 German Reich (1939)
German Reich (1939)
Tracked Reconnaissance Vehicle – 64-70 Built
What were they used for?
A German Army Aufklärung Abteilung’s (reconnaissance battalions) job was to go ahead of the main attack until they could see the enemy positions. They would then radio back what the strength was and where the enemy forces were deployed. Sometimes they would call in an artillery barrage or an airstrike. They relied heavily on fast vehicles to get them deep into enemy territory quickly. This reconnaissance function had traditionally been the work for mounted cavalry units.
During the late 1930’s horses were slowly replaced with motorbikes. These Kradshützen Abteilungs (Motorcycle Rifle Battalions) were incorporated into reconnaissance units which made use of lightweight armored vehicles with the ability to fight back in a limited capacity if they should be engaged. The Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) 2cm KwK 38 (Sd.Kfz.140/1) was one of these lightly armored reconnaissance vehicles.
The composition of reconnaissance units differed across Europe. As an example, in 1943-44, the German Army Grossdeutschland (Greater Germany) Regiment was a four battalion Infantry Regiment. It had its own armoured reconnaissance battalion. This battalion was comprised of a HQ unit, five Recce Companies and a Supply Company (Versorgungskompanie). No.1 Company was an Armored Reconnaissance Company (Panzerspähkompanie). Company No.2, No.3 and No.4 would be Reconnaissance Companies (Aufkläerungskompanie) and No.5 Company was a Heavy Company that consisted of an assault pioneer troop, a close support troop and a mortar troop. The Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) 2cm KwK 38 would normally be posted to No.1 Company.
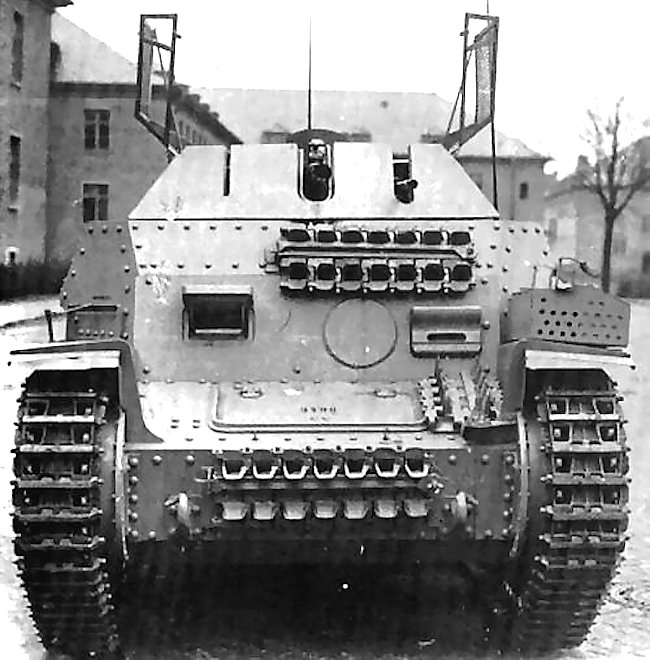

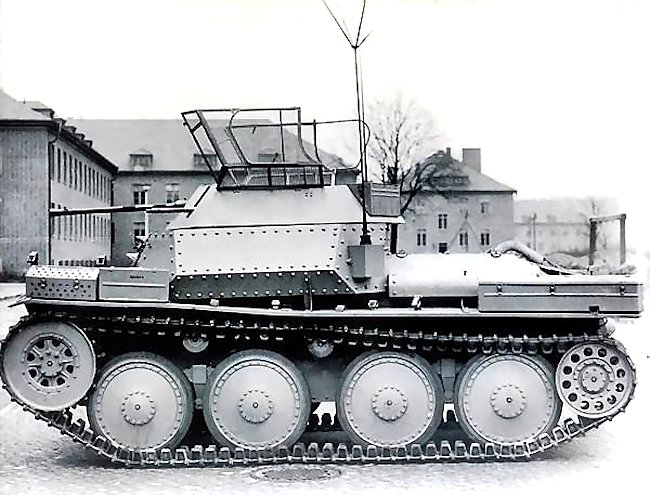
This Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) 2cm KwK 38 Sd.Kfz.140/1 was photographed as it had just came off the production line. It has spare tracks bolted onto the front hull in three positions.
Production and Design
German half-tracked and wheeled armored cars engaged in the role of armored reconnaissance, but struggled to cope with the poor conditions experienced on the Eastern Front. The Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) was developed as a primary reconnaissance vehicle to replace both these kinds of vehicles. Between 64 – 70 Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) vehicles were converted from old stocks of the Czech built Panzer 38(t) tanks. In 1943 ,the Panzer 38(t) tank had been withdrawn from front line operations, as it was considered obsolete.
The turret was removed and fitted with a ‘Hangelafette turret’ armed with a 2 cm (0.79 in) KwK 38 gun and a single 7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 42 machine gun which was capable of both anti aircraft and a ground fire. This turret configuration was not new. It had already been employed on reconnaissance vehicles used in combat operations on the Eastern Front, such as the Sd.Kfz.222, Sd.Kfz.234/1 and the Sd.Kfz.250/9. It had all-round traverse. The German word “Hangelafette” can be translated as “free pivot gun mount”. The open top was fitted with anti-grenade grilles for use when moving through villages and potential ambush locations.
The engineers had to strip down the upper hull superstructure of the Pz.Kpfw.38(t) tank and fabricate a new boxed upper hull structure to mount the Hangelafette turret. They were built in relatively small numbers. This may be due to the high demand for Panzer 38(t) tank chassis needed for converting into the famous Jagdpanzer 38(t) Hetzer Tank Destroyer during 1944.

Front view of a captured Aufklärungspanzer 38(t). It is missing its turret guns, but a circular armoured disk has been welded to the front of the Panzer 38(t) tank chassis where the hull machine gun used to be.
It was very unsophisticated in its design. Allied bombing had reduced Germany’s capability to produce new armored fighting vehicles at the required levels. It was sensible to use well proven reliable tank chassis such as the Panzer 38(t) and convert it into machines that could perform different roles.
The initial reaction to seeing a Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) was that it must have been designed in the late 1930s. It was a step backwards in AFV technological design. It used the old technique of riveting in the upper hull construction, not welding. The use of rivets to join sections of armored panels was recognised as a danger to the health of the tank crew inside the vehicle.
When a rivet was struck by small arms fire they had a tendency to fly off, ricochet around the interior of the vehicle and striking the crew, causing often fatal or life changing injuries. The decision to use the old riveting construction method in 1944 was probably taken in an effort to reduce costs and accelerate production time. It allowed for less experienced workers to assemble the vehicle, as highly trained workers were required to weld armor plates together.
The Gun
This vehicle was not designed to fight tanks. The crew were expected to race in front of the main Panzer Division and search out the enemy. Once they had found them they were to use speed to get out of range and report what they had seen. The 2 cm Kw.K.38 gun and the single 7.92 mm M.G.42 machine gun were only designed for self defence against infantry, artillery, soft skinned and lightly armored vehicles.
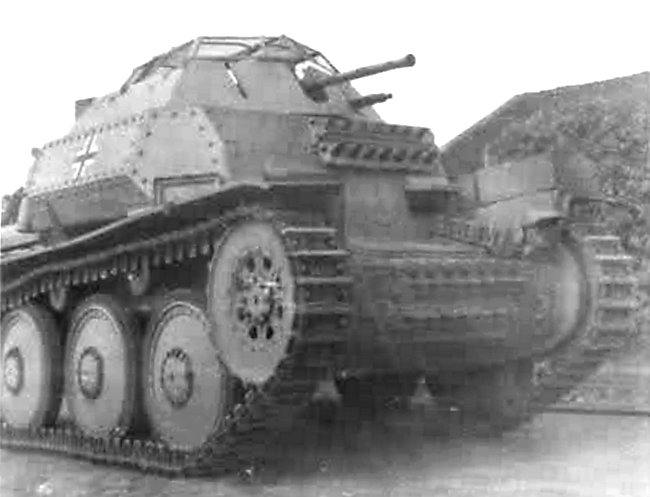

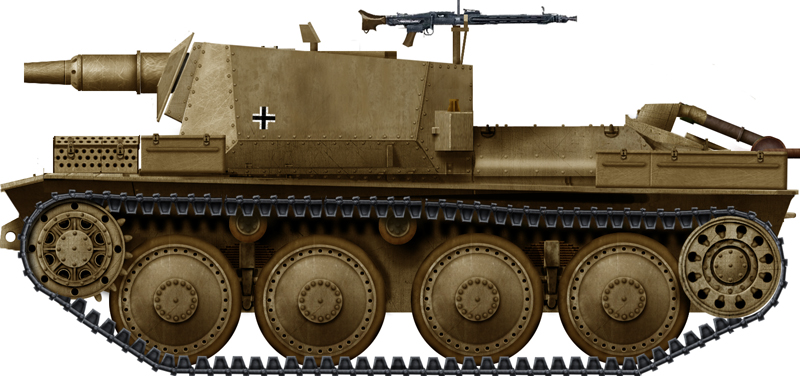
Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) armoured tracked reconnaissance vehicle.
Operational Service
Very few records of the operational service of the Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) armored tracked reconnaissance vehicle in 1944 have survived. Military records show that twenty five were allocated to the 2.PanzerAufklärung GD/PzGr-Div. Grossdeutschland on 27th April 1944. One was known to have been issued to Ersatz-Brigade (replacement brigade) Grossdeutschland on 30th April 1944. Another one was sent to the 2.PanzerAufklärung GD/PzGr-Div. Grossdeutschland on 27th June 1944. Twenty five were allocated to the 1.PanzerAufklärung. 3.Abteilung (3rd Battalion), 3.Panzer Division on 1st September 1944. They received a further six vehicles on 30th October 1944 as replacements. Seven replacement vehicles were sent to 2.PanzerAufklärung GD/PzGr-Div. Grossdeutschland on 19th December of the same year.
Little else is known about the attrition rates for these vehicles or indeed the performance amongst the crews as the war entered the desperate final stages of the last few months, few survived and none are known to have entered museums or private collections. Only rare photographs preserve their usage. Of the 32 to be issued to the Grossdeutschland division, how many made it to Pillau in the last days of GD’s existence is impossible to say and 3rd Panzer lost most of its machines in the abortive offensive around Lake Balaton and the fighting for Budapest in Hungary.
However, one might surmise that, since the Pz.Kpfw.38(t) was an outstanding chassis that was extremely successful in its application for the Jadgpanzer 38(t), the Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) might also have been equally successful in its role with the combination of excellent reliability, good cross country performance and speed. Unfortunately, its single biggest downfall would lie in its light armor which, whilst fine for fast reconnaissance missions, would have been hopeless in the defensive nature that the war had turned into for the German Wehrmacht. It was no match against the massed ranks of Soviet T-34s.
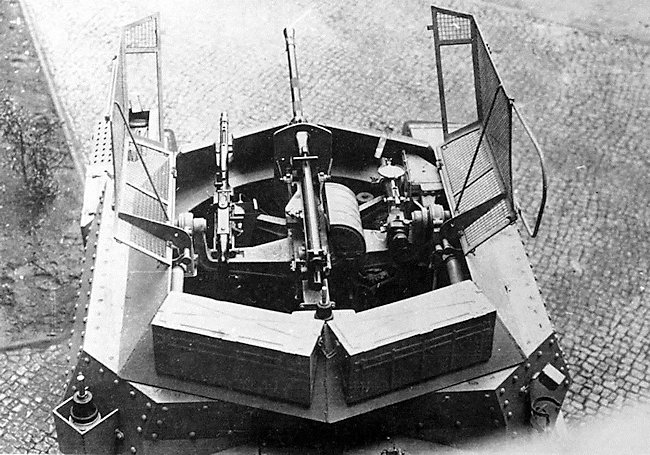
German tracked reconnaissance Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) vehicles were armed with a 2cm KwK 38 gun and 7.92mm M.G.42 machine gun. The anti-grenade wire mesh turret covers were used when going into action.
Sources
German Armoured Cars and Reconnaissance Half-Tracks 1939-45 by Bryan Perrett
Grossdeutschland Aufklärung www.panzeraufgd.co.uk
T.L. Jentz & H.L. Doyle, Panzer Tracts No. 11-2 (Aufklärungspanzerwagen)
Specifications |
|
| Dimensions (L,W,H) | 4.61m x 2.15m x 2.40m (15’1″ x 7’6″ x 7’10” ft.in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 9.7-9.8 tons |
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, driver, co-driver) |
| Propulsion | Praga Typ TNHPS/II 6-cylinder gasoline, 125 bhp (92 kW) |
| Speed (on/off road) | 42/15 km/h (26/9 mph) |
| Suspension | Leaf spring type |
| Armament | 2 cm (0.79 in) KwK 38 gun 7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 42 machine gun |
| Armor | Front 50 mm (1.97 in) Sides 10-30 mm (0.39-1.18 in) |
| Max Range on/off road | 250/100 km (160/62 mi) |
| Total production | 64 (70) |
.png)
Panzer-Aufklärungs-Abteilung 2. 2.Panzer-Division Eastern Front 1944-45
mit_2cm_KwK-38-EastFt-win44.png)
Aufklärungspanzers 38(t) mit 2cm KwK 38 (SdKfz 140/1) were painted in a dark sand color at the factory in 1944.
mit_2cm_KwK-38-UFtWwin44.png)
Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) mit 2cm KwK 38, Eastern Front, 1944-45
mit_2cm_KwK-38.png)
Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) mit 2cm KwK 38, Western Front, 1944-45
Operational Photographs

Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) mit 2cm KwK 38 (SdKfz 140/1) outside the former CKD (Ceskomoravska Kolben-Danek) works in Czechoslovakia, renamed the BMM (Böhmisch-Mährische Maschinenfabrik AG) under German occupation.
This Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) has been photographed with its radio aerial deployed, its areal holder in an armored box and a rear long rectangular equipment box attached to the back of the track mud guard.

Notice the track drive wheels on this 1944 early production Aufklärungspanzer 38(t). They are different to the wheels on later versions.
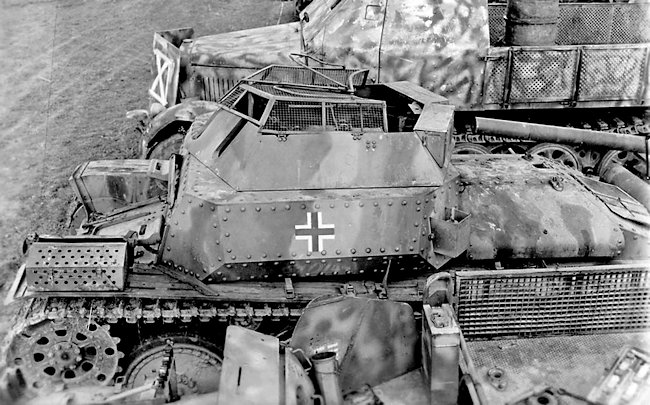

This Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) has a three colour camouflage pattern. It is missing its guns and exhaust system. The track drive wheels are different to the earlier version and the aerial holder at the rear left side of the upper hull superstructure now has an armoured protective box.
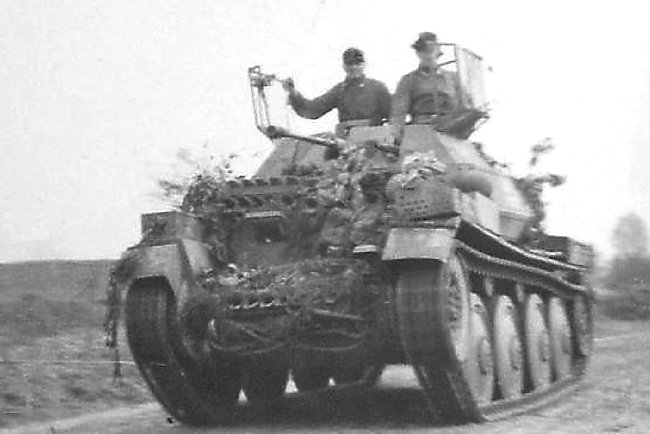

This is one of the few operational photographs of an Aufklärungspanzer 38(t). It has additional spare tracks bolted to the front for added protection and a rear long rectangular equipment box attached to the vehicle above the tank track mud guards.
Anti-grenade turret cover
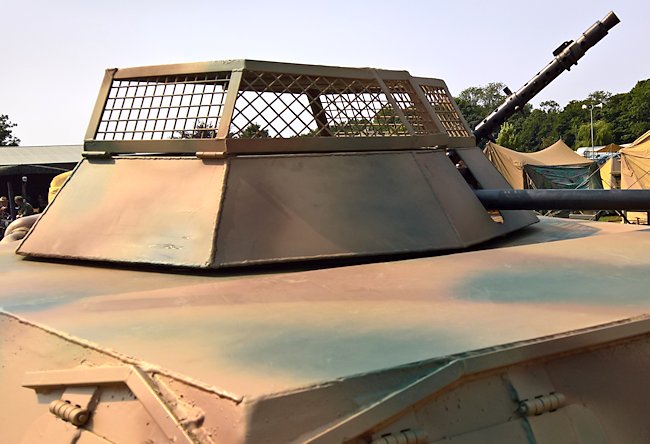
The photographs below are taken of a replica Sd.Kfz.222 armored car. It has the same style of hinged wire mesh anti-grenade cover over its open Hangelafette turret as was fitted to the Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) tracked reconnaissance vehicle.




11 replies on “Aufklärungspanzer 38(t)”
was this updated or a new article?
New article
You are incorrect in the statement that Hetzers( named that after the war) were made from converted 38t’s
The Hetzer was made from a whole new chassis inorder to fit the gun and casement.
The Hetzer was a light tank destroyer, not a self propelled gun.
The distinction between what classifies a vehicle as a Tank destroyer vs a Self Propelled Gun can vary depending on the vehicle in question and also the practices of the operating nation. However in this case tank destroyer is the more accurate term and the article has been changed
-T E Moderator
The Aufk 38 was a very good match of turret with chassis. When compared to the Luchs, another small production recon tank, it was slower, better armored (50mm hull front), and had a turret whose weapons could be aimed at targets above the vehicle . . . something especially useful in urban/close environments. So useful was this combination, that the PSW222, PSW234/1, SdKfz250/9, and SdKfz251/23 are all essentially the same vehicle, meant for the same purpose, though differing in all terrain performance, while Luchs, with its tanklike turret and pair of what were almost the same weapons, was a deadend . . . until it re-appeared as-yes-the PSW Luchs again, this time in achrad form, in the late 1970s.
Love your site it’s Outstanding! Have seen having a problem with Color plates and pics loading. God Bless you for this Great Info. here:)
Dave In Va. USA
The opening illustration shows a 38(t) chassis with the short 75mm gun, not the turreted vehicle in the article. Is this a misplaced illustration?
No, it was a sub variant.
How thick is the frontal armor of the new casemate?
What a fantastic site well informed and the photos are some of the best i have seen well done