat-92145452/?originalSubdomain=kw
https://caatunis.net/wp-content/uploads/BAE-AGM-2011-info.pdf
https://www.irishtimes.com/news/nine-held-after-arms-protest-1.69462
http://wpik.org/Src/indonesia-1099.html
https://edm.parliament.uk/early-day-motion/14143
https://www.theguardian.com/world/1999/jan/25/indonesia
https://stopwapenhandel.org/app/uploads/2010/10/Indonesia_0.pdf
https://www.tapol.org/bulletin/181-december-2005#watercannons
https://www.indomiliter.com/tactica-patrol-4×4-rantis-lapis-baja-korps-brimob-dari-era-90-an/
https://www.indomiliter.com/tactica-panser-korban-tragedi-priok/
https://www.militaryvehiclerental.co.uk/vehicles/alvis-tactica/
https://dvandam.nl/collections/voertuigen/products/pantserwagen-tactica#
https://thearmstradetreaty.org/download/256f1d08-e49c-3de8-a2d0-cb23a59df973
https://caat.org.uk/news/2011-03-16-2/
https://car-from-uk.com/sale.php?id=233176
Internal Security and Riot Control Vehicles, part I and II, Fulvio Bianchi, Military Technology, 2003.
https://www.eldisenso.com/politica/blindados-un-son-9-los-compro-argentina-y-son-del-ejercito/
https://bos-fahrzeuge.info/einsatzfahrzeuge/17790/Nicosia_-_UNFICYP_-_SW_T5/photo/17790
https://www.defensa.com/argentina/vuelven-blindados-argentinos-chipre
https://www.joint-forces.com/features/28496-glover-webb-tactica-apv-unficyp
https://www.rum-ua.org/en/reports-en/fundraising-for-artillery-division/
https://www.truck1-ci.com/camions/alvis-tactica-a6931871.html
Videos
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YI-aqBjj7UQ Saudi Tacticas, arriving in Bahrain in 2011.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GZvUNc2dl4g Alvis Tactica medevac in Ukraine, September 2022.

